SNIA049 November 2022 TMP61 , TMP61-Q1 , TMP63 , TMP63-Q1 , TMP64 , TMP64-Q1
3 Oversampling
Oversampling is one software method used to reduce the impact of noise. Simply put, oversampling indicates that rather than each individual sample resulting in a temperature measurement, N samples are accumulated and averaged, resulting in one averaged temperature measurement. This process reduces noise according to the number of oversamples, as shown by the difference between the raw and oversampled signals in Figure 3-1.
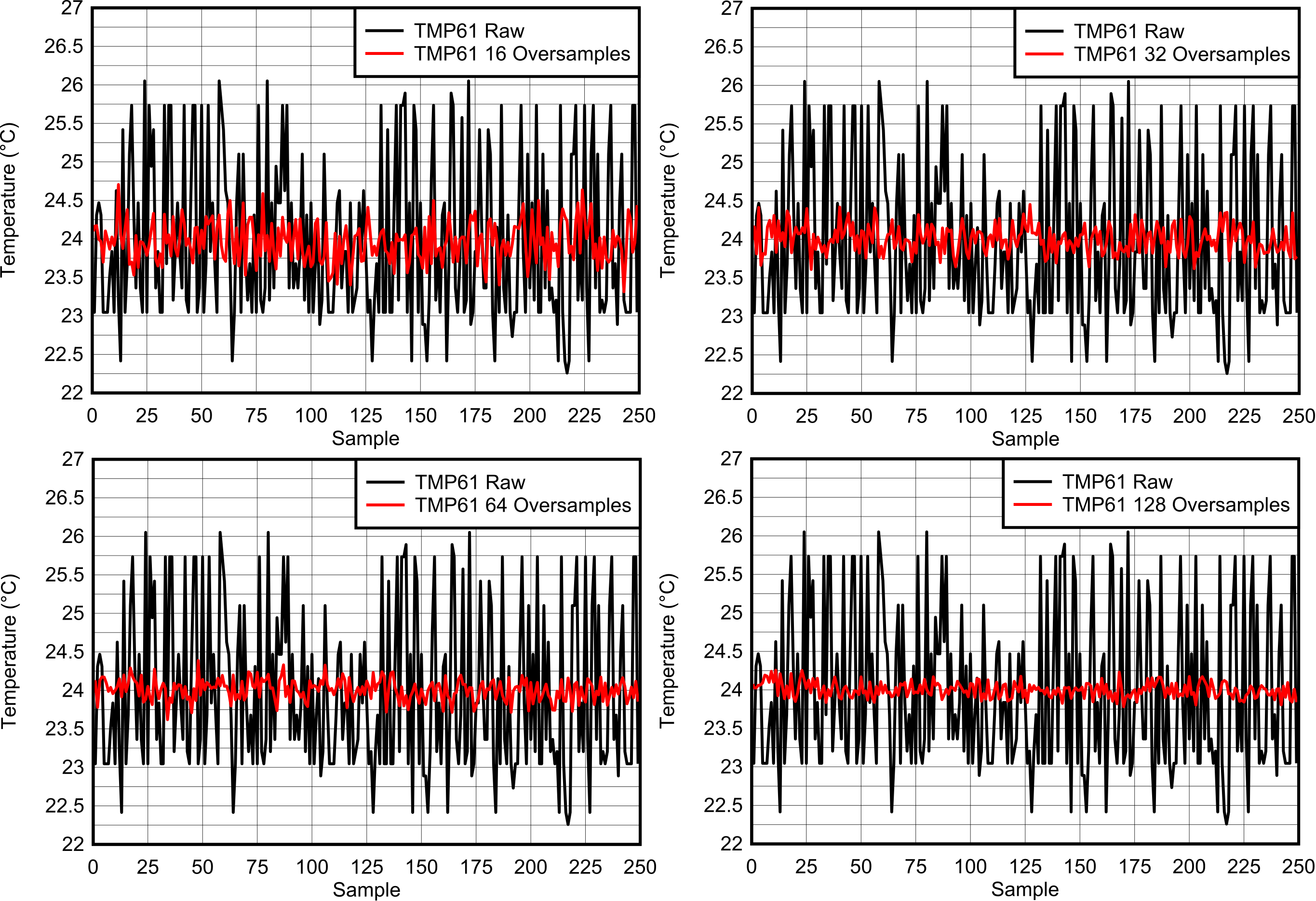 Figure 3-1 Impact of 16 ×, 32 ×, 64 ×,
and 128 × Oversampling on Noise
Figure 3-1 Impact of 16 ×, 32 ×, 64 ×,
and 128 × Oversampling on NoiseThe following pseudocode provides an example implementation of oversampling, which allows modification of the number of oversamples.
int sensorPin = ; // EDIT indicate pin # for analog input to read VTEMP from TMP6
float Vbias = ; // EDIT indicate Vref voltage for ADC
int ADC_bits = ; // EDIT number of bits of resolution for ADC
int ADC_resolution = pow(2, ADC_bits) - 1; // number of ADC steps
int rawADC; // variable for measured ADC value
float VTEMP; // variable for measured ADC voltage
float VTEMP_averaged; // variable for averaged ADC voltage
int oversamples = ; // EDIT number of oversamples
float TMP6oversampled; // variable for oversampled temperature reading
/* EDIT 4th order polynomial coefficients from Thermistor Design Tool */
float THRM_A0 = ;
float THRM_A1 = ;
float THRM_A2 = ;
float THRM_A3 = ;
float THRM_A4 = ;
for(int i = 0; i < oversamples; i++){
rawADC = analogRead(sensorPin); // read ADC value
VTEMP += Vbias / ADC_resolution * rawADC; // convert to voltage and sum for desired number of oversamples
}
VTEMP_averaged = VTEMP / oversamples; // average the summed VTEMP
// convert voltage to temperature
TMP6oversampled = (THRM_A4 * powf(VTEMP_averaged, 4)) + (THRM_A3 * powf(VTEMP_averaged, 3)) + (THRM_A2 * powf(VTEMP_averaged, 2)) + (THRM_A1 * powf(VTEMP_averaged, 1)) + THRM_A0;
VTEMP = 0; // reset VTEMP to 0 for next sample to be taken