ZHCS277C August 2011 – April 2014 TMS320C5532 , TMS320C5533 , TMS320C5534 , TMS320C5535
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1器件概述
- 2修订历史记录
- 3Device Comparison
-
4Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 4.1 Pin Diagram
- 4.2
Signal Descriptions
- 4.2.1 Oscillator and PLL
- 4.2.2 Real-Time Clock (RTC)
- 4.2.3 RESET, Interrupts, and JTAG
- 4.2.4 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 4.2.5 Inter-IC Sound (I2S)
- 4.2.6 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 4.2.7 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 4.2.8 Universal Serial Bus (USB) 2.0
- 4.2.9 LCD Bridge
- 4.2.10 Secure Digital (SD)
- 4.2.11 Successive Approximation (SAR) Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC)
- 4.2.12 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 4.2.13 Regulators and Power Management
- 4.2.14 Reserved and No Connects
- 4.2.15 Supply Voltage
- 4.2.16 Ground
- 4.3 Pin Multiplexing
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.3 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.4 Handling Ratings
- 5.5 Thermal Characteristics
- 5.6 Power-On Hours
- 5.7
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 5.7.1 Parameter Information
- 5.7.2
Power Supplies
- 5.7.2.1 Power Considerations for C5535 and C5534
- 5.7.2.2 Power Considerations for C5533
- 5.7.2.3 Power Considerations for C5532
- 5.7.2.4 Power-Supply Sequencing
- 5.7.2.5 Digital I/O Behavior When Core Power (CVDD) is Down
- 5.7.2.6 Power-Supply Design Considerations
- 5.7.2.7 Power-Supply Decoupling
- 5.7.2.8 LDO Input Decoupling
- 5.7.2.9 LDO Output Decoupling
- 5.7.3
Reset
- 5.7.3.1 Power-On Reset (POR) Circuits
- 5.7.3.2 Pin Behavior at Reset
- 5.7.3.3 Reset Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.7.3.4 Configurations at Reset
- 5.7.3.5
Configurations After Reset
- 5.7.3.5.1 External Bus Selection Register (EBSR)
- 5.7.3.5.2 LDO Control Register [7004h]
- 5.7.3.5.3 USB System Control Registers (USBSCR) [1C32h]
- 5.7.3.5.4 Peripheral Clock Gating Control Registers (PCGCR1 and PCGCR2) [1C02h and 1C03h]
- 5.7.3.5.5 Pullup and Pulldown Inhibit Registers (PDINHIBR1, 2, and 3) [1C17h, 1C18h, and 1C19h]
- 5.7.3.5.6 Output Slew Rate Control Register (OSRCR) [1C16h]
- 5.7.4
Clock Specifications
- 5.7.4.1 Recommended Clock and Control Signal Transition Behavior
- 5.7.4.2 Clock Considerations
- 5.7.4.3 PLLs
- 5.7.4.4 Input and Output Clocks Electrical Data and Timing
- 5.7.4.5 Wake-up Events, Interrupts, and XF
- 5.7.5 Direct Memory Access (DMA) Controller
- 5.7.6 General-Purpose Input/Output
- 5.7.7 General-Purpose Timers
- 5.7.8 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 5.7.9 Inter-IC Sound (I2S)
- 5.7.10 Liquid Crystal Display Controller (LCDC) — C5535 Only
- 5.7.11 Real-Time Clock (RTC)
- 5.7.12 SAR ADC (10-Bit) — C5535 Only
- 5.7.13 Secure Digital (SD)
- 5.7.14 Serial Port Interface (SPI)
- 5.7.15 Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART)
- 5.7.16 Universal Serial Bus (USB) 2.0 Controller — Does Not Apply to C5532
- 5.7.17 Emulation and Debug
- 5.7.18 IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1 CPU
- 6.2
Memory
- 6.2.1 Internal Memory
- 6.2.2 Memory Map
- 6.2.3
Register Map
- 6.2.3.1 General-Purpose Input/Output Peripheral Register Descriptions
- 6.2.3.2 I2C Peripheral Register Descriptions
- 6.2.3.3 I2S Peripheral Register Descriptions
- 6.2.3.4 LCDC Peripheral Register Descriptions
- 6.2.3.5 RTC Peripheral Register Descriptions
- 6.2.3.6 SAR ADC Peripheral Register Descriptions
- 6.2.3.7 SD Peripheral Register Descriptions
- 6.2.3.8 SPI Peripheral Register Descriptions
- 6.2.3.9 System Registers
- 6.2.3.10 Timers Peripheral Register Descriptions
- 6.2.3.11 UART Peripheral Register Descriptions
- 6.2.3.12 USB2.0 Peripheral Register Descriptions
- 6.3 Identification
- 6.4 Boot Modes
- 7Device and Documentation Support
- 8Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
6 Detailed Description
6.1 CPU
The fixed-point digital signal processors (DSP) are based on the C55x CPU 3.3 generation processor core. The C55x DSP architecture achieves high performance and low power through increased parallelism and total focus on power savings. The CPU supports an internal bus structure that is composed of one program bus, three data read buses (one 32-bit data read bus and two 16-bit data read buses), two 16-bit data write buses, and additional buses dedicated to peripheral and DMA activity. These buses provide the ability to perform up to four data reads and two data writes in a single cycle. Each DMA controller can perform one 32-bit data transfer per cycle, in parallel and independent of the CPU activity.
The C55x CPU provides two multiply-accumulate (MAC) units, each capable of 17-bit x 17-bit multiplication in a single cycle. A central 40-bit arithmetic and logic unit (ALU) is supported by an additional 16-bit ALU. Use of the ALUs is under instruction set control, providing the ability to optimize parallel activity and power consumption. These resources are managed in the Address Unit (AU) and Data Unit (DU) of the C55x CPU.
The C55x DSP generation supports a variable byte width instruction set for improved code density. The Instruction Unit (IU) performs 32-bit program fetches from internal or external memory, stores them in a 128-byte Instruction Buffer Queue, and queues instructions for the Program Unit (PU). The Program Unit decodes the instructions, directs tasks to AU and DU resources, and manages the fully protected pipeline. Predictive branching capability avoids pipeline flushes on execution of conditional instruction calls.
For more detailed information on the CPU, see the TMS320C55x CPU 3.0 CPU Reference Guide (literature number SWPU073).
6.2 Memory
6.2.1 Internal Memory
6.2.1.1 On-Chip Dual-Access RAM (DARAM)
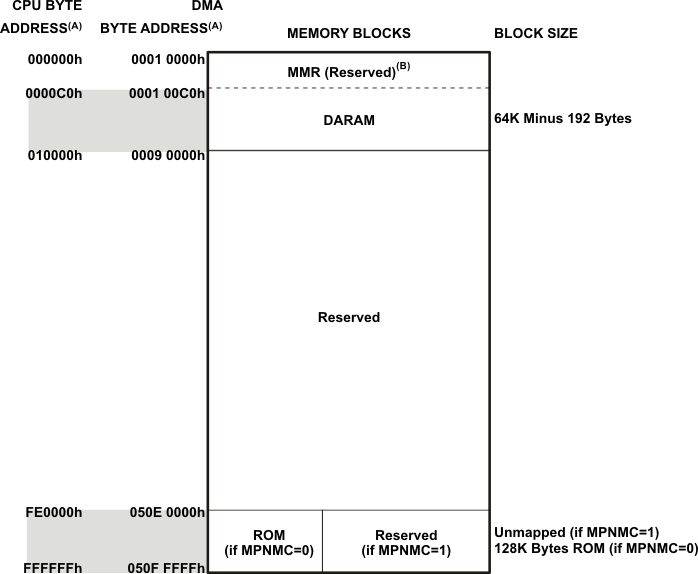
The DARAM is located in the byte address range 000000h − 00FFFFh and is composed of eight blocks of 4K words each (see Table 6-1). Each DARAM block can perform two accesses per cycle (two reads, two writes, or a read and a write). The DARAM can be accessed by the internal program, data, or DMA buses.
Table 6-1 DARAM Blocks
| CPU BYTE ADDRESS RANGE |
DMA CONTROLLER BYTE ADDRESS RANGE |
MEMORY BLOCK |
|---|---|---|
| 000000h – 001FFFh | 0001 0000h – 0001 1FFFh | DARAM 0(1) |
| 002000h – 003FFFh | 0001 2000h – 0001 3FFFh | DARAM 1 |
| 004000h – 005FFFh | 0001 4000h – 0001 5FFFh | DARAM 2 |
| 006000h – 007FFFh | 0001 6000h – 0001 7FFFh | DARAM 3 |
| 008000h – 009FFFh | 0001 8000h – 0001 9FFFh | DARAM 4 |
| 00A000h – 00BFFFh | 0001 A000h – 0001 BFFFh | DARAM 5 |
| 00C000h – 00DFFFh | 0001 C000h – 0001 DFFFh | DARAM 6 |
| 00E000h – 00FFFFh | 0001 E000h – 0001 FFFFh | DARAM 7 |
6.2.1.2 On-Chip Read-Only Memory (ROM)
The zero-wait-state ROM is located at the byte address range FE0000h – FFFFFFh. The ROM is composed of four 16K-word blocks, for a total of 128K bytes of ROM. The ROM address space can be mapped by software to the internal ROM.
The standard device includes a bootloader program resident in the ROM.
When the MPNMC bit field of the ST3 status register is cleared (by default), the byte address range FE0000h – FFFFFFh is reserved for the on-chip ROM. When the MPNMC bit field of the ST3 status register is set through software, the on-chip ROM is disabled and not present in the memory map, and byte address range FE0000h – FFFFFFh is unmapped. A hardware reset always clears the MPNMC bit, so it is not possible to disable the ROM at reset. However, the software reset instruction does not affect the MPNMC bit. The ROM can be accessed by the program and data buses. Each on-chip ROM block is a one cycle per word access memory.
6.2.1.3 On-Chip Single-Access RAM (SARAM)
Section 6.2.1.3.1 explains the SARAM blocks for the C5535. Section 6.2.1.3.2 explains the SARAM blocks for the C5534. Section 6.2.1.3.3 explains the SARAM blocks for the C5533. The C5532 has no SARAM blocks.
6.2.1.3.1 SARAM for C5535
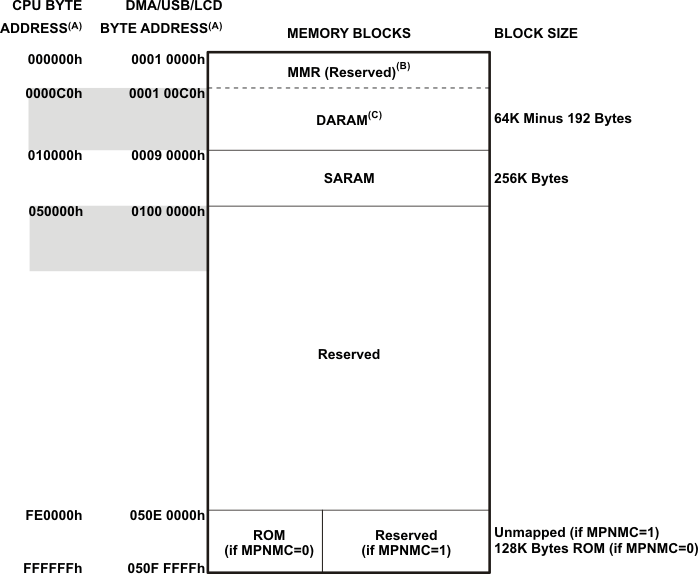
The SARAM is located at the byte address range 010000h – 04FFFFh and is composed of 32 blocks of 4K words each (see Table 6-2). Each SARAM block can perform one access per cycle (one read or one write). SARAM can be accessed by the internal program, data, or DMA buses.
SARAM is also accessed by the USB and LCD DMA buses.
Table 6-2 SARAM Blocks for C5535
| CPU BYTE ADDRESS RANGE |
DMA and USB CONTROLLER
BYTE ADDRESS RANGE |
MEMORY BLOCK |
|---|---|---|
| 010000h − 011FFFh | 0009 0000h – 0009 1FFFh | SARAM 0 |
| 012000h − 013FFFh | 0009 2000h – 0009 3FFFh | SARAM 1 |
| 014000h − 015FFFh | 0009 4000h – 0009 5FFFh | SARAM 2 |
| 016000h − 017FFFh | 0009 6000h – 0009 7FFFh | SARAM 3 |
| 018000h − 019FFFh | 0009 8000h – 0009 9FFFh | SARAM 4 |
| 01A000h − 01BFFFh | 0009 A000h – 0009 BFFFh | SARAM 5 |
| 01C000h − 01DFFFh | 0009 C000h – 0009 DFFFh | SARAM 6 |
| 01E000h − 01FFFFh | 0009 E000h – 0009 FFFFh | SARAM 7 |
| 020000h − 021FFFh | 000A 0000h – 000A 1FFFh | SARAM 8 |
| 022000h − 023FFFh | 000A 2000h – 000A 3FFFh | SARAM 9 |
| 024000h − 025FFFh | 000A 4000h – 000A 5FFFh | SARAM 10 |
| 026000h − 027FFFh | 000A 6000h – 000A 7FFFh | SARAM 11 |
| 028000h − 029FFFh | 000A 8000h – 000A 9FFFh | SARAM 12 |
| 02A000h − 02BFFFh | 000A A000h – 000A BFFFh | SARAM 13 |
| 02C000h − 02DFFFh | 000A C000h – 000A DFFFh | SARAM 14 |
| 02E000h − 02FFFFh | 000A E000h – 000A FFFFh | SARAM 15 |
| 030000h − 031FFFh | 000B 0000h – 000B 1FFFh | SARAM 16 |
| 032000h − 033FFFh | 000B 2000h – 000B 3FFFh | SARAM 17 |
| 034000h − 035FFFh | 000B 4000h – 000B 5FFFh | SARAM 18 |
| 036000h − 037FFFh | 000B 6000h – 000B 7FFFh | SARAM 19 |
| 038000h − 039FFFh | 000B 8000h – 000B 9FFFh | SARAM 20 |
| 03A000h − 03BFFFh | 000B A000h – 000B BFFFh | SARAM 21 |
| 03C000h − 03DFFFh | 000B C000h – 000B DFFFh | SARAM 22 |
| 03E000h − 03FFFFh | 000B E000h – 000B FFFFh | SARAM 23 |
| 040000h – 041FFFh | 000C 0000h – 000C 1FFFh | SARAM 24 |
| 042000h – 043FFFh | 000C 2000h – 000C 3FFFh | SARAM 25 |
| 044000h – 045FFFh | 000C 4000h – 000C 5FFFh | SARAM 26 |
| 046000h – 047FFFh | 000C 6000h – 000C 7FFFh | SARAM 27 |
| 048000h – 049FFFh | 000C 8000h – 000C 9FFFh | SARAM 28 |
| 04A000h – 04BFFFh | 000C A000h – 000C BFFFh | SARAM 29 |
| 04C000h – 04DFFFh | 000C C000h – 000C DFFFh | SARAM 30 |
| 04E000h – 04FFFFh | 000C E000h – 000C FFFFh | SARAM 31(1) |
6.2.1.3.2 SARAM for C5534
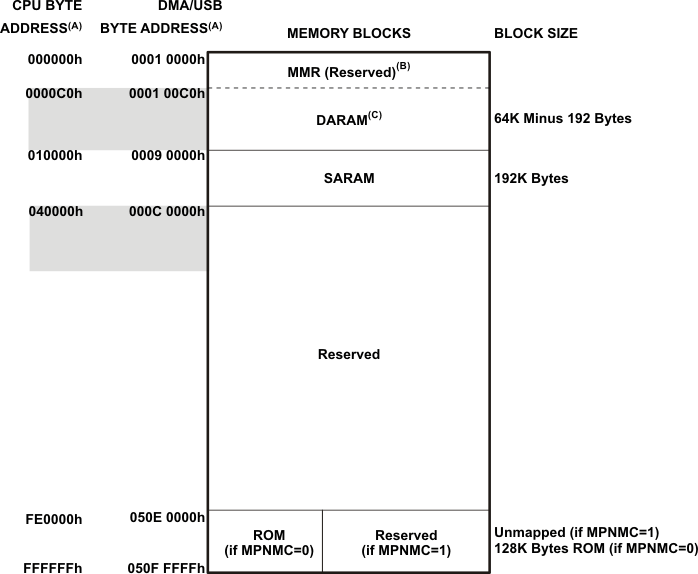
The SARAM is located at the byte address range 010000h – 03FFFFh and is composed of 24 blocks of 4K words each (see Table 6-3). Each SARAM block can perform one access per cycle (one read or one write). SARAM can be accessed by the internal program, data, or DMA buses. SARAM is also accessed by the USB bus.
Table 6-3 SARAM Blocks for C5534
| CPU BYTE ADDRESS RANGE |
DMA and USB CONTROLLER BYTE ADDRESS RANGE |
MEMORY BLOCK |
|---|---|---|
| 010000h − 011FFFh | 0009 0000h – 0009 1FFFh | SARAM 0 |
| 012000h − 013FFFh | 0009 2000h – 0009 3FFFh | SARAM 1 |
| 014000h − 015FFFh | 0009 4000h – 0009 5FFFh | SARAM 2 |
| 016000h − 017FFFh | 0009 6000h – 0009 7FFFh | SARAM 3 |
| 018000h − 019FFFh | 0009 8000h – 0009 9FFFh | SARAM 4 |
| 01A000h − 01BFFFh | 0009 A000h – 0009 BFFFh | SARAM 5 |
| 01C000h − 01DFFFh | 0009 C000h – 0009 DFFFh | SARAM 6 |
| 01E000h − 01FFFFh | 0009 E000h – 0009 FFFFh | SARAM 7 |
| 020000h − 021FFFh | 000A 0000h – 000A 1FFFh | SARAM 8 |
| 022000h − 023FFFh | 000A 2000h – 000A 3FFFh | SARAM 9 |
| 024000h − 025FFFh | 000A 4000h – 000A 5FFFh | SARAM 10 |
| 026000h − 027FFFh | 000A 6000h – 000A 7FFFh | SARAM 11 |
| 028000h − 029FFFh | 000A 8000h – 000A 9FFFh | SARAM 12 |
| 02A000h − 02BFFFh | 000A A000h – 000A BFFFh | SARAM 13 |
| 02C000h − 02DFFFh | 000A C000h – 000A DFFFh | SARAM 14 |
| 02E000h − 02FFFFh | 000A E000h – 000A FFFFh | SARAM 15 |
| 030000h − 031FFFh | 000B 0000h – 000B 1FFFh | SARAM 16 |
| 032000h − 033FFFh | 000B 2000h – 000B 3FFFh | SARAM 17 |
| 034000h − 035FFFh | 000B 4000h – 000B 5FFFh | SARAM 18 |
| 036000h − 037FFFh | 000B 6000h – 000B 7FFFh | SARAM 19 |
| 038000h − 039FFFh | 000B 8000h – 000B 9FFFh | SARAM 20 |
| 03A000h − 03BFFFh | 000B A000h – 000B BFFFh | SARAM 21 |
| 03C000h − 03DFFFh | 000B C000h – 000B DFFFh | SARAM 22 |
| 03E000h − 03FFFFh | 000B E000h – 000B FFFFh | SARAM 23 |
6.2.1.3.3 SARAM for C5533
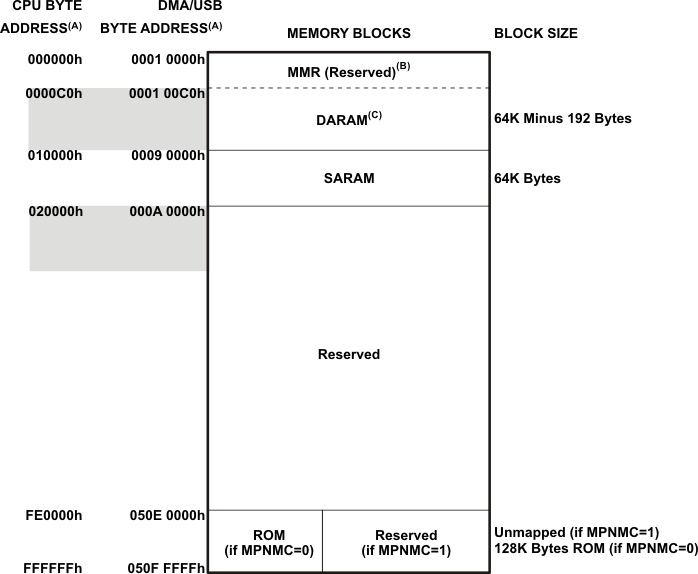
The SARAM is located at the byte address range 010000h – 01FFFFh and is composed of 8 blocks of 4K words each (see Table 6-4). Each SARAM block can perform one access per cycle (one read or one write). SARAM can be accessed by the internal program, data, or DMA buses. SARAM is also accessed by the USB bus.
Table 6-4 SARAM Blocks for C5533
| CPU BYTE ADDRESS RANGE |
DMA and USB CONTROLLER BYTE ADDRESS RANGE |
MEMORY BLOCK |
|---|---|---|
| 010000h − 011FFFh | 0009 0000h – 0009 1FFFh | SARAM 0 |
| 012000h − 013FFFh | 0009 2000h – 0009 3FFFh | SARAM 1 |
| 014000h − 015FFFh | 0009 4000h – 0009 5FFFh | SARAM 2 |
| 016000h − 017FFFh | 0009 6000h – 0009 7FFFh | SARAM 3 |
| 018000h − 019FFFh | 0009 8000h – 0009 9FFFh | SARAM 4 |
| 01A000h − 01BFFFh | 0009 A000h – 0009 BFFFh | SARAM 5 |
| 01C000h − 01DFFFh | 0009 C000h – 0009 DFFFh | SARAM 6 |
| 01E000h − 01FFFFh | 0009 E000h – 0009 FFFFh | SARAM 7 |
6.2.1.4 I/O Memory
Each device includes a 64K byte I/O space for the memory-mapped registers of the DSP peripherals and system registers used for idle control, status monitoring and system configuration. I/O space is separate from program and memory space and is accessed with separate instruction opcodes or via the DMAs.
Table 6-5, Table 6-6 and Table 6-7 list the memory-mapped registers of each device. Note that not all addresses in the 64K byte I/O space are used; these addresses must be treated as reserved and not accessed by the CPU nor DMA. For the expanded tables of each peripheral, see , Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications of this document.
Some DMA controllers have access to the I/O-Space memory-mapped registers of the following peripherals registers: I2C, UART, I2S, SD, USB, and SAR ADC.
Before accessing any peripheral memory-mapped register, make sure the peripheral being accessed is not held in reset via the Peripheral Reset Control Register (PRCR) and its internal clock is enabled via the Peripheral Clock Gating Control Registers (PCGCR1 and PCGCR2).
Table 6-5 Peripheral I/O-Space Control Registers for C5535
| WORD ADDRESS | PERIPHERAL |
|---|---|
| 0x0000 – 0x0004 | Idle Control |
| 0x0005 – 0x000D through 0x0803 – 0x0BFF | Reserved |
| 0x0C00 – 0x0C7F | DMA0 |
| 0x0C80 – 0x0CFF | Reserved |
| 0x0D00 – 0x0D7F | DMA1 |
| 0x0D80 – 0x0DFF | Reserved |
| 0x0E00 – 0x0E7F | DMA2 |
| 0x0E80 – 0x0EFF | Reserved |
| 0x0F00 – 0x0F7F | DMA3 |
| 0x0F80 – 0x17FF | Reserved |
| 0x1800 – 0x181F | Timer0 |
| 0x1820 – 0x183F | Reserved |
| 0x1840 – 0x185F | Timer1 |
| 0x1860 – 0x187F | Reserved |
| 0x1880 – 0x189F | Timer2 |
| 0x1900 – 0x197F | RTC |
| 0x1980 – 0x19FF | Reserved |
| 0x1A00 – 0x1A6C | I2C |
| 0x1A6D – 0x1AFF | Reserved |
| 0x1B00 – 0x1B1F | UART |
| 0x1B80 – 0x1BFF | Reserved |
| 0x1C00 – 0x1CFF | System Control |
| 0x1D00 – 0x1FFF through 0x2600 – 0x27FF | Reserved |
| 0x2800 – 0x2840 | I2S0 |
| 0x2900 – 0x2940 | I2S1 |
| 0x2A00 – 0x2A40 | I2S2 |
| 0x2B00 – 0x2B40 | I2S3 |
| 0x2C41 – 0x2DFF | Reserved |
| 0x2E00 – 0x2E40 | LCD |
| 0x2E41 – 0x2FFF | Reserved |
| 0x3000 – 0x300F | SPI |
| 0x3010 – 0x39FF | Reserved |
| 0x3A00 – 0x3A7F | SD0 |
| 0x3A80 – 0x3AFF | Reserved |
| 0x3B00 – 0x3B7F | SD1 |
| 0x3B80 – 0x6FFF | Reserved |
| 0x7000 – 0x70FF | SAR and Analog Control Registers |
| 0x7100 – 0x7FFF | Reserved |
| 0x8000 – 0xFFFF | USB |
Table 6-6 Peripheral I/O-Space Control Registers for C5534 and C5533
| WORD ADDRESS | PERIPHERAL |
|---|---|
| 0x0000 – 0x0004 | Idle Control |
| 0x0005 – 0x000D through 0x0803 – 0x0BFF | Reserved |
| 0x0C00 – 0x0C7F | DMA0 |
| 0x0C80 – 0x0CFF | Reserved |
| 0x0D00 – 0x0D7F | DMA1 |
| 0x0D80 – 0x0DFF | Reserved |
| 0x0E00 – 0x0E7F | DMA2 |
| 0x0E80 – 0x0EFF | Reserved |
| 0x0F00 – 0x0F7F | DMA3 |
| 0x0F80 – 0x0FFF | Reserved |
| 0x1000 – 0x10DD | Reserved |
| 0x10EE – 0x10FF through 0x1300 – 0x17FF | Reserved |
| 0x1800 – 0x181F | Timer0 |
| 0x1820 – 0x183F | Reserved |
| 0x1840 – 0x185F | Timer1 |
| 0x1860 – 0x187F | Reserved |
| 0x1880 – 0x189F | Timer2 |
| 0x1900 – 0x197F | RTC |
| 0x1980 – 0x19FF | Reserved |
| 0x1A00 – 0x1A6C | I2C |
| 0x1A6D – 0x1AFF | Reserved |
| 0x1B00 – 0x1B1F | UART |
| 0x1B80 – 0x1BFF | Reserved |
| 0x1C00 – 0x1CFF | System Control |
| 0x1D00 – 0x1FFF through 0x2600 – 0x27FF | Reserved |
| 0x2800 – 0x2840 | I2S0 |
| 0x2900 – 0x2940 | I2S1 |
| 0x2A00 – 0x2A40 | I2S2 |
| 0x2B00 – 0x2B40 | I2S3 |
| 0x2C41 – 0x2FFF | Reserved |
| 0x3000 – 0x300F | SPI |
| 0x3010 – 0x39FF | Reserved |
| 0x3A00 – 0x3A7F | SD0 |
| 0x3A80 – 0x3AFF | Reserved |
| 0x3B00 – 0x3B7F | SD1 |
| 0x3B80 – 0x7FFF | Reserved |
| 0x8000 – 0xFFFF | USB |
Table 6-7 Peripheral I/O-Space Control Registers for C5532
| WORD ADDRESS | PERIPHERAL |
|---|---|
| 0x0000 – 0x0004 | Idle Control |
| 0x0005 – 0x000D through 0x0803 – 0x0BFF | Reserved |
| 0x0C00 – 0x0C7F | DMA0 |
| 0x0C80 – 0x0CFF | Reserved |
| 0x0D00 – 0x0D7F | DMA1 |
| 0x0D80 – 0x0DFF | Reserved |
| 0x0E00 – 0x0E7F | DMA2 |
| 0x0E80 – 0x0EFF | Reserved |
| 0x0F00 – 0x0F7F | DMA3 |
| 0x0F80 – 0x0FFF | Reserved |
| 0x1000 – 0x10DD | Reserved |
| 0x10EE – 0x10FF through 0x1300 – 0x17FF | Reserved |
| 0x1800 – 0x181F | Timer0 |
| 0x1820 – 0x183F | Reserved |
| 0x1840 – 0x185F | Timer1 |
| 0x1860 – 0x187F | Reserved |
| 0x1880 – 0x189F | Timer2 |
| 0x1900 – 0x197F | RTC |
| 0x1980 – 0x19FF | Reserved |
| 0x1A00 – 0x1A6C | I2C |
| 0x1A6D – 0x1AFF | Reserved |
| 0x1B00 – 0x1B1F | UART |
| 0x1B80 – 0x1BFF | Reserved |
| 0x1C00 – 0x1CFF | System Control |
| 0x1D00 – 0x1FFF through 0x2600 – 0x27FF | Reserved |
| 0x2800 – 0x2840 | I2S0 |
| 0x2900 – 0x2940 | I2S1 |
| 0x2A00 – 0x2A40 | I2S2 |
| 0x2B00 – 0x2B40 | I2S3 |
| 0x2C41 – 0x2DFF through 0x2E41 - 0x2FFF | Reserved |
| 0x3000 – 0x300F | SPI |
| 0x3010 – 0x39FF | Reserved |
| 0x3A00 – 0x3A7F | SD0 |
| 0x3A80 – 0x3AFF | Reserved |
| 0x3B00 – 0x3B7F | SD1 |
| 0x3B80 – 0xFFFF | Reserved |
6.2.2 Memory Map
The on-chip, dual-access RAM allows two accesses to a given block during the same cycle. There are 8 blocks of 8K bytes of dual-access RAM. The on-chip, single-access RAM allows one access to a given block per cycle. In addition, there are 32 blocks of 8K bytes of single-access RAM.
The DSP memory is accessible by different master modules within the DSP, including the C55x CPU and the four DMA controllers, LCD, and USB's CDMA (see Figure 6-1).
6.2.3 Register Map
6.2.3.1 General-Purpose Input/Output Peripheral Register Descriptions
The external parallel port interface includes a 16-bit general purpose I/O that can be individually programmed as input or output with interrupt capability. Control of the general purpose I/O is maintained through a set of I/O memory-mapped registers shown in Table 6-8.
Table 6-8 GPIO Registers
| HEX ADDRESS RANGE | ACRONYM | REGISTER NAME |
|---|---|---|
| 1C06h | IODIR1 | GPIO Direction Register 1 |
| 1C07h | IODIR2 | GPIO Direction Register 2 |
| 1C08h | IOINDATA1 | GPIO Data In Register 1 |
| 1C09h | IOINDATA2 | GPIO Data In Register 2 |
| 1C0Ah | IODATAOUT1 | GPIO Data Out Register 1 |
| 1C0Bh | IODATAOUT2 | GPIO Data Out Register 2 |
| 1C0Ch | IOINTEDG1 | GPIO Interrupt Edge Trigger Enable Register 1 |
| 1C0Dh | IOINTEDG2 | GPIO Interrupt Edge Trigger Enable Register 2 |
| 1C0Eh | IOINTEN1 | GPIO Interrupt Enable Register 1 |
| 1C0Fh | IOINTEN2 | GPIO Interrupt Enable Register 2 |
| 1C10h | IOINTFLG1 | GPIO Interrupt Flag Register 1 |
| 1C11h | IOINTFLG2 | GPIO Interrupt Flag Register 2 |
6.2.3.2 I2C Peripheral Register Descriptions
Table 6-9 shows the Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) registers.
Table 6-9 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) Registers
| HEX ADDRESS RANGE | ACRONYM | REGISTER NAME |
|---|---|---|
| 1A00h | ICOAR | I2C Own Address Register |
| 1A04h | ICIMR | I2C Interrupt Mask Register |
| 1A08h | ICSTR | I2C Interrupt Status Register |
| 1A0Ch | ICCLKL | I2C Clock Low-Time Divider Register |
| 1A10h | ICCLKH | I2C Clock High-Time Divider Register |
| 1A14h | ICCNT | I2C Data Count Register |
| 1A18h | ICDRR | I2C Data Receive Register |
| 1A1Ch | ICSAR | I2C Slave Address Register |
| 1A20h | ICDXR | I2C Data Transmit Register |
| 1A24h | ICMDR | I2C Mode Register |
| 1A28h | ICIVR | I2C Interrupt Vector Register |
| 1A2Ch | ICEMDR | I2C Extended Mode Register |
| 1A30h | ICPSC | I2C Prescaler Register |
| 1A34h | ICPID1 | I2C Peripheral Identification Register 1 |
| 1A38h | ICPID2 | I2C Peripheral Identification Register 2 |
6.2.3.3 I2S Peripheral Register Descriptions
Table 6-10 through Table 6-13 show the I2S0 through I2S3 registers.
Table 6-10 I2S0 Registers
| HEX ADDRESS RANGE | ACRONYM | REGISTER NAME |
|---|---|---|
| 2800h | I2S0SCTRL | I2S0 Serializer Control Register |
| 2804h | I2S0SRATE | I2S0 Sample Rate Generator Register |
| 2808h | I2S0TXLT0 | I2S0 Transmit Left Data 0 Register |
| 2809h | I2S0TXLT1 | I2S0 Transmit Left Data 1 Register |
| 280Ch | I2S0TXRT0 | I2S0 Transmit Right Data 0 Register |
| 280Dh | I2S0TXRT1 | I2S0 Transmit Right Data 1 Register |
| 2810h | I2S0INTFL | I2S0 Interrupt Flag Register |
| 2814h | I2S0INTMASK | I2S0 Interrupt Mask Register |
| 2828h | I2S0RXLT0 | I2S0 Receive Left Data 0 Register |
| 2829h | I2S0RXLT1 | I2S0 Receive Left Data 1 Register |
| 282Ch | I2S0RXRT0 | I2S0 Receive Right Data 0 Register |
| 282Dh | I2S0RXRT1 | I2S0 Receive Right Data 1 Register |
Table 6-11 I2S1 Registers
| HEX ADDRESS RANGE | ACRONYM | REGISTER NAME |
|---|---|---|
| 2900h | I2S1SCTRL | I2S1 Serializer Control Register |
| 2904h | I2S1SRATE | I2S1 Sample Rate Generator Register |
| 2908h | I2S1TXLT0 | I2S1 Transmit Left Data 0 Register |
| 2909h | I2S1TXLT1 | I2S1 Transmit Left Data 1 Register |
| 290Ch | I2S1TXRT0 | I2S1 Transmit Right Data 0 Register |
| 290Dh | I2S1TXRT1 | I2S1 Transmit Right Data 1 Register |
| 2910h | I2S1INTFL | I2S1 Interrupt Flag Register |
| 2914h | I2S1INTMASK | I2S1 Interrupt Mask Register |
| 2928h | I2S1RXLT0 | I2S1 Receive Left Data 0 Register |
| 2929h | I2S1RXLT1 | I2S1 Receive Left Data 1 Register |
| 292Ch | I2S1RXRT0 | I2S1 Receive Right Data 0 Register |
| 292Dh | I2S1RXRT1 | I2S1 Receive Right Data 1 Register |
Table 6-12 I2S2 Registers
| HEX ADDRESS RANGE | ACRONYM | REGISTER NAME |
|---|---|---|
| 2A00h | I2S2SCTRL | I2S2 Serializer Control Register |
| 2A04h | I2S2SRATE | I2S2 Sample Rate Generator Register |
| 2A08h | I2S2TXLT0 | I2S2 Transmit Left Data 0 Register |
| 2A09h | I2S2TXLT1 | I2S2 Transmit Left Data 1 Register |
| 2A0Ch | I2S2TXRT0 | I2S2 Transmit Right Data 0 Register |
| 2A0Dh | I2S2TXRT1 | I2S2 Transmit Right Data 1 Register |
| 2A10h | I2S2INTFL | I2S2 Interrupt Flag Register |
| 2A14h | I2S2INTMASK | I2S2 Interrupt Mask Register |
| 2A28h | I2S2RXLT0 | I2S2 Receive Left Data 0 Register |
| 2A29h | I2S2RXLT1 | I2S2 Receive Left Data 1 Register |
| 2A2Ch | I2S2RXRT0 | I2S2 Receive Right Data 0 Register |
| 2A2Dh | I2S2RXRT1 | I2S2 Receive Right Data 1 Register |
Table 6-13 I2S3 Registers
| HEX ADDRESS RANGE | ACRONYM | REGISTER NAME |
|---|---|---|
| 2B00h | I2S3SCTRL | I2S3 Serializer Control Register |
| 2B04h | I2S3SRATE | I2S3 Sample Rate Generator Register |
| 2B08h | I2S3TXLT0 | I2S3 Transmit Left Data 0 Register |
| 2B09h | I2S3TXLT1 | I2S3 Transmit Left Data 1 Register |
| 2B0Ch | I2S3TXRT0 | I2S3 Transmit Right Data 0 Register |
| 2B0Dh | I2S3TXRT1 | I2S3 Transmit Right Data 1 Register |
| 2B10h | I2S3INTFL | I2S3 Interrupt Flag Register |
| 2B14h | I2S3INTMASK | I2S3 Interrupt Mask Register |
| 2B28h | I2S3RXLT0 | I2S3 Receive Left Data 0 Register |
| 2B29h | I2S3RXLT1 | I2S3 Receive Left Data 1 Register |
| 2B2Ch | I2S3RXRT0 | I2S3 Receive Right Data 0 Register |
| 2B2Dh | I2S3RXRT1 | I2S3 Receive Right Data 1 Register |
6.2.3.4 LCDC Peripheral Register Descriptions
Table 6-14 shows the LCDC peripheral registers.
Table 6-14 LCD Controller Registers
| CPU WORD ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 2E00h | LCDREVMIN | LCD Minor Revision Register |
| 2E01h | LCDREVMAJ | LCD Major Revision Register |
| 2E04h | LCDCR | LCD Control Register |
| 2E08h | LCDSR | LCD Status Register |
| 2E0Ch | LCDLIDDCR | LCD LIDD Control Register |
| 2E10h | LCDLIDDCS0CONFIG0 | LCD LIDD CS0 Configuration Register 0 |
| 2E11h | LCDLIDDCS0CONFIG1 | LCD LIDD CS0 Configuration Register 1 |
| 2E14h | LCDLIDDCS0ADDR | LCD LIDD CS0 Address Read and Write Register |
| 2E18h | LCDLIDDCS0DATA | LCD LIDD CS0 Data Read and Write Register |
| 2E1Ch | LCDLIDDCS1CONFIG0 | LCD LIDD CS1 Configuration Register 0 |
| 2E1Dh | LCDLIDDCS1CONFIG1 | LCD LIDD CS1 Configuration Register 1 |
| 2E20h | LCDLIDDCS1ADDR | LCD LIDD CS1 Address Read and Write Register |
| 2E24h | LCDLIDDCS1DATA | LCD LIDD CS1 Data Read and Write Register |
| 2E28h – 2E3Ah | — | Reserved |
| 2E40h | LCDDMACR | LCD DMA Control Register |
| 2E44h | LCDDMAFB0BAR0 | LCD DMA Frame Buffer 0 Base Address Register 0 |
| 2E45h | LCDDMAFB0BAR1 | LCD DMA Frame Buffer 0 Base Address Register 1 |
| 2E48h | LCDDMAFB0CAR0 | LCD DMA Frame Buffer 0 Ceiling Address Register 0 |
| 2E49h | LCDDMAFB0CAR1 | LCD DMA Frame Buffer 0 Ceiling Address Register 1 |
| 2E4Ch | LCDDMAFB1BAR0 | LCD DMA Frame Buffer 1 Base Address Register 0 |
| 2E4Dh | LCDDMAFB1BAR1 | LCD DMA Frame Buffer 1 Base Address Register 1 |
| 2E50h | LCDDMAFB1CAR0 | LCD DMA Frame Buffer 1 Ceiling Address Register 0 |
| 2E51h | LCDDMAFB1CAR1 | LCD DMA Frame Buffer 1 Ceiling Address Register 1 |
6.2.3.5 RTC Peripheral Register Descriptions
Table 6-15 shows the RTC registers.
Table 6-15 Real-Time Clock (RTC) Registers
| HEX ADDRESS RANGE | ACRONYM | REGISTER NAME |
|---|---|---|
| 1900h | RTCINTEN | RTC Interrupt Enable Register |
| 1901h | RTCUPDATE | RTC Update Register |
| 1904h | RTCMIL | Milliseconds Register |
| 1905h | RTCMILA | Milliseconds Alarm Register |
| 1908h | RTCSEC | Seconds Register |
| 1909h | RTCSECA | Seconds Alarm Register |
| 190Ch | RTCMIN | Minutes Register |
| 190Dh | RTCMINA | Minutes Alarm Register |
| 1910h | RTCHOUR | Hours Register |
| 1911h | RTCHOURA | Hours Alarm Register |
| 1914h | RTCDAY | Days Register |
| 1915h | RTCDAYA | Days Alarm Register |
| 1918h | RTCMONTH | Months Register |
| 1919h | RTCMONTHA | Months Alarm Register |
| 191Ch | RTCYEAR | Years Register |
| 191Dh | RTCYEARA | Years Alarm Register |
| 1920h | RTCINTFL | RTC Interrupt Flag Register |
| 1921h | RTCNOPWR | RTC Lost Power Status Register |
| 1924h | RTCINTREG | RTC Interrupt Register |
| 1928h | RTCDRIFT | RTC Compensation Register |
| 192Ch | RTCOSC | RTC Oscillator Register |
| 1930h | RTCPMGT | RTC Power Management Register |
| 1960h | RTCSCR1 | RTC LSW Scratch Register 1 |
| 1961h | RTCSCR2 | RTC MSW Scratch Register 2 |
| 1964h | RTCSCR3 | RTC LSW Scratch Register 3 |
| 1965h | RTCSCR4 | RTC MSW Scratch Register 4 |
6.2.3.6 SAR ADC Peripheral Register Descriptions
Table 6-16 shows the SAR ADC peripheral registers.
Note: SAR ADC applies only to C5535.
Table 6-16 SAR Analog Control Registers
| CPU WORD ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 7012h | SARCTRL | SAR A/D Control Register |
| 7014h | SARDATA | SAR A/D Data Register |
| 7016h | SARCLKCTRL | SAR A/D Clock Control Register |
| 7018h | SARPINCTRL | SAR A/D Reference and Pin Control Register |
| 701Ah | SARGPOCTRL | SAR A/D GPO Control Register |
6.2.3.7 SD Peripheral Register Descriptions
Table 6-17and Table 6-18 shows the SD registers. The SD0 registers start at address 3A00h and the SD1 registers start at address 3B00h.
Table 6-17 SD0 Registers
| HEX ADDRESS RANGE | ACRONYM | REGISTER NAME |
|---|---|---|
| 3A00h | SDCTL | SD Control Register |
| 3A04h | SDCLK | SD Memory Clock Control Register |
| 3A08h | SDST0 | SD Status Register 0 |
| 3A0Ch | SDST1 | SD Status Register 1 |
| 3A10h | SDIM | SD Interrupt Mask Register |
| 3A14h | SDTOR | SD Response Time-Out Register |
| 3A18h | SDTOD | SD Data Read Time-Out Register |
| 3A1Ch | SDBLEN | SD Block Length Register |
| 3A20h | SDNBLK | SD Number of Blocks Register |
| 3A24h | SDNBLC | SD Number of Blocks Counter Register |
| 3A28h | SDDRR1 | SD Data Receive 1 Register |
| 3A29h | SDDRR2 | SD Data Receive 2 Register |
| 3A2Ch | SDDXR1 | SD Data Transmit 1 Register |
| 3A2Dh | SDDXR2 | SD Data Transmit 2 Register |
| 3A30h | SDCMD | SD Command Register |
| 3A34h | SDARGHL | SD Argument Register |
| 3A38h | SDRSP0 | SD Response Register 0 |
| 3A39h | SDRSP1 | SD Response Register 1 |
| 3A3Ch | SDRSP2 | SD Response Register 2 |
| 3A3Dh | SDRSP3 | SD Response Register 3 |
| 3A40h | SDRSP4 | SD Response Register 4 |
| 3A41h | SDRSP5 | SD Response Register 5 |
| 3A44h | SDRSP6 | SD Response Register 6 |
| 3A45h | SDRSP7 | SD Response Register 7 |
| 3A48h | SDDRSP | SD Data Response Register |
| 3A50h | SDCIDX | SD Command Index Register |
| 3A64h – 3A70h | – | Reserved |
| 3A74h | SDFIFOCTL | SD FIFO Control Register |
Table 6-18 SD1 Registers
| HEX ADDRESS RANGE | ACRONYM | REGISTER NAME |
|---|---|---|
| 3B00h | SDCTL | SD Control Register |
| 3B04h | SDCLK | SD Memory Clock Control Register |
| 3B08h | SDST0 | SD Status Register 0 |
| 3B0Ch | SDST1 | SD Status Register 1 |
| 3B10h | SDIM | SD Interrupt Mask Register |
| 3B14h | SDTOR | SD Response Time-Out Register |
| 3B18h | SDTOD | SD Data Read Time-Out Register |
| 3B1Ch | SDBLEN | SD Block Length Register |
| 3B20h | SDNBLK | SD Number of Blocks Register |
| 3B24h | SDNBLC | SD Number of Blocks Counter Register |
| 3B28h | SDDRR1 | SD Data Receive 1 Register |
| 3B29h | SDDRR2 | SD Data Receive 2 Register |
| 3B2Ch | SDDXR1 | SD Data Transmit 1 Register |
| 3B2Dh | SDDXR2 | SD Data Transmit 2 Register |
| 3B30h | SDCMD | SD Command Register |
| 3B34h | SDARGHL | SD Argument Register |
| 3B38h | SDRSP0 | SD Response Register 0 |
| 3B39h | SDRSP1 | SD Response Register 1 |
| 3B3Ch | SDRSP2 | SD Response Register 2 |
| 3B3Dh | SDRSP3 | SD Response Register 3 |
| 3B40h | SDRSP4 | SD Response Register 4 |
| 3B41h | SDRSP5 | SD Response Register 5 |
| 3B44h | SDRSP6 | SD Response Register 6 |
| 3B45h | SDRSP7 | SD Response Register 7 |
| 3B48h | SDDRSP | SD Data Response Register |
| 3B50h | SDCIDX | SD Command Index Register |
| 3B74h | SDFIFOCTL | SD FIFO Control Register |
6.2.3.8 SPI Peripheral Register Descriptions
Table 6-19 shows the SPI registers.
Table 6-19 SPI Module Registers
| CPU WORD ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER NAME |
|---|---|---|
| 3000h | SPICDR | Clock Divider Register |
| 3001h | SPICCR | Clock Control Register |
| 3002h | SPIDCR1 | Device Configuration Register 1 |
| 3003h | SPIDCR2 | Device Configuration Register 2 |
| 3004h | SPICMD1 | Command Register 1 |
| 3005h | SPICMD2 | Command Register 2 |
| 3006h | SPISTAT1 | Status Register 1 |
| 3007h | SPISTAT2 | Status Register 2 |
| 3008h | SPIDAT1 | Data Register 1 |
| 3009h | SPIDAT2 | Data Register 2 |
6.2.3.9 System Registers
The system registers are used to configure the device and monitor its status. Brief descriptions of the various system registers are shown in Table 6-20.
Table 6-20 Idle Control, Status, and System Registers
| CPU WORD ADDRESS | ACRONYM | Register Description | COMMENTS |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0001h | ICR | Idle Control Register | |
| 0002h | ISTR | Idle Status Register | |
| 1C00h | EBSR | External Bus Selection Register | See Section 5.7.3.5.1 of this document. |
| 1C02h | PCGCR1 | Peripheral Clock Gating Control Register 1 | |
| 1C03h | PCGCR2 | Peripheral Clock Gating Control Register 2 | |
| 1C04h | PSRCR | Peripheral Software Reset Counter Register | |
| 1C05h | PRCR | Peripheral Reset Control Register | |
| 1C14h | TIAFR | Timer Interrupt Aggregation Flag Register | |
| 1C16h | ODSCR | Output Drive Strength Control Register | |
| 1C17h | PDINHIBR1 | Pulldown Inhibit Register 1 | |
| 1C18h | PDINHIBR2 | Pulldown Inhibit Register 2 | |
| 1C19h | PDINHIBR3 | Pulldown Inhibit Register 3 | |
| 1C1Ah | DMA0CESR1 | DMA0 Channel Event Source Register 1 | |
| 1C1Bh | DMA0CESR2 | DMA0 Channel Event Source Register 2 | |
| 1C1Ch | DMA1CESR1 | DMA1 Channel Event Source Register 1 | |
| 1C1Dh | DMA1CESR2 | DMA1 Channel Event Source Register 2 | |
| 1C28h | RAMSLPMDCNTLR1 | RAM Sleep Mode Control Register 1 | |
| 1C2Ah | RAMSLPMDCNTLR2 | RAM Sleep Mode Control Register 2 | |
| 1C2Bh | RAMSLPMDCNTLR3 | RAM Sleep Mode Control Register 3 | |
| 1C2Ch | RAMSLPMDCNTLR4 | RAM Sleep Mode Control Register 4 | |
| 1C2Dh | RAMSLPMDCNTLR5 | RAM Sleep Mode Control Register 5 | |
| 1C30h | DMAIFR | DMA Interrupt Flag Aggregation Register | |
| 1C31h | DMAIER | DMA Interrupt Enable Register | |
| 1C32h | USBSCR | USB System Control Register | Does not apply to TMS320C5532. |
| 1C36h | DMA2CESR1 | DMA2 Channel Event Source Register 1 | |
| 1C37h | DMA2CESR2 | DMA2 Channel Event Source Register 2 | |
| 1C38h | DMA3CESR1 | DMA3 Channel Event Source Register 1 | |
| 1C39h | DMA3CESR2 | DMA3 Channel Event Source Register 2 | |
| 1C3Ah | CLKSTOP | Peripheral Clock Stop Request and Acknowledge Register | |
| 1C40h | DIEIDR0 | Die ID Register 0 | |
| 1C41h | DIEIDR1 | Die ID Register 1 | |
| 1C42h | DIEIDR2 | Die ID Register 2 | |
| 1C43h | DIEIDR3 | Die ID Register 3 | |
| 1C44h | DIEIDR4 | Die ID Register 4 | |
| 1C45h | DIEIDR5 | Die ID Register 5 | |
| 1C46h | DIEIDR6 | Die ID Register 6 | |
| 1C47h | DIEIDR7 | Die ID Register 7 | |
| 7004h | LDOCNTL | LDO Control Register | see Section 5.7.2.1.1.3 of this document. |
6.2.3.10 Timers Peripheral Register Descriptions
Table 6-21 through Table 6-24 show the timer and watchdog registers.
Table 6-21 Watchdog Timer Registers (Timer2 only)
| CPU WORD ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 1880h | WDKCKLK | Watchdog Kick Lock Register |
| 1882h | WDKICK | Watchdog Kick Register |
| 1884h | WDSVLR | Watchdog Start Value Lock Register |
| 1886h | WDSVR | Watchdog Start Value Register |
| 1888h | WDENLOK | Watchdog Enable Lock Register |
| 188Ah | WDEN | Watchdog Enable Register |
| 188Ch | WDPSLR | Watchdog Prescale Lock Register |
| 188Eh | WDPS | Watchdog Prescale Register |
Table 6-22 General-Purpose Timer 0 Registers
| CPU WORD ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 1810h | TCR | Timer 0 Control Register |
| 1812h | TIMPRD1 | Timer 0 Period Register 1 |
| 1813h | TIMPRD2 | Timer 0 Period Register 2 |
| 1814h | TIMCNT1 | Timer 0 Counter Register 1 |
| 1815h | TIMCNT2 | Timer 0 Counter Register 2 |
Table 6-23 General-Purpose Timer 1 Registers
| CPU WORD ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 1850h | TCR | Timer 1 Control Register |
| 1852h | TIMPRD1 | Timer 1 Period Register 1 |
| 1853h | TIMPRD2 | Timer 1 Period Register 2 |
| 1854h | TIMCNT1 | Timer 1 Counter Register 1 |
| 1855h | TIMCNT2 | Timer 1 Counter Register 2 |
Table 6-24 General-Purpose Timer 2 Registers
| CPU WORD ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 1890h | TCR | Timer 2 Control Register |
| 1892h | TIMPRD1 | Timer 2 Period Register 1 |
| 1893h | TIMPRD2 | Timer 2 Period Register 2 |
| 1894h | TIMCNT1 | Timer 2 Counter Register 1 |
| 1895h | TIMCNT2 | Timer 2 Counter Register 2 |
6.2.3.11 UART Peripheral Register Descriptions
Table 6-25 shows the UART registers.
Table 6-25 UART Registers
| HEX ADDRESS RANGE | ACRONYM | REGISTER NAME |
|---|---|---|
| 1B00h | RBR | Receiver Buffer Register (read only) |
| 1B00h | THR | Transmitter Holding Register (write only) |
| 1B02h | IER | Interrupt Enable Register |
| 1B04h | IIR | Interrupt Identification Register (read only) |
| 1B04h | FCR | FIFO Control Register (write only) |
| 1B06h | LCR | Line Control Register |
| 1B08h | MCR | Modem Control Register |
| 1B0Ah | LSR | Line Status Register |
| 1B0Ch | MSR | Modem Status Register |
| 1B0Eh | SCR | Scratch Register |
| 1B10h | DLL | Divisor LSB Latch |
| 1B12h | DLH | Divisor MSB Latch |
| 1B18h | PWREMU_MGMT | Power and Emulation Management Register |
6.2.3.12 USB2.0 Peripheral Register Descriptions
Table 6-26 lists of the USB2.0 peripheral registers.
Note: USB does not apply to C5532.
Table 6-26 Universal Serial Bus (USB) Registers(1)
| CPU WORD ADDRESS | ACRONYM | REGISTER DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 8000h | REVID1 | Revision Identification Register 1 |
| 8001h | REVID2 | Revision Identification Register 2 |
| 8004h | CTRLR | Control Register |
| 8008h | STATR | Status Register |
| 800Ch | EMUR | Emulation Register |
| 8010h | MODER1 | Mode Register 1 |
| 8011h | MODER2 | Mode Register 2 |
| 8014h | AUTOREQ | Auto Request Register |
| 8018h | SRPFIXTIME1 | SRP Fix Time Register 1 |
| 8019h | SRPFIXTIME2 | SRP Fix Time Register 2 |
| 801Ch | TEARDOWN1 | Teardown Register 1 |
| 801Dh | TEARDOWN2 | Teardown Register 2 |
| 8020h | INTSRCR1 | USB Interrupt Source Register 1 |
| 8021h | INTSRCR2 | USB Interrupt Source Register 2 |
| 8024h | INTSETR1 | USB Interrupt Source Set Register 1 |
| 8025h | INTSETR2 | USB Interrupt Source Set Register 2 |
| 8028h | INTCLRR1 | USB Interrupt Source Clear Register 1 |
| 8029h | INTCLRR2 | USB Interrupt Source Clear Register 2 |
| 802Ch | INTMSKR1 | USB Interrupt Mask Register 1 |
| 802Dh | INTMSKR2 | USB Interrupt Mask Register 2 |
| 8030h | INTMSKSETR1 | USB Interrupt Mask Set Register 1 |
| 8031h | INTMSKSETR2 | USB Interrupt Mask Set Register 2 |
| 8034h | INTMSKCLRR1 | USB Interrupt Mask Clear Register 1 |
| 8035h | INTMSKCLRR2 | USB Interrupt Mask Clear Register 2 |
| 8038h | INTMASKEDR1 | USB Interrupt Source Masked Register 1 |
| 8039h | INTMASKEDR2 | USB Interrupt Source Masked Register 2 |
| 803Ch | EOIR | USB End of Interrupt Register |
| 8040h | INTVECTR1 | USB Interrupt Vector Register 1 |
| 8041h | INTVECTR2 | USB Interrupt Vector Register 2 |
| 8050h | GREP1SZR1 | Generic RNDIS EP1Size Register 1 |
| 8051h | GREP1SZR2 | Generic RNDIS EP1Size Register 2 |
| 8054h | GREP2SZR1 | Generic RNDIS EP2 Size Register 1 |
| 8055h | GREP2SZR2 | Generic RNDIS EP2 Size Register 2 |
| 8058h | GREP3SZR1 | Generic RNDIS EP3 Size Register 1 |
| 8059h | GREP3SZR2 | Generic RNDIS EP3 Size Register 2 |
| 805Ch | GREP4SZR1 | Generic RNDIS EP4 Size Register 1 |
| 805Dh | GREP4SZR2 | Generic RNDIS EP4 Size Register 2 |
| Common USB Registers | ||
| 8401h | FADDR_POWER | Function Address Register, Power Management Register |
| 8402h | INTRTX | Interrupt Register for Endpoint 0 plus Transmit Endpoints 1 to 4 |
| 8405h | INTRRX | Interrupt Register for Receive Endpoints 1 to 4 |
| 8406h | INTRTXE | Interrupt enable register for INTRTX |
| 8409h | INTRRXE | Interrupt Enable Register for INTRRX |
| 840Ah | INTRUSB_INTRUSBE | Interrupt Register for Common USB Interrupts, Interrupt Enable Register |
| 840Dh | FRAME | Frame Number Register |
| 840Eh | INDEX_TESTMODE | Index Register for Selecting the Endpoint Status and Control Registers, Register to Enable the USB 2.0 Test Modes |
| USB Indexed Registers | ||
| 8411h | TXMAXP_INDX | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral and Host Transmit Endpoint. (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4) |
| 8412h | PERI_CSR0_INDX | Control Status Register for Endpoint 0 in Peripheral Mode. (Index register set to select Endpoint 0) |
| PERI_TXCSR_INDX | Control Status Register for Peripheral Transmit Endpoint. (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4) | |
| 8415h | RXMAXP_INDX | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral and Host Receive Endpoint. (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4) |
| 8416h | PERI_RXCSR_INDX | Control Status Register for Peripheral Receive Endpoint. (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4) |
| 8419h | COUNT0_INDX | Number of Received Bytes in Endpoint 0 FIFO. (Index register set to select Endpoint 0) |
| RXCOUNT_INDX | Number of Bytes in Host Receive Endpoint FIFO. (Index register set to select Endpoints 1- 4) | |
| 841Ah | - | Reserved |
| 841Dh | - | Reserved |
| 841Eh | CONFIGDATA_INDC (Upper byte of 841Eh) |
Returns details of core configuration. (index register set to select Endpoint 0) |
| USB FIFO Registers | ||
| 8421h | FIFO0R1 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register 1 for Endpoint 0 |
| 8422h | FIFO0R2 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register 2 for Endpoint 0 |
| 8425h | FIFO1R1 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register 1 for Endpoint 1 |
| 8426h | FIFO1R2 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register 2 for Endpoint 1 |
| 8429h | FIFO2R1 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register 1 for Endpoint 2 |
| 842Ah | FIFO2R2 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register 2 for Endpoint 2 |
| 842Dh | FIFO3R1 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register 1 for Endpoint 3 |
| 842Eh | FIFO3R2 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register 2 for Endpoint 3 |
| 8431h | FIFO4R1 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register 1 for Endpoint 4 |
| 8432h | FIFO4R2 | Transmit and Receive FIFO Register 2 for Endpoint 4 |
| Dynamic FIFO Control Registers | ||
| 8461h | DEVCTL | Device Control Register |
| 8462h | TXFIFOSZ_RXFIFOSZ | Transmit Endpoint FIFO Size, Receive Endpoint FIFO Size (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4) |
| 8465h | TXFIFOADDR | Transmit Endpoint FIFO Address (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4) |
| 8466h | RXFIFOADDR | Receive Endpoint FIFO Address (Index register set to select Endpoints 1-4) |
| 846Dh | - | Reserved |
| Control and Status Register for Endpoint 0 | ||
| 8501h | - | Reserved |
| 8502h | PERI_CSR0 | Control Status Register for Peripheral Endpoint 0 |
| 8505h | - | Reserved |
| 8506h | - | Reserved |
| 8509h | COUNT0 | Number of Received Bytes in Endpoint 0 FIFO |
| 850Ah | - | Reserved |
| 850Dh | - | Reserved |
| 850Eh | CONFIGDATA (Upper byte of 850Eh) |
Returns details of core configuration. |
| Control and Status Register for Endpoint 1 | ||
| 8511h | TXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral and Host Transmit Endpoint |
| 8512h | PERI_TXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Transmit Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| 8515h | RXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral and Host Receive Endpoint |
| 8516h | PERI_RXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Receive Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| 8519h | RXCOUNT | Number of Bytes in the Receiving Endpoint's FIFO |
| 851Ah | - | Reserved |
| 851Dh | - | Reserved |
| 851Eh | - | Reserved |
| Control and Status Register for Endpoint 2 | ||
| 8521h | TXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral and Host Transmit Endpoint |
| 8522h | PERI_TXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Transmit Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| 8525h | RXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral and Host Receive Endpoint |
| 8526h | PERI_RXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Receive Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| 8529h | RXCOUNT | Number of Bytes in Host Receive endpoint FIFO |
| 852Ah | - | Reserved |
| 852Dh | - | Reserved |
| 852Eh | - | Reserved |
| Control and Status Register for Endpoint 3 | ||
| 8531h | TXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral and Host Transmit Endpoint |
| 8532h | PERI_TXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Transmit Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| 8535h | RXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral and Host Receive Endpoint |
| 8536h | PERI_RXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Receive Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| 8539h | RXCOUNT | Number of Bytes in Host Receive endpoint FIFO |
| 853Ah | - | Reserved |
| 853Dh | - | Reserved |
| 853Eh | - | Reserved |
| Control and Status Register for Endpoint 4 | ||
| 8541h | TXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral and Host Transmit Endpoint |
| 8542h | PERI_TXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Transmit Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| 8545h | RXMAXP | Maximum Packet Size for Peripheral and Host Receive Endpoint |
| 8546h | PERI_RXCSR | Control Status Register for Peripheral Receive Endpoint (peripheral mode) |
| 8549h | RXCOUNT | Number of Bytes in Host Receive endpoint FIFO |
| 854Ah | - | Reserved |
| 854Dh | - | Reserved |
| 854Eh | - | Reserved |
| CPPI DMA (CMDA) Registers | ||
| 9000h | - | Reserved |
| 9001h | - | Reserved |
| 9004h | TDFDQ | CDMA Teardown Free Descriptor Queue Control Register |
| 9008h | DMAEMU | CDMA Emulation Control Register |
| 9800h | TXGCR1[0] | Transmit Channel 0 Global Configuration Register 1 |
| 9801h | TXGCR2[0] | Transmit Channel 0 Global Configuration Register 2 |
| 9808h | RXGCR1[0] | Receive Channel 0 Global Configuration Register 1 |
| 9809h | RXGCR2[0] | Receive Channel 0 Global Configuration Register 2 |
| 980Ch | RXHPCR1A[0] | Receive Channel 0 Host Packet Configuration Register 1 A |
| 980Dh | RXHPCR2A[0] | Receive Channel 0 Host Packet Configuration Register 2 A |
| 9810h | RXHPCR1B[0] | Receive Channel 0 Host Packet Configuration Register 1 B |
| 9811h | RXHPCR2B[0] | Receive Channel 0 Host Packet Configuration Register 2 B |
| 9820h | TXGCR1[1] | Transmit Channel 1 Global Configuration Register 1 |
| 9821h | TXGCR2[1] | Transmit Channel 1 Global Configuration Register 2 |
| 9828h | RXGCR1[1] | Receive Channel 1 Global Configuration Register 1 |
| 9829h | RXGCR2[1] | Receive Channel 1 Global Configuration Register 2 |
| 982Ch | RXHPCR1A[1] | Receive Channel 1 Host Packet Configuration Register 1 A |
| 982Dh | RXHPCR2A[1] | Receive Channel 1 Host Packet Configuration Register 2 A |
| 9830h | RXHPCR1B[1] | Receive Channel 1 Host Packet Configuration Register 1 B |
| 9831h | RXHPCR2B[1] | Receive Channel 1 Host Packet Configuration Register 2 B |
| 9840h | TXGCR1[2] | Transmit Channel 2 Global Configuration Register 1 |
| 9841h | TXGCR2[2] | Transmit Channel 2 Global Configuration Register 2 |
| 9848h | RXGCR1[2] | Receive Channel 2 Global Configuration Register 1 |
| 9849h | RXGCR2[2] | Receive Channel 2 Global Configuration Register 2 |
| 984Ch | RXHPCR1A[2] | Receive Channel 2 Host Packet Configuration Register 1 A |
| 984Dh | RXHPCR2A[2] | Receive Channel 2 Host Packet Configuration Register 2 A |
| 9850h | RXHPCR1B[2] | Receive Channel 2 Host Packet Configuration Register 1 B |
| 9851h | RXHPCR2B[2] | Receive Channel 2 Host Packet Configuration Register 2 B |
| 9860h | TXGCR1[3] | Transmit Channel 3 Global Configuration Register 1 |
| 9861h | TXGCR2[3] | Transmit Channel 3 Global Configuration Register 2 |
| 9868h | RXGCR1[3] | Receive Channel 3 Global Configuration Register 1 |
| 9869h | RXGCR2[3] | Receive Channel 3 Global Configuration Register 2 |
| 986Ch | RXHPCR1A[3] | Receive Channel 3 Host Packet Configuration Register 1 A |
| 986Dh | RXHPCR2A[3] | Receive Channel 3 Host Packet Configuration Register 2 A |
| 9870h | RXHPCR1B[3] | Receive Channel 3 Host Packet Configuration Register 1 B |
| 9871h | RXHPCR2B[3] | Receive Channel 3 Host Packet Configuration Register 2 B |
| A000h | DMA_SCHED_CTRL1 | CDMA Scheduler Control Register 1 |
| A001h | DMA_SCHED_CTRL2 | CDMA Scheduler Control Register 1 |
| A800h + 4 × N | ENTRYLSW[N] | CDMA Scheduler Table Word N Registers LSW (N = 0 to 63) |
| A801h + 4 × N | ENTRYMSW[N] | CDMA Scheduler Table Word N Registers MSW (N = 0 to 63) |
| Queue Manager (QMGR) Registers | ||
| C000h | - | Reserved |
| C001h | - | Reserved |
| C008h | DIVERSION1 | Queue Manager Queue Diversion Register 1 |
| C009h | DIVERSION2 | Queue Manager Queue Diversion Register 2 |
| C020h | FDBSC0 | Queue Manager Free Descriptor and Buffer Starvation Count Register 0 |
| C021h | FDBSC1 | Queue Manager Free Descriptor and Buffer Starvation Count Register 1 |
| C024h | FDBSC2 | Queue Manager Free Descriptor and Buffer Starvation Count Register 2 |
| C025h | FDBSC3 | Queue Manager Free Descriptor and Buffer Starvation Count Register 3 |
| C028h | FDBSC4 | Queue Manager Free Descriptor and Buffer Starvation Count Register 4 |
| C029h | FDBSC5 | Queue Manager Free Descriptor and Buffer Starvation Count Register 5 |
| C02Ch | FDBSC6 | Queue Manager Free Descriptor and Buffer Starvation Count Register 6 |
| C02Dh | FDBSC7 | Queue Manager Free Descriptor and Buffer Starvation Count Register 7 |
| C080h | LRAM0BASE1 | Queue Manager Linking RAM Region 0 Base Address Register 1 |
| C081h | LRAM0BASE2 | Queue Manager Linking RAM Region 0 Base Address Register 2 |
| C084h | LRAM0SIZE | Queue Manager Linking RAM Region 0 Size Register |
| C085h | - | Reserved |
| C088h | LRAM1BASE1 | Queue Manager Linking RAM Region 1 Base Address Register 1 |
| C089h | LRAM1BASE2 | Queue Manager Linking RAM Region 1 Base Address Register 2 |
| C090h | PEND0 | Queue Manager Queue Pending 0 |
| C091h | PEND1 | Queue Manager Queue Pending 1 |
| C094h | PEND2 | Queue Manager Queue Pending 2 |
| C095h | PEND3 | Queue Manager Queue Pending 3 |
| C098h | PEND4 | Queue Manager Queue Pending 4 |
| C099h | PEND5 | Queue Manager Queue Pending 5 |
| D000h + 16 × R | QMEMRBASE1[R] | Queue Manager Memory Region R Base Address Register 1 (R = 0 to 15) |
| D001h + 16 × R | QMEMRBASE2[R] | Queue Manager Memory Region R Base Address Register 2 (R = 0 to 15) |
| D004h + 16 × R | QMEMRCTRL1[R] | Queue Manager Memory Region R Control Register (R = 0 to 15) |
| D005h + 16 × R | QMEMRCTRL2[R] | Queue Manager Memory Region R Control Register (R = 0 to 15) |
| E000h + 16 × N | CTRL1A | Queue Manager Queue N Control Register 1A (N = 0 to 63) |
| E001h + 16 × N | CTRL2A | Queue Manager Queue N Control Register 2A (N = 0 to 63) |
| E004h + 16 × N | CTRL1B | Queue Manager Queue N Control Register 1B (N = 0 to 63) |
| E005h + 16 × N | CTRL2B | Queue Manager Queue N Control Register 2B (N = 0 to 63) |
| E008h + 16 × N | CTRL1C | Queue Manager Queue N Control Register 1C (N = 0 to 63) |
| E009h + 16 × N | CTRL2C | Queue Manager Queue N Control Register 2C (N = 0 to 63) |
| E00Ch + 16 × N | CTRL1D | Queue Manager Queue N Control Register 1D (N = 0 to 63) |
| E00Dh + 16 × N | CTRL2D | Queue Manager Queue N Control Register 2D (N = 0 to 63) |
| E800h + 16 × N | QSTAT1A | Queue Manager Queue N Status Register 1A (N = 0 to 63) |
| E801h + 16 × N | QSTAT2A | Queue Manager Queue N Status Register 2A (N = 0 to 63) |
| E804h + 16 × N | QSTAT1B | Queue Manager Queue N Status Register 1B (N = 0 to 63) |
| E805h + 16 × N | QSTAT2B | Queue Manager Queue N Status Register 2B (N = 0 to 63) |
| E808h + 16 × N | QSTAT1C | Queue Manager Queue N Status Register 1C (N = 0 to 63) |
| E809h + 16 × N | QSTAT1C | Queue Manager Queue N Status Register 2C (N = 0 to 63) |
6.3 Identification
6.3.1 JTAG Identification
Table 6-27 JTAG ID Register
| HEX ADDRESS RANGE | ACRONYM | REGISTER NAME | COMMENTS |
|---|---|---|---|
| N/A | JTAGID | JTAG Identification Register | Read-only. Provides 32-bit JTAG ID of the device. |
The JTAG ID register is a read-only register that identifies to the customer the JTAG/Device ID. The register hex value for the device is: 0x1B8F E02F. For the actual register bit names and their associated bit field descriptions, see Figure 6-5 and Table 6-28.
| 31-28 | 27-12 | 11-1 | 0 | ||||
| VARIANT (4-Bit) | PART NUMBER (16-Bit) | MANUFACTURER (11-Bit) | LSB | ||||
| R-0001 | R-1011 1000 1111 1110 | R-0000 0010 111 | R-1 | ||||
| LEGEND: R = Read, W = Write, n = value at reset |
Table 6-28 JTAG ID Register Selection Bit Descriptions
| BIT | NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| 31:28 | VARIANT | Variant (4-Bit) value: 0001. |
| 27:12 | PART NUMBER | Part Number (16-Bit) value: 1011 1000 1111 1110. |
| 11:1 | MANUFACTURER | Manufacturer (11-Bit) value: 0000 0010 111. |
| 0 | LSB | LSB. This bit is read as a "1". |
6.4 Boot Modes
The DSP supports the following boot modes in the following device order: SPI 16-bit EEPROM, SPI 24-bit Flash, I2C EEPROM, and eMMC boot partition, eMMC, SD, or SDHC card. The boot mode is determined by checking for a valid boot signature on each supported boot device. The first boot device with a valid boot signature will be used to load and execute the user code. If none of the supported boot devices have a valid boot signature, the bootloader goes into an endless loop checking the UART or USB boot mode and the device must be reset to search for another valid boot image in the supported boot modes.
Note: For detailed information on eMMC boot partition, eMMC, SD, or SDHC and UART or USB boot modes, contact your local sales representative.
6.4.1 Invocation Sequence
The boot sequence is a process by which the device's on-chip memory is loaded with program and data sections from an external image file (in flash memory, for example). The boot sequence also allows, optionally, for some of the device's internal registers to be programmed with predetermined values. The boot sequence is started automatically after each device reset. For more details on device reset, see Section 5.7.3, Reset.
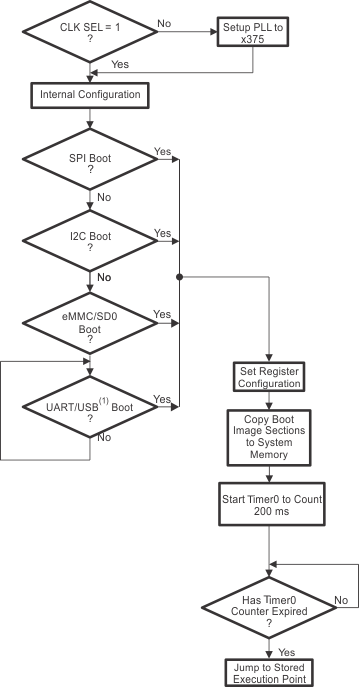
There are several methods by which the memory and register initialization can take place. Each of these methods is referred to as a boot mode. At reset, the device cycles through different boot modes until an image is found with a valid boot signature. The on-chip bootloader allows the DSP registers to be configured during the boot process, if the optional register configuration section is present in the boot image (see Figure 6-6). For more information on the boot modes supported, see Section 6.4, Boot Modes.
The device bootloader follows the following steps as shown in Figure 6-6
- Immediately after reset, the CPU fetches the reset vector from 0xFFFF00. MP or MC is 0 by default, so 0xFFFF00 is mapped to internal ROM. The PLL is in bypass mode.
- Set CLKOUT slew rate control to slow slew rate.
- Idle all peripherals, MPORT and HWA.
- If CLK_SEL = 0, the bootloader powers up the PLL and sets its output frequency to 12.288 MHz (with a 375x multiplier using VP = 749, VS = 0, input divider disabled, output divide-by-8 enabled, and output divider enabled with VO = 0). If CLK_SEL = 1, the bootloader keeps the PLL bypassed. Enable Timer0 to count the settling time of BG_CAP.
- Apply manufacturing trim to the bandgap references.
- Disable CLKOUT.
- Test for 16-bit and 24-bit SPI EEPROM boot on SPI_CS[0] with a 500-kHz clock rate and set to Parallel Port Mode on the External Bus Selection Register to 5, then set to 6:
- Check the first 2 bytes read from boot table for a boot signature match using 16-bit address mode.
- If the boot signature is not valid, read the first 2 bytes again using 24-bit address mode.
- If the boot signature is not valid from either case (16-bit and 24-bit address modes), go to step 8.
- Set Register Configuration, if present in boot image.
- Attempt SPI Serial Memory boot, go to step 12.
- Test for I2C EEPROM boot with a 7-bit slave address 0x50 and 400-kHz clock rate.
- Check the first 2 bytes read from boot table for a boot signature match.
- If the boot signature is not valid, go to step 9.
- Set Register Configuration, if present in boot image.
- Attempt I2C EEPROM boot, go to step 12.
- Test for eMMC partitions, eMMC, SD0 boot:
- For an eMMC, SD, or SDHC card, the card must be formatted to FAT16 or FAT32. The boot image file must be renamed to "bootimg.bin" and copied to the foot directory of the formatted card.
- If an eMMC boot partition is desired (for only eMMC 4.3 and up), then the boot image file must be programmed to one of the two boot partitions (1 or 2) on the eMMC card. PARTITION_CONFIG in the EXT_CSD must be set accordingly.
- If the boot signature is found, attempt eMMC, SD, or SDHC boot and go to step 12.
If boot signature is not found, go to step 10.
- Set the PLL output to approximately 36 MHz. If CLK_SEL = 1, CLKIN multiplied by 3x. If CLK_SEL = 0, CLKIN is multiplied by 1125x. Re-enable TIMER0 to start counting the settling time of BG_CAP due to the PLL change.
- Test for UART or USB1 boot:
- The USB internal LDO will be enabled and the device is configured to accept a boot image on EP1 OUT.
- UART will be set to 57600 baud, 8 bit, 1 stop bit, CTS or RTS auto flow control, and odd parity will be enabled to accept a boot image from the UART transmitter.
- The device will poll UART and USB in turns. If a valid boot signature is detected on either device, a boot image will attempt to download on that device. Go to step 12.
If a valid signature is not detected, return to the start of this step.
- Copy the boot image sections to system memory.
- Ensure a minimum of 200 ms has elapsed before proceeding to execute the bootloaded code.
- Jump to the entry point specified in the boot image.
6.4.2 Boot Configuration
After reset, the on-chip bootloader programs the system clock generator based on the input clock selected via the CLK_SEL pin. If CLK_SEL = 0, the bootloader programs the system clock generator and sets the system clock to 12.288 MHz (multiply the 32.768-kHz RTC oscillator clock by 375). If CLK_SEL = 1, the bootloader bypasses the system clock generator altogether and the system clock is driven by the CLKIN pin.
Note:
- When CLK_SEL =1, the CLKIN frequency is expected to be 11.2896 MHz, 12.0 MHz, or 12.288 MHz.
- The on-chip bootloader allows for DSP registers to be configured during the boot process. However, this feature must not be used to change the output frequency of the system clock generator during the boot process. Timer0 is also used by the bootloader to allow for 200 ms of BG_CAP settling time. The bootloader register modification feature must not modify the PLL or Timer0 registers.
After hardware reset, the DSP boots via the bootloader code in ROM. During the boot process, the bootloader queries each peripheral to determine if it can boot from that peripheral. At that time, the individual peripheral clocks will be enabled for the query and then disabled when the bootloader is finished with the peripheral. By the time the bootloader releases control to the user code, all peripheral clocks will be "off" and all domains in the ICR, except the CPU domain, will be idled.
6.4.3 DSP Resources Used By the Bootloader
The bootloader uses SARAM block 31 for the storing of temporary data. This block of memory is reserved during the boot process. However, after the boot process is complete, it can be used by the user application.