SFFS546A november 2022 – june 2023 TLC555-Q1
4 Pin Failure Mode Analysis (Pin FMA)
This section provides a failure mode analysis (FMA) for the pins of the TLC555-Q1. The failure modes covered in this document include the typical pin-by-pin failure scenarios:
- Pin short-circuited to ground (see Table 4-2)
- Pin open-circuited (see Table 4-3)
- Pin short-circuited to an adjacent pin (see Table 4-4)
- Pin short-circuited to supply (see Table 4-5)
Table 4-2 through Table 4-5 also indicate how these pin conditions can affect the device as per the failure effects classification in Table 4-1.
| Class | Failure Effects |
|---|---|
| A | Potential device damage that affects functionality. |
| B | No device damage, but loss of functionality. |
| C | No device damage, but performance degradation. |
| D | No device damage, no impact to functionality or performance. |
Figure 4-1 shows the TLC555-Q1 pin diagram. For a detailed description of the device pins, see the Pin Configuration and Functions section in the TLC555-Q1 data sheet.
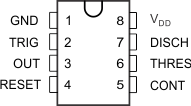 Figure 4-1 Pin Diagram
Figure 4-1 Pin DiagramFollowing are the assumptions of use and the device configuration assumed for the pin FMA in this section:
- 'Short circuit to Power' means short to VDD
- 'Short circuit to GND or Ground' means short to GND
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
TRIG | 2 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior. | B |
OUT | 3 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the device is likely forced into a short-circuit condition with the OUT voltage ultimately forced to the GND voltage. Prolonged exposure to short-circuit conditions can result in long-term reliability issues. | A |
RESET | 4 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior. | B |
CONT | 5 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior and spiked current dissipated though the device. | B |
DISCH | 6 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of an inability to discharge the timing capacitors. | B |
THRES | 7 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior. | B |
VDD | 8 | Timer supplies are shorted together leaving the VDD pin at some voltage between the VDD and GND sources (depending on the source impedance). | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
GND | 1 | Negative supply is left floating. The timer ceases to function because no current can source or sink to the device. There is a potential for damage if any input pins are biased. | A |
TRIG | 2 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior. | B |
OUT | 3 | No negative feedback or ability for OUT to drive the application. | B |
RESET | 4 | Leaving the RESET pin floating
can effect application performance. Leaving the RESET pin open can force an output to either rail or cause irregular toggling of the output. | B |
CONT | 5 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior. | B |
DISCH | 6 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of an inability to discharge the timing capacitors. | B |
THRES | 7 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior. | B |
VDD | 8 | Positive supply is left floating. The timer ceases to function because no current can source or sink to the device. There is a potential for damage if any input pins are biased. | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Shorted to | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|
GND | 1 | 2 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior. | B |
TRIG | 2 | 3 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior. | B |
OUT | 3 | 4 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior. | B |
RESET | 4 | 5 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior. | B |
CONT | 5 | 6 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior. | B |
DISCH | 6 | 7 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior. | B |
THRES | 7 | 8 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior. | B |
VDD | 8 | 1 | Timer supplies are shorted together, leaving the GND pin at some voltage between the GND and VDD sources (depending on the source impedance). | A |
| Pin Name | Pin No. | Description of Potential Failure Effects | Failure Effect Class |
|---|---|---|---|
GND | 1 | Timer supplies are shorted together, leaving the GND pin at some voltage between the GND and VDD sources (depending on the source impedance). | A |
TRIG | 2 | Timer supplies are shorted together, leaving the GND pin at some voltage between the GND and VDD sources (depending on the source impedance). | B |
OUT | 3 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the device is likely forced into a short-circuit condition with the OUT voltage ultimately forced to the VDD voltage. Prolonged exposure to short-circuit conditions can result in long-term reliability issues. | A |
RESET | 4 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is likely not to function due to unexpected output behavior. | B |
CONT | 5 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is likely not to function due to unexpected output behavior and spiked current dissipated though the device. | B |
DISCH | 6 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of an inability to discharge the timing capacitors. Potential for damage is high because of large currents flowing through the discharge transistor. | A |
THRES | 7 | Depending on the circuit configuration, the application is not likely to function because of unexpected output behavior. | B |