ZHCSHW6B October 2017 – October 2018 ADS122C04
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Multiplexer
- 8.3.2 Low-Noise Programmable Gain Stage
- 8.3.3 Voltage Reference
- 8.3.4 Modulator and Internal Oscillator
- 8.3.5 Digital Filter
- 8.3.6 Conversion Times
- 8.3.7 Excitation Current Sources
- 8.3.8 Sensor Detection
- 8.3.9 System Monitor
- 8.3.10 Temperature Sensor
- 8.3.11 Offset Calibration
- 8.3.12 Conversion Data Counter
- 8.3.13 Data Integrity Features
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Map
- 8.6.1 Configuration Registers
- 8.6.2 Register Descriptions
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- RTE|16
订购信息
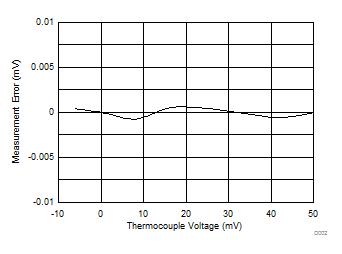
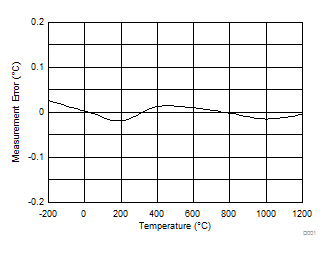
9.2.1.3 Application Curves
Figure 72 and Figure 73 show the measurement results. The measurements are taken at TA = T(CJ) = 25°C. A system offset calibration is performed at T(TC) = 25°C, which translates to a V(TC) = 0 V when T(CJ) = 25°C. No gain calibration is implemented. The data in Figure 72 are taken using a precision voltage source as the input signal instead of a thermocouple. The respective temperature measurement error in Figure 73 is calculated from the data in Figure 72 using the NIST tables.
The design meets the required temperature measurement accuracy given in Table 24. The measurement error shown in Figure 73 does not include the error of the thermocouple itself nor the measurement error of the cold-junction temperature. Those two error sources are in general larger than 0.2°C and therefore, in many cases, dominate the overall system measurement accuracy.