ZHCSJC0 January 2019 ADS1260-Q1 , ADS1261-Q1
ADVANCE INFORMATION for pre-production products; subject to change without notice.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Parameter Measurement Information
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3 Feature Description
- 9.4
Device Functional Modes
- 9.4.1 Conversion Control
- 9.4.2 Chop Mode
- 9.4.3 AC-Excitation Mode
- 9.4.4 ADC Clock Mode
- 9.4.5 Power-Down Mode
- 9.4.6 Reset
- 9.4.7 Calibration
- 9.5 Programming
- 9.6
Register Map
- 9.6.1 Device Identification (ID) Register (address = 00h) [reset = xxh]
- 9.6.2 Device Status (STATUS) Register (address = 01h) [reset = 01h]
- 9.6.3 Mode 0 (MODE0) Register (address = 02h) [reset = 24h]
- 9.6.4 Mode 1 (MODE1) Register (address = 03h) [reset = 01h]
- 9.6.5 Mode 2 (MODE2) Register (address = 04h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.6 Mode 3 (MODE3) Register (address = 05h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.7 Reference Configuration (REF) Register (address = 06h) [reset = 05h]
- 9.6.8 Offset Calibration (OFCALx) Registers (address = 07h, 08h, 09h) [reset = 00h, 00h, 00h]
- 9.6.9 Full-Scale Calibration (FSCALx) Registers (address = 0Ah, 0Bh, 0Ch) [reset = 00h, 00h, 40h]
- 9.6.10 IDAC Multiplexer (IMUX) Register (address = 0Dh) [reset = FFh]
- 9.6.11 IDAC Magnitude (IMAG) Register (address = 0Eh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.12 Reserved (RESERVED) Register (address = 0Fh) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.13 PGA Configuration (PGA) Register (address = 10h) [reset = 00h]
- 9.6.14 Input Multiplexer (INPMUX) Register (address = 11h) [reset = FFh]
- 9.6.15 Input Bias (INPBIAS) Register (address = 12h) [reset = 00h]
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
9.3.10.1.1 Sinc Filter Frequency Response
The characteristic of the sinc filter is low pass. The filter reduces noise present in the signal and noise present within the ADC. Changing the data rate and filter order changes the filter bandwidth.
As shown in Figure 22 and Figure 23, the first-stage sinc5 filter has frequency response nulls occurring at N · fDATA, where N = 1, 2, 3 and so on. At the null frequencies, the filter has zero gain. Data rates of 25600 SPS and 19200 SPS have similar frequency response.
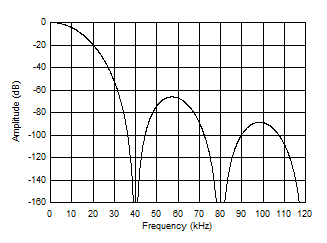 Figure 22. Frequency Response (40000 SPS)
Figure 22. Frequency Response (40000 SPS) 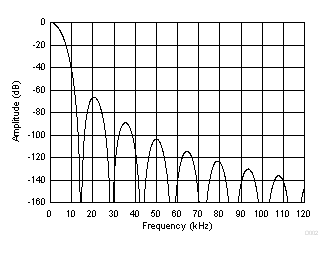 Figure 23. Frequency Response (14400 SPS)
Figure 23. Frequency Response (14400 SPS) The second stage superimposes frequency response nulls to the nulls of the first stage 14400 SPS output. The first of the superimposed response nulls occurs at the data rate, followed by nulls occurring at multiples of the data rate. Figure 24 illustrates the frequency response for various orders of sinc at data rate of 2400 SPS. This data rate has five nulls between the larger nulls at multiples of 14400 Hz. This frequency response is similar to that of data rates 2.5 SPS to 7200 SPS. Figure 25 shows the frequency response nulls for 10 SPS.
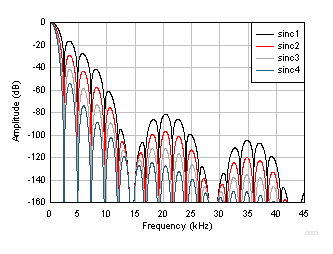 Figure 24. Sinc Frequency Response (2400 SPS)
Figure 24. Sinc Frequency Response (2400 SPS) 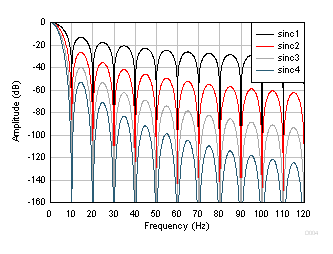 Figure 25. Sinc Frequency Response (10 SPS)
Figure 25. Sinc Frequency Response (10 SPS) Figure 26 and Figure 27 show the frequency response of data rates 50 SPS and 60 SPS, respectively. Increase the attenuation at 50 Hz or 60 Hz and harmonics by increasing the order of the sinc filter, as shown in the figures.
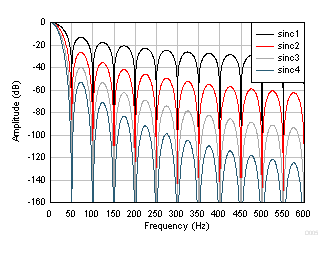 Figure 26. Sinc Frequency Response (50 SPS)
Figure 26. Sinc Frequency Response (50 SPS) 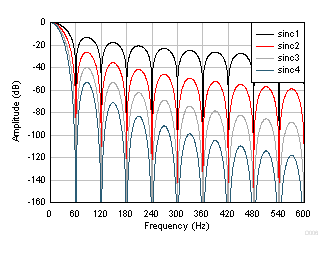 Figure 27. Sinc Frequency Response (60 SPS)
Figure 27. Sinc Frequency Response (60 SPS) Figure 28 and Figure 29 show the detailed frequency response at 50 SPS and 60 SPS, respectively.
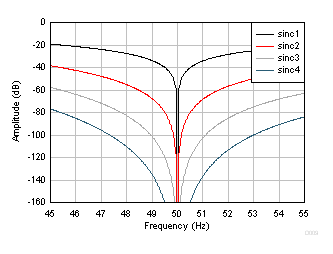 Figure 28. Detail Sinc Frequency Response (50 SPS)
Figure 28. Detail Sinc Frequency Response (50 SPS) 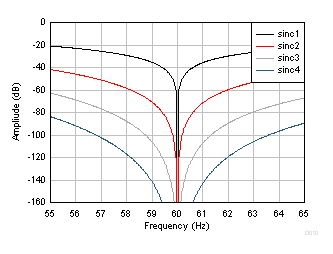 Figure 29. Detail Sinc Frequency Response (60 SPS)
Figure 29. Detail Sinc Frequency Response (60 SPS)