SWRA657 June 2020 CC3100 , CC3200
-
SimpleLink Wi-Fi CC3100, CC3200 Serial Flash
- Trademarks
- 1 Introduction
- 2 How File System Content Gets to the Serial Flash
- 3 File System Guidelines
- 4 User File Mathematics
- 5 System and Configuration Files
- 6 Implementing File System Features From Host Processor
- 7 Factors to Consider in Designing With Serial Flash
- 8 Design Recommendations for Ensuring the Integrity of the Power Supply to the Serial Flash
- 9 Recommended Best Practices
- 10 Implications of Data Integrity Compromise to CC3100/CC3200
- 11 References
7.4 Sudden Power Off (power removal during a write/erase phase)
All systems using serial flash are vulnerable to the effects of sudden power removal. As noted in most serial flash data sheets, data corruption may occur if the power is removed while a write/erase operation is in progress. This can happen if the system operating voltage goes below Vmin of the serial flash (2.3 V typical) before the erase/write operation is completed. Figure 5 shows a typical scenario.
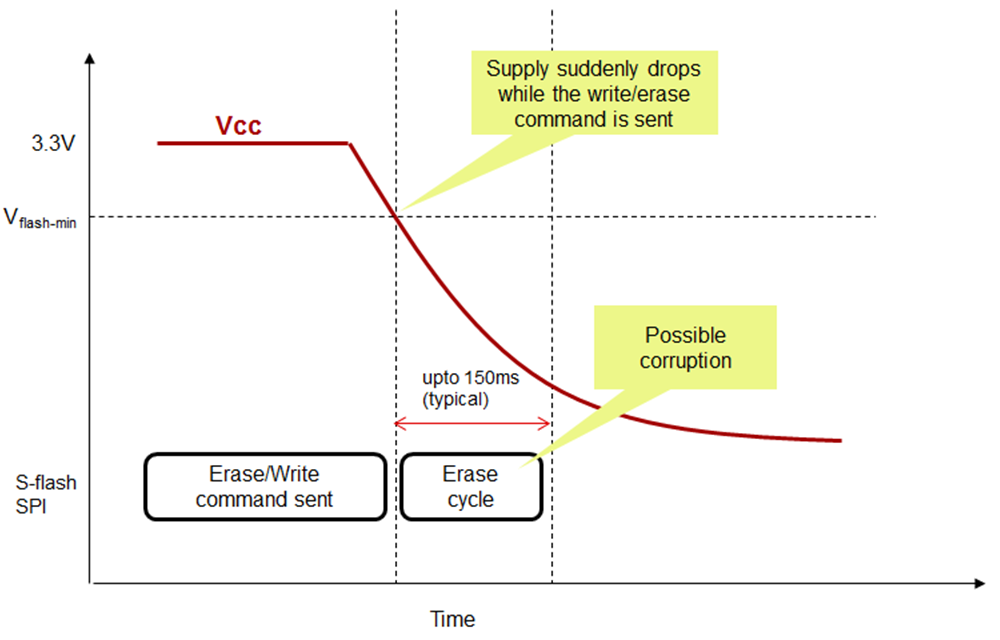 Figure 5. Serial Flash Corruption During a Sudden Power Off Event
Figure 5. Serial Flash Corruption During a Sudden Power Off Event This scenario may occur in battery or line powered end equipment.
- Battery Powered Products: Removal of battery from the product without a soft shutdown
- Line Powered Products: Electrical supply failure or sudden unplugging without a soft shutdown
The sections below explain how the potential for serial flash corruption can be minimized in both types of end equipment.