SLAS476H March 2006 – June 2017 DAC8550
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supply voltage | GND | –0.3 | 6 | V |
| Digital input voltage range | GND | –0.3 | VDD + 0.3 | V |
| Output voltage | GND | –0.3 | VDD + 0.3 | V |
| Junction temperature, TJ(max) | 150 | °C | ||
| Operating temperature, TA | –40 | 105 | °C | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –65 | 150 | °C | |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, which do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human-body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged-device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101(2) | ±500 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating ambient temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| POWER SUPPLY | ||||||
| VDD | Supply voltage | 2.7 | 5.5 | V | ||
| DIGITAL INPUTS | ||||||
| DIN | Digital input voltage | SCLK and SYNC | 0 | VDD | V | |
| REFERENCE INPUT | ||||||
| VREF | Reference input voltage | 0 | VDD | V | ||
| AMPLIFIER FEEDBACK INPUT | ||||||
| VFB | Output amplifier feedback input | VO | V | |||
| TEMPERATURE RANGE | ||||||
| TA | Operating ambient temperature | –40 | 105 | °C | ||
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | DAC8550 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| DGK (VSSOP) | |||
| 8 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 206 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 44 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 94.2 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 10.2 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 92.7 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
VDD = 2.7 V to 5.5 V, –40°C to 105°C range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STATIC PERFORMANCE(1) | |||||||
| Resolution | 16 | Bits | |||||
| EL | Relative accuracy | Measured by line passing through codes –32283 and 32063 at VREF = 5 V, codes –31798 and 31358 at VREF = 2.5 V | DAC8550 | ±16 | LSB | ||
| DAC8550B | ±12 | ||||||
| ED | Differential nonlinearity | 2.5 V ≤ VREF ≤ 5.5 V, 0°C ≤ TA ≤ 105°C | ±1 | LSB | |||
| 4.2 V < VREF ≤ 5.5 V, -40°C ≤ TA ≤ 105°C | ±1 | LSB | |||||
| 2.5 V ≤ VREF ≤ 4.2 V, -40°C ≤ TA ≤ 0°C | ±2 | LSB | |||||
| EO | Zero-code error | Measured by line passing through codes –32283 and 32063 | ±2 | ±12 | mV | ||
| EFS | Full-scale error | Measured by line passing through codes –32283 and 32063 | ±0.05% | ±0.5% | mV | ||
| EG | Gain error | Measured by line passing through codes –32283 and 32063 | ±0.02% | ±0.2% | mV | ||
| Zero-code error drift | ±5 | μV/°C | |||||
| Gain temperature coefficient | ±1 | ppm of FSR/°C | |||||
| PSRR | Power-supply rejection ratio | RL = 2 kΩ, CL = 200 pF | 0.75 | mV/V | |||
| OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS(2) | |||||||
| VO | Output voltage range | 0 | VREF | V | |||
| tSD | Output voltage settling time | To ±0.003% FSR, 1200h to 8D00h, RL = 2 kΩ, 0 pF < CL < 200 pF | 8 | 10 | μs | ||
| RL = 2 kΩ, CL = 500 pF | 12 | ||||||
| SR | Slew rate | 1.8 | V/μs | ||||
| Capacitive load stability | RL = ∞ | 470 | pF | ||||
| RL = 2 kΩ | 1000 | ||||||
| Code change glitch impulse | 1 LSB change around major carry | 0.1 | nV-s | ||||
| Digital feedthrough | SCLK toggling, FSYNC high | 0.1 | nV-s | ||||
| zO | DC output impedance | At mid-code input | 1 | Ω | |||
| IOS | Short-circuit current | VDD = 5 V | 50 | mA | |||
| VDD = 3 V | 20 | ||||||
| tON | Power-up time | Coming out of power-down mode, VDD = 5 V | 2.5 | μs | |||
| Coming out of power-down mode, VDD = 3 V | 5 | ||||||
| AC PERFORMANCE | |||||||
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio | BW = 20 kHz, VDD = 5 V, fOUT = 1 kHz, 1st 19 harmonics removed for SNR calculation |
95 | dB | |||
| THD | Total harmonic distortion | BW = 20 kHz, VDD = 5 V, fOUT = 1 kHz, 1st 19 harmonics removed for SNR calculation |
–85 | dB | |||
| SFDR | Spurious-free dynamic range | BW = 20 kHz, VDD = 5 V, fOUT = 1 kHz, 1st 19 harmonics removed for SNR calculation |
87 | dB | |||
| SINAD | Signal-to-noise and distortion | BW = 20 kHz, VDD = 5 V, fOUT = 1 kHz, 1st 19 harmonics removed for SNR calculation |
84 | dB | |||
| REFERENCE INPUT | |||||||
| VREF | Reference voltage | 0 | VDD | V | |||
| II(REF) | Reference current input range | VREF = VDD = 5 V | 40 | 75 | μA | ||
| VREF = VDD = 3.6 V | 30 | 45 | |||||
| zI(REF) | Reference input impedance | 125 | kΩ | ||||
| LOGIC INPUTS (2) | |||||||
| Input current | ±1 | μA | |||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 3 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V | 0.3 × VDD | V | |||
| 2.7 V ≤ VDD < 3 V | 0.1 × VDD | ||||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 3 V ≤ VDD ≤ 5.5 V | 0.7 × VDD | V | |||
| 2.7 V ≤ VDD < 3 V | 0.9 × VDD | ||||||
| Pin capacitance | 3 | pF | |||||
| POWER REQUIREMENTS | |||||||
| IDD | Supply current | Normal mode, input code equals mid-scale, no load, does not include reference current, VIH = VDD, VIL = GND | VDD = 3.6 V to 5.5 V | 160 | 250 | μA | |
| VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 140 | 240 | |||||
| All power-down modes, VIH = VDD, VIL = GND |
VDD = 3.6 V to 5.5 V | 0.2 | 2 | ||||
| VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 0.05 | 2 | |||||
| POWER EFFICIENCY | |||||||
| IOUT/IDD | ILOAD = 2 mA, VDD = 5 V | 89% | |||||
(1) Linearity calculated using a reduced code range –32283 and 32063 at VREF = 5V, codes –31798 and 31358 at VREF = 2.5V; output unloaded, 100mV headroom between reference and supply.
(2) Specified by design and characterization, not production tested.
6.6 Timing Characteristics
VDD = 2.7 V to 5.5 V, all specifications –40°C to 105°C (unless otherwise noted)(1)(2)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| t1(3) | SCLK cycle time | VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 50 | ns | ||
| VDD = 3.6 V to 5.5 V | 33 | |||||
| t2 | SCLK HIGH time | VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 13 | ns | ||
| VDD = 3.6 V to 5.5 V | 13 | |||||
| t3 | SCLK LOW time | VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 22.5 | ns | ||
| VDD = 3.6 V to 5.5 V | 13 | |||||
| t4 | SYNC to SCLK rising edge setup time | VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 0 | ns | ||
| VDD = 3.6 V to 5.5 V | 0 | |||||
| t5 | Data setup time | VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 5 | ns | ||
| VDD = 3.6 V to 5.5 V | 5 | |||||
| t6 | Data hold time | VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 4.5 | ns | ||
| VDD = 3.6 V to 5.5 V | 4.5 | |||||
| t7 | 24th SCLK falling edge to SYNC rising edge | VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 0 | ns | ||
| VDD = 3.6 V to 5.5 V | 0 | |||||
| t8 | Minimum SYNC HIGH time | VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V | 50 | ns | ||
| VDD = 3.6 V to 5.5 V | 33 | |||||
| t9 | 24th SCLK falling edge to SYNC falling edge | VDD = 2.7 V to 5.5 V | 100 | ns | ||
(1) All input signals are specified with tR = tF = 5 ns (10% to 90% of VDD) and timed from a voltage level of (VIL + VIH) / 2.
(2) See Figure 1.
(3) Maximum SCLK frequency is 30 MHz at VDD = 3.6 V to 5.5 V and 20 MHz at VDD = 2.7 V to 3.6 V.
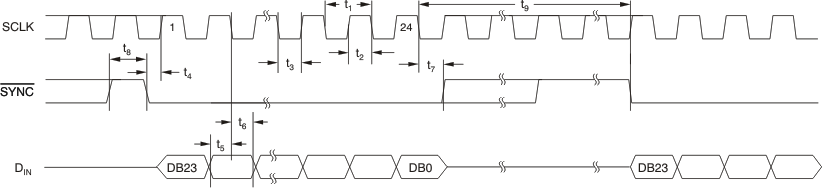 Figure 1. Serial Write Operation
Figure 1. Serial Write Operation
6.7 Typical Characteristics
6.7.1 VDD = 5 V
at TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted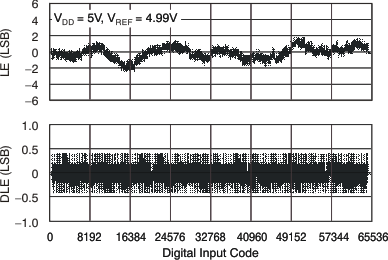 Figure 2. Linearity Error and Differential Linearity Error
Figure 2. Linearity Error and Differential Linearity Errorvs Digital Input Code (–40°C)
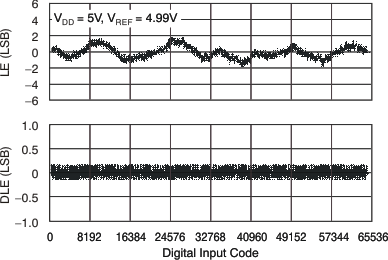 Figure 4. Linearity Error and Differential Linearity Error
Figure 4. Linearity Error and Differential Linearity Errorvs Digital Input Code (105°C)
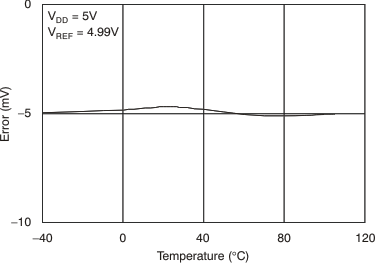 Figure 6. Full-Scale Error vs Temperature
Figure 6. Full-Scale Error vs Temperature
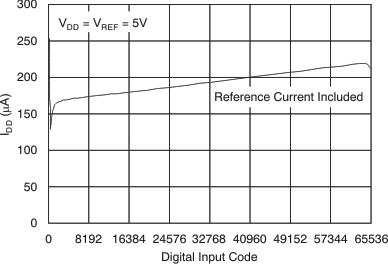 Figure 8. Supply Current vs Digital Input Code
Figure 8. Supply Current vs Digital Input Code
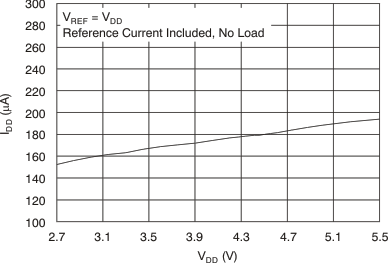 Figure 10. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 10. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage
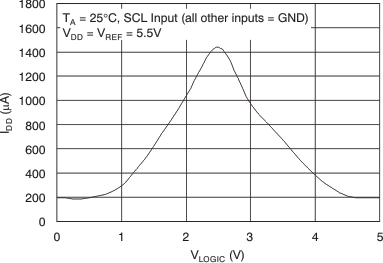 Figure 12. Supply Current vs Logic Input Voltage
Figure 12. Supply Current vs Logic Input Voltage
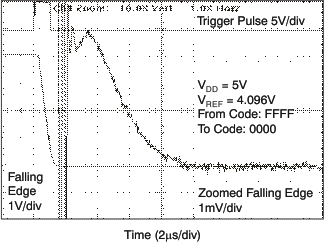
| 5 V |
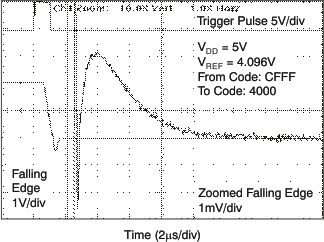
| 5 V |
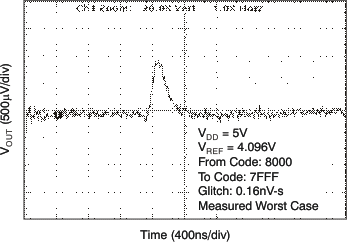
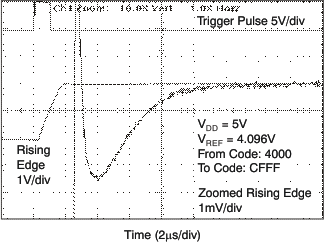
| 5 V | 1-LSB Step |
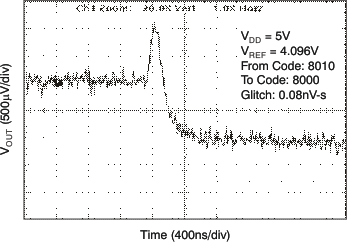
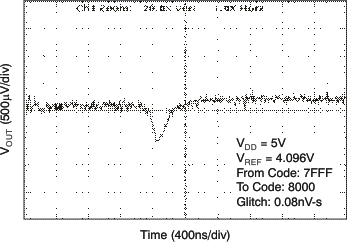
| 5 V | 16-LSB Step |
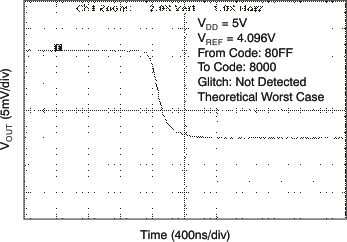
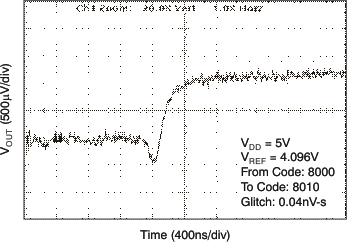
| 5 V | 256-LSB Step |
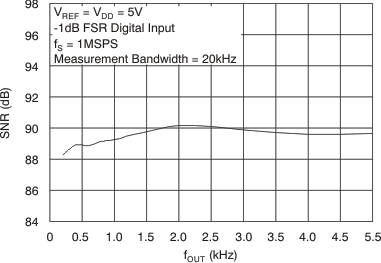 Figure 24. Signal-to-Noise Ratio vs Output Frequency
Figure 24. Signal-to-Noise Ratio vs Output Frequency
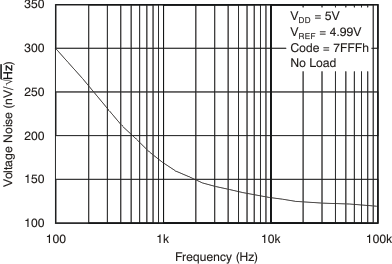 Figure 26. Output Noise Density
Figure 26. Output Noise Density
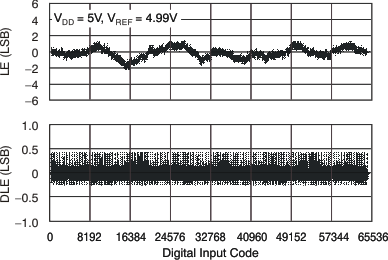 Figure 3. Linearity Error and Differential Linearity Error
Figure 3. Linearity Error and Differential Linearity Errorvs Digital Input Code
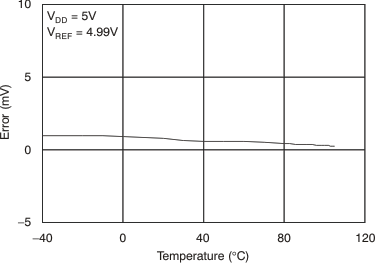 Figure 5. Zero-Scale Error vs Temperature
Figure 5. Zero-Scale Error vs Temperature
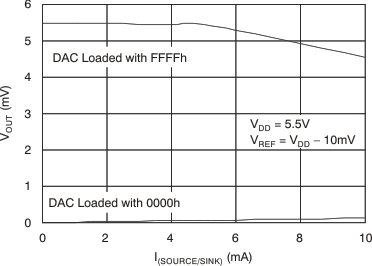 Figure 7. Source and Sink Current Capability
Figure 7. Source and Sink Current Capability
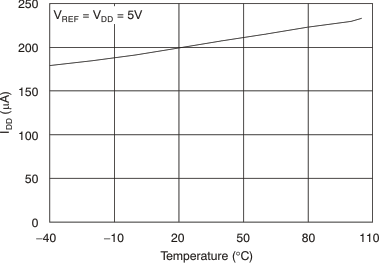 Figure 9. Power-Supply Current vs Temperature
Figure 9. Power-Supply Current vs Temperature
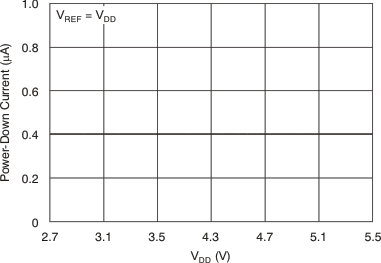 Figure 11. Power-Down Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 11. Power-Down Current vs Supply Voltage
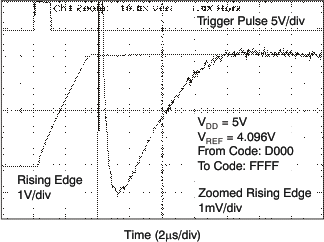
| 5 V |
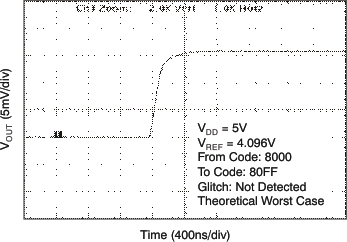
| 5 V |
| 5 V | 1-LSB Step |
| 5 V | 16-LSB Step |
| 5 V | 256-LSB Step |
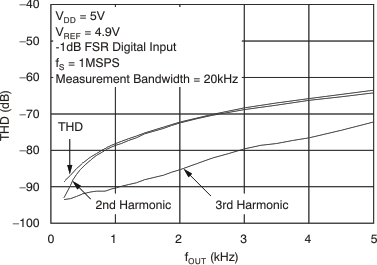 Figure 23. Total Harmonic Distortion vs Output Frequency
Figure 23. Total Harmonic Distortion vs Output Frequency
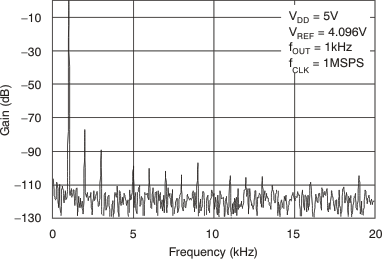 Figure 25. Power Spectral Density
Figure 25. Power Spectral Density
6.7.2 VDD = 2.7 V
at TA = 25°C, unless otherwise noted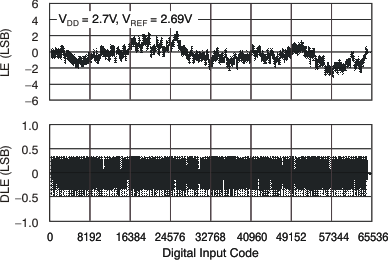 Figure 27. Linearity Error and Differential Linearity Error
Figure 27. Linearity Error and Differential Linearity Errorvs Digital Input Code (–40°C)
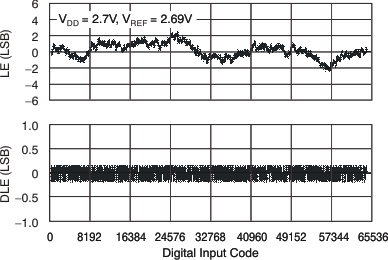 Figure 29. Linearity Error and Differential Linearity Error
Figure 29. Linearity Error and Differential Linearity Errorvs Digital Input Code (105°C)
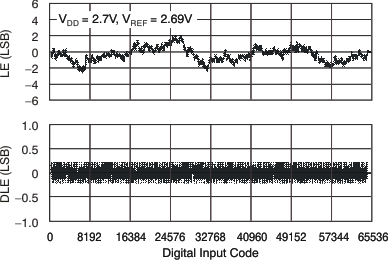 Figure 28. Linearity Error and Differential Linearity Error
Figure 28. Linearity Error and Differential Linearity Errorvs Digital Input Code
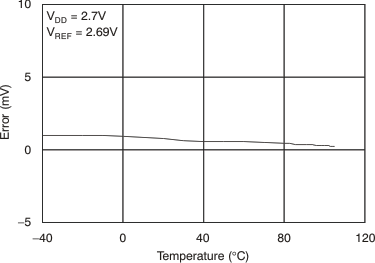 Figure 30. Zero-Scale Error vs Temperature
Figure 30. Zero-Scale Error vs Temperature
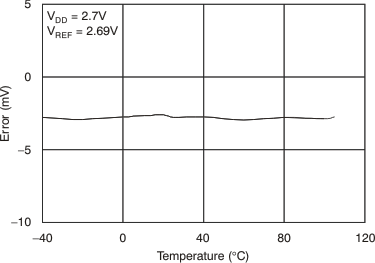 Figure 31. Full-Scale Error vs Temperature
Figure 31. Full-Scale Error vs Temperature
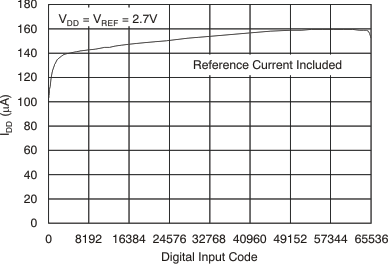 Figure 33. Supply Current vs Digital Input Code
Figure 33. Supply Current vs Digital Input Code
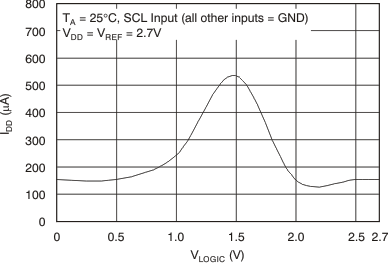 Figure 35. Supply Current vs Logic Input Voltage
Figure 35. Supply Current vs Logic Input Voltage
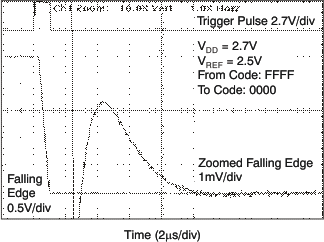
| 2.7 V |
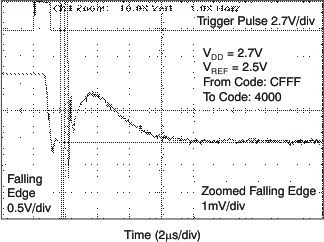
| 2.7 V |
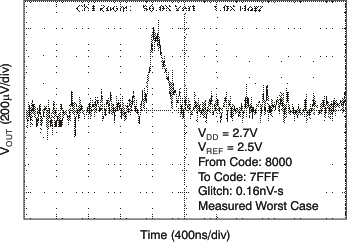
| 2.7 V | 1-LSB Step |
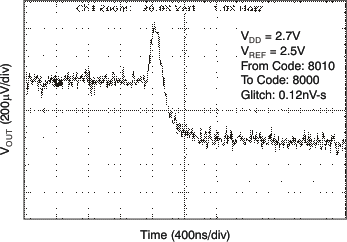
| 2.7 V | 16-LSB Step |
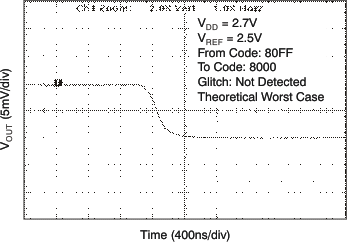
| 2.7 V | 256-LSB Step |
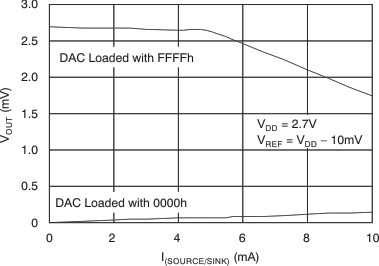 Figure 32. Source and Sink Current Capability
Figure 32. Source and Sink Current Capability
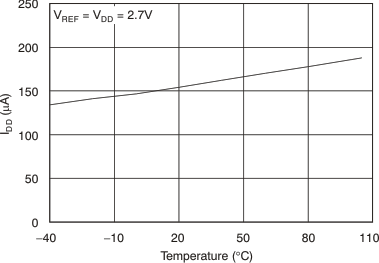 Figure 34. Power-Supply Current vs Temperature
Figure 34. Power-Supply Current vs Temperature
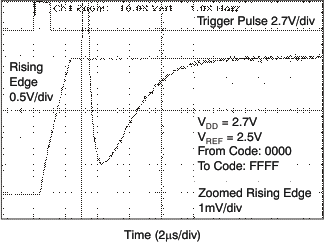
| 2.7 V |
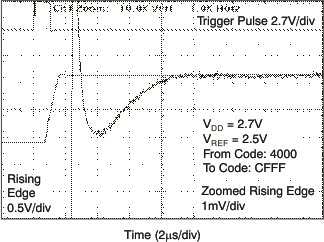
| 2.7 V |
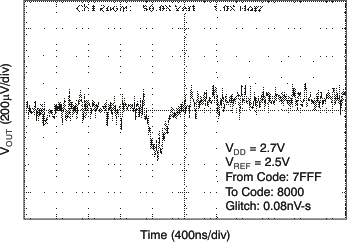
| 2.7 V | 1-LSB Step |
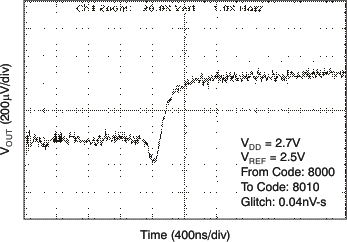
| 2.7 V | 16-LSB Step |
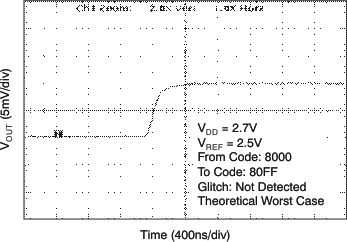
| 2.7 V | 256-LSB Step |