ZHCSDH3 November 2014 PCM5252
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics
- 7.6 Switching Characteristics
- 7.7 Timing Requirements: SCK Input
- 7.8 Timing Requirements: PCM Audio Data
- 7.9 Timing Requirements: I2S Master, See
- 7.10 Timing Requirements: XSMT
- 7.11 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Terminology
- 8.3.2 Audio Data Interface
- 8.3.3 XSMT Pin (Soft Mute / Soft Un-Mute)
- 8.3.4 Audio Processing
- 8.3.5 DAC and Differential Analog Outputs
- 8.3.6
Reset and System Clock Functions
- 8.3.6.1 Clocking Overview
- 8.3.6.2 Clock Slave Mode With Master and System Clock (SCK) Input (4 Wire I2S)
- 8.3.6.3 Clock Slave Mode With BCK PLL to Generate Internal Clocks (3-Wire PCM)
- 8.3.6.4 Clock Generation Using the PLL
- 8.3.6.5 PLL Calculation
- 8.3.6.6 Clock Master Mode from Audio Rate Master Clock
- 8.3.6.7 Clock Master from a Non-Audio Rate Master Clock
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Programming
- 13Register Maps
- 14器件和文档支持
- 15机械、封装和可订购信息
1 特性
- 差分 DirectPath™ 接地偏置输出
- 智能放大器技术
- 市场领先的低带外噪声
- 可选数字滤波器延迟与性能
- 无需隔离直流电流的电容器
- 集成的负电荷泵
- 智能静音系统;软斜升或斜降搭配模拟静音,实现 120dB 静音信噪比 (SNR)
- 具有 BCK 基准的集成高性能音频锁相环 (PLL),可在内部生成 SCK
- 接收 16 位、24 位和 32 位音频数据
- PCM 数据样式:I2S,左对齐
- 通用串行接口 (SPI) 或者 I2C 控制
- 硬件配置
- 当 LRCK 和 BCK 被置为无效时,自动进入省电模式
- 1.8V 或 3.3V 故障安全低电压互补金属氧化物半导体 (LVCMOS) 数字输入
- 单电源运算:
- 3.3V 模拟电源、1.8V 或 3.3V 数字电源
- 集成型加电复位
- 小型32-pin VQFN封装
2 应用
- HiFi 智能手机
- A/V 接收器
- DVD,BD 播放器
- HDTV 接收器
3 说明
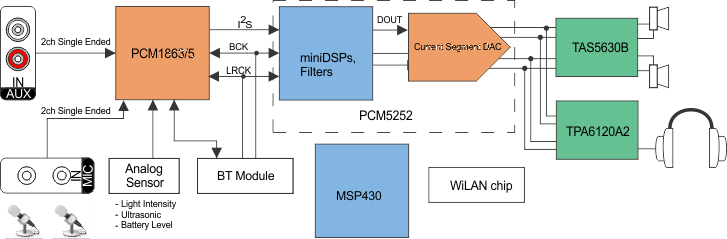
PCM5252是一款单片互补金属氧化物半导体 (CMOS) 集成电路,由立体声数模转换器 (DAC) 和采用薄型小外形尺寸 (TSSOP) 封装的附加支持电路组成。PCM5252使用 TI 最新一代高级分段 DAC 架构产品,可实现出色的动态性能并提升针对时钟抖动的耐受度。
PCM5252集成了一个完全可编程的 miniDSP 内核,允许开发人员将滤波器、动态范围控件、定制插值器等各类 功能 集成到相关产品中。
PCM5252集成了德州仪器 (TI) PurePath™ 智能放大器技术的 ROM 组件,可更多地以峰值功率(而非平均额定功率)驱动扬声器,同时不必担心扬声器因音圈偏移或热过载而受损。
PCM5252提供 4.2 VRMS 中央接地差分输出(设计人员无需在输出端连接隔直电容)以及传统意义上与单电源线路驱动器相关的外部静音电路。”
器件上集成的 PLL 免除了对于系统时钟(通常称为主时钟)的需要,从而实现一个 3 线制 I2C 连接并减少了系统电磁干扰 (EMI)。
相关框图请参见Functional Block Diagram。
器件信息(1)
| 部件名称 | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|
| PCM5252 | VQFN (32) | 5.00mm x 5.00mm |
- 要了解所有可用封装,请参见数据表末尾的可订购产品附录。
简化系统图