SSZTA18 july 2017 BQ25700A , BQ25703A , BQ25790 , BQ25792

Nowadays, we see more and more electronics with USB Type-C™ and USB Power Delivery (PD) ports on the market. They range from cellphones, laptops and power banks to drones, power tools, and smart home and portable applications. The USB PD standard allows the transmission of high power after negotiation and presents new requirements for what’s behind the port: the charger IC.
On one hand, as a device, your equipment should be able to negotiate the highest voltage (5-20V) and current provided by the source to charge the battery and provide power to the system. On the other hand, as a host, your equipment should provide the maximum voltage (5 V to 20 V) and current from the battery in the on-the-go (OTG) direction to peripheral devices.
For devices with single- or multiple-cell lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery systems, a buck-boost battery charger is a good solution for compatibility with the requirements I’ve described. When the device is charging, a buck-boost battery charger can buck (step down) the source voltage to charge the battery if the source voltage is higher than the battery, or can boost (step up) the source voltage otherwise. When providing power to the peripherals, a buck-boost charger can buck the battery voltage if the peripheral device asks for a lower voltage, and boost if the peripheral asks for a higher voltage.
Buck-boost chargers have gained a lot of popularity as more and more applications adopt USB PD and USB Type-C ports. Take drones, for example. Drones are power-hungry devices. Depending on the power level and battery capacity, most drones can fly six to 30 minutes per charge. Due to their short flight times, it’s convenient for users to buy extra batteries and have multiple charging options, from charging from the port on the drone itself to using cradle chargers in the car or at home.
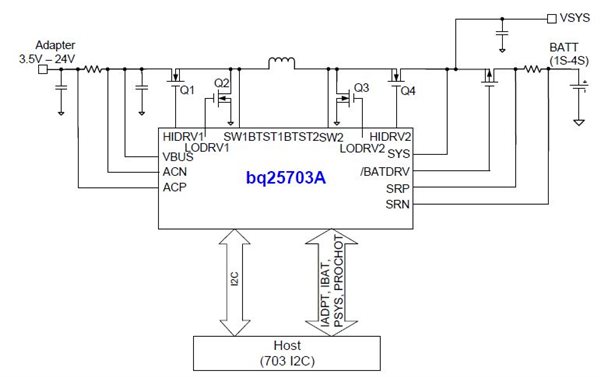 Figure 1 BQ25703A Application
Diagram
Figure 1 BQ25703A Application
DiagramBecause the USB Type-C port is universal and has high power delivery capability, it is a good choice here. To be compatible with power sources with different voltage and power levels, a multicell battery system, like a drone, needs to take advantage of a buck-boost charger. It’s also critical for users to be able to charge their batteries quickly and safely during flight intervals. TI has various buck-boost charging solutions that include a controller and integrated FET to help engineers optimize their designs for different power levels.
The BQ25703A and BQ25700A support up to a 6.35-A charging current and has extensive protection features, including input current optimization (ICO) that helps get the maximum power out of a wide variety of adapters. The BQ25790 and BQ25792 deliver the industry's highest power density of 155 mW/mm2 and are optimized for 30-W applications while maintaining high-efficiency and a high number of integrated components to streamline designs and bill of materials. Figure 1 provides additional information in the BQ25703A application diagram.
Finally, a drone should operate and charge at different temperature conditions. The BQ25703A family provides ±0.6% battery-charging regulation accuracy from -40°C to 85°C. This high level of charging accuracy ensures that the batteries are optimally charged across temperatures.
A buck-boost battery charger is a desirable solution for applications that use USB PD ports and require smooth transitions between operation modes, adaptability for different adapters and extensive safety features.
Additional Resources
- Read the technical articles, Maximize power density with buck-boost charging and USB Type C Power Delivery and Universal and fast charging - a future trend for battery-powered applications.
- Check out the BQ25700A-EVM and the BQ25703A-EVM.
- Watch the training video: Advanced applications of buck-boost chargers