ZHCSGW0E October 2017 – February 2020 OPA202 , OPA2202 , OPA4202
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
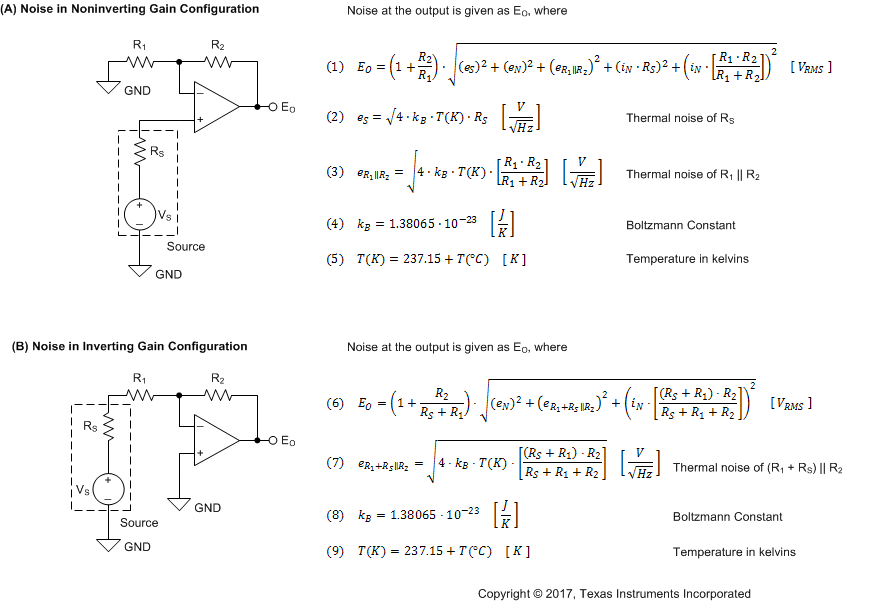
8.1.1 Basic Noise Calculations
Low-noise circuit design requires careful analysis of all noise sources. External noise sources dominates in many cases; consider the effect of source resistance on overall op amp noise performance. Total noise of the circuit is the root-sum-square combination of all noise components.
The resistive portion of the source impedance produces thermal noise proportional to the square root of the resistance. Figure 42 shows this function. The source impedance is usually fixed; consequently, select the op amp and the feedback resistors to minimize the respective contributions to the total noise.
Figure 46 shows noninverting (A) and inverting (B) op amp circuit configurations with gain. In circuit configurations with gain, the feedback network resistors contribute noise. Typically, the current noise of the op amp reacts with the feedback resistors to create additional noise components. However, the extremely low current noise of the OPAx202 means that the current noise contribution is neglected.
The feedback resistor values are typically selected to make these noise sources negligible. Low impedance feedback resistors load the output of the amplifier. The equations for total noise are shown for both configurations.