ZHCSCS6B September 2014 – December 2018 OPA2320-Q1 , OPA320-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
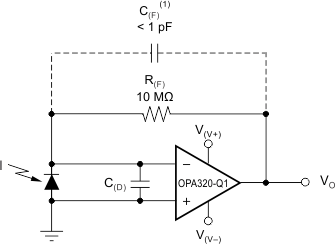
8.2.1 Transimpedance Amplifier
Wide gain bandwidth, low input bias current, low input voltage, and current noise make the OPAx320-Q1 an excellent wideband photodiode transimpedance amplifier. Low-voltage noise is important because photodiode capacitance causes the effective noise gain of the circuit to increase at high frequency.
The key elements to a transimpedance design, as shown in Figure 36, are the expected diode capacitance (C(D)), which should include the parasitic input common-mode and differential-mode input capacitance (4 pF + 5 pF); the desired transimpedance gain (R(FB)); and the gain-bandwidth (GBW) for the OPAx320-Q1 (20 MHz). With these three variables set, the feedback capacitor value (C(FB)) can be set to control the frequency response. C(FB) includes the stray capacitance of R(FB), which is 0.2 pF for a typical surface-mount resistor.
NOINDENT:
C(FB) is optional to prevent gain peaking. C(FB) includes the stray capacitance of R(FB).