ZHCSCH4H June 2013 – November 2016 TPS65132
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用范围
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1
Low-current Applications (≤ 40 mA)
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.2
Mid-current Applications (≤ 80 mA)
- 9.2.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.3 High-current Applications (≤ 150 mA)
- 9.2.1
Low-current Applications (≤ 40 mA)
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- RVC|20
订购信息
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
PCB layout is an important task in the power supply design. Good PCB layout minimizes EMI and allows very good output voltage regulation. For the TPS65132 the following PCB layout guidelines are recommended.
- Keep the power ground plane on the top layer (all capacitor grounds and PGND pins must be connected together with one uninterrupted ground plane).
- AGND and PGND must be connected together on the same ground plane.
- Place the flying capacitor as close as possible to the IC.
- Always avoid vias when possible. They have high inductance and resistance. If vias are necessary, always use more than one in parallel to decrease parasitics especially for power lines.
- Connect REG pins together.
- For high dv/dt signals (switch pin traces): keep copper area to a minimum to prevent making unintentional parallel plate capacitors with other traces or to a ground plane. Best to route signal and return on same layer.
- For high di/dt signals: keep traces short, wide and closely spaced. This will reduce stray inductance and decrease the current loop area to help prevent EMI.
- Keep input capacitor close to the IC with low inductance traces.
- Keep trace from switching node pin to inductor short if possible: it reduces EMI emissions and noise that may couple into other portions of the converter.
- Isolate analog signal paths from power paths.
11.2 Layout Example
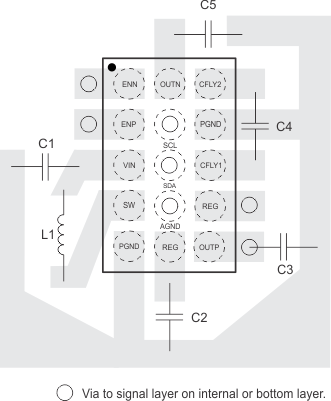
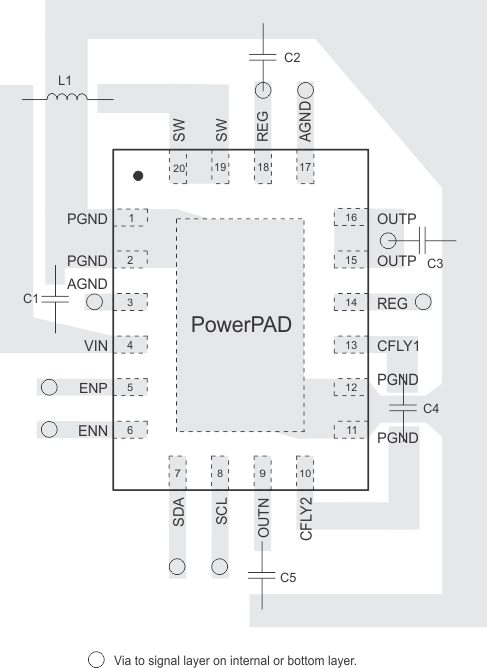 Figure 117. PCB Layout Example for QFN Package
Figure 117. PCB Layout Example for QFN Package