SLOS719F August 2011 – January 2016 DRV8301
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.3 Thermal Information
- 6.4 Electrical Characteristics
- 6.5 Current Shunt Amplifier Characteristics
- 6.6 Buck Converter Characteristics
- 6.7 SPI Timing Requirements (Slave Mode Only)
- 6.8 Gate Timing and Protection Switching Characteristics
- 6.9 Typical Characteristics
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
10 Layout
10.1 Layout Guidelines
Use these layout recommendations when designing a PCB for the DRV8301.
- The DRV8301 makes an electrical connection to GND through the PowerPAD. Always check to ensure that the PowerPAD has been properly soldered (See PowerPAD™ Thermally Enhanced Package application report, SLMA002).
- PVDD bypass capacitors should be placed close to their corresponding pins with a low impedance path to device GND (PowerPAD).
- GVDD bypass capacitor should be placed close its corresponding pin with a low impedance path to device GND (PowerPAD).
- AVDD and DVDD bypass capacitors should be placed close to their corresponding pins with a low-impedance path to the AGND pin. It is preferable to make this connection on the same layer.
- AGND should be tied to device GND (PowerPAD) through a low impedance trace/copper fill.
- Add stitching vias to reduce the impedance of the GND path from the top to bottom side.
- Try to clear the space around and underneath the DRV8301 to allow for better heat spreading from the PowerPAD.
10.2 Layout Example
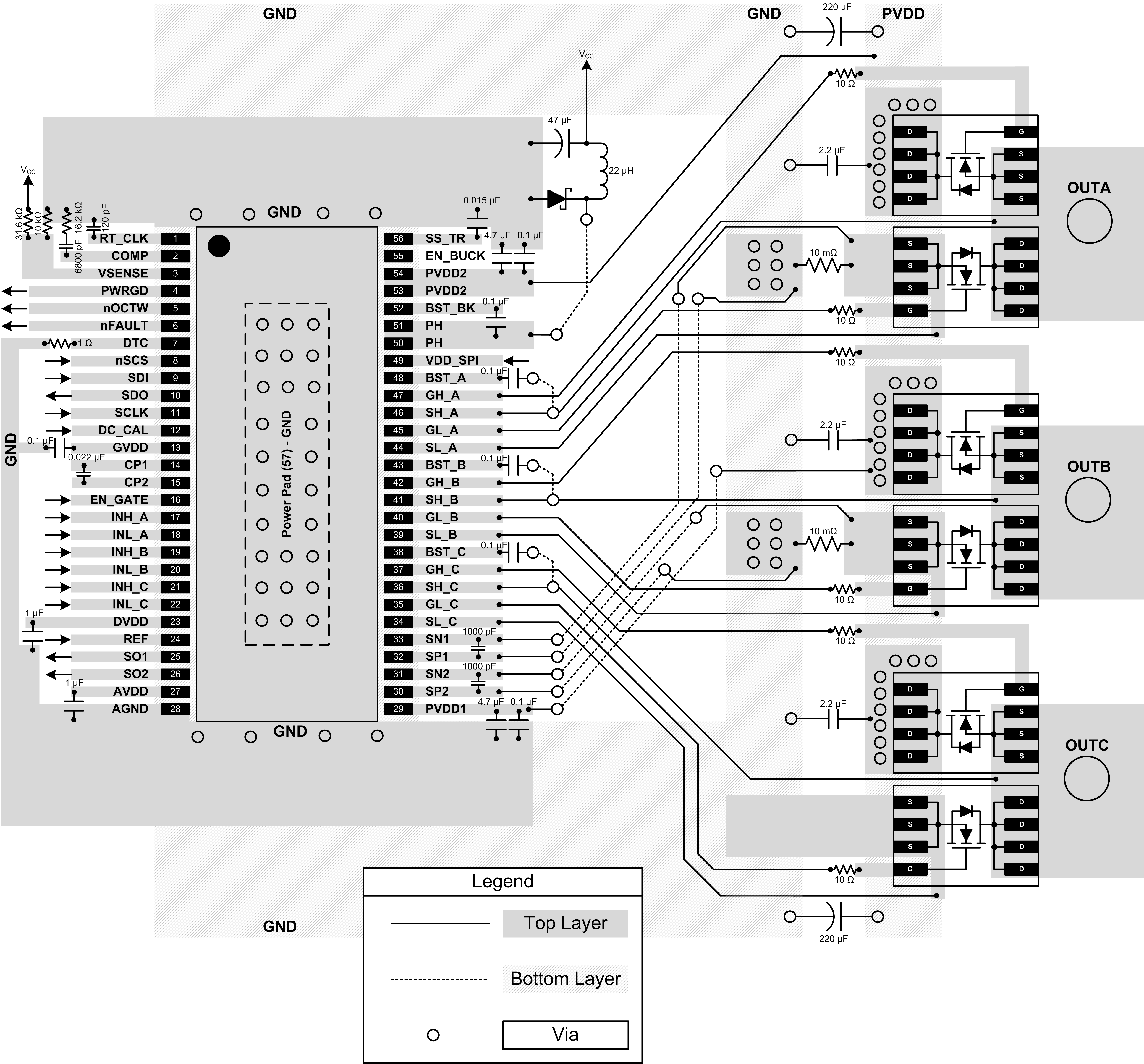 Figure 13. Top and Bottom Layer Layout Schematic
Figure 13. Top and Bottom Layer Layout Schematic