ZHCS898O October 2003 – March 2019 TMS320F2801 , TMS320F28015 , TMS320F28016 , TMS320F2802 , TMS320F2806 , TMS320F2808 , TMS320F2809
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1器件概述
- 2修订历史记录
- 3Device Comparison
- 4Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings – Automotive
- 5.3 ESD Ratings – Commercial
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5
Power Consumption Summary
- Table 5-1 TMS320F2809, TMS320F2808 Current Consumption by Power-Supply Pins at 100-MHz SYSCLKOUT
- Table 5-2 TMS320F2806 Current Consumption by Power-Supply Pins at 100-MHz SYSCLKOUT
- Table 5-3 TMS320F2802, TMS320F2801 Current Consumption by Power-Supply Pins at 100-MHz SYSCLKOUT
- Table 5-4 TMS320C2802, TMS320C2801 Current Consumption by Power-Supply Pins at 100-MHz SYSCLKOUT
- 5.5.1 Reducing Current Consumption
- 5.5.2 Current Consumption Graphs
- 5.6 Electrical Characteristics
- 5.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for F280x 100-Ball GGM Package
- 5.8 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for F280x 100-Pin PZ Package
- 5.9 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for C280x 100-Ball GGM Package
- 5.10 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for C280x 100-Pin PZ Package
- 5.11 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for F2809 100-Ball GGM Package
- 5.12 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for F2809 100-Pin PZ Package
- 5.13 Thermal Design Considerations
- 5.14
Timing and Switching Characteristics
- 5.14.1 Timing Parameter Symbology
- 5.14.2 Power Sequencing
- 5.14.3 Clock Requirements and Characteristics
- 5.14.4
Peripherals
- 5.14.4.1 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 5.14.4.2 Enhanced Control Peripherals
- 5.14.4.3 External Interrupt Timing
- 5.14.4.4 I2C Electrical Specification and Timing
- 5.14.4.5 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Timing
- 5.14.5 Emulator Connection Without Signal Buffering for the DSP
- 5.14.6 Flash Timing
- 5.15 On-Chip Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 5.16 Migrating From F280x Devices to C280x Devices
- 5.17 ROM Timing (C280x only)
-
6Detailed Description
- 6.1
Brief Descriptions
- 6.1.1 C28x CPU
- 6.1.2 Memory Bus (Harvard Bus Architecture)
- 6.1.3 Peripheral Bus
- 6.1.4 Real-Time JTAG and Analysis
- 6.1.5 Flash
- 6.1.6 ROM
- 6.1.7 M0, M1 SARAMs
- 6.1.8 L0, L1, H0 SARAMs
- 6.1.9 Boot ROM
- 6.1.10 Security
- 6.1.11 Peripheral Interrupt Expansion (PIE) Block
- 6.1.12 External Interrupts (XINT1, XINT2, XNMI)
- 6.1.13 Oscillator and PLL
- 6.1.14 Watchdog
- 6.1.15 Peripheral Clocking
- 6.1.16 Low-Power Modes
- 6.1.17 Peripheral Frames 0, 1, 2 (PFn)
- 6.1.18 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) Multiplexer
- 6.1.19 32-Bit CPU-Timers (0, 1, 2)
- 6.1.20 Control Peripherals
- 6.1.21 Serial Port Peripherals
- 6.2
Peripherals
- 6.2.1 32-Bit CPU-Timers 0/1/2
- 6.2.2 Enhanced PWM Modules (ePWM1/2/3/4/5/6)
- 6.2.3 Hi-Resolution PWM (HRPWM)
- 6.2.4 Enhanced CAP Modules (eCAP1/2/3/4)
- 6.2.5 Enhanced QEP Modules (eQEP1/2)
- 6.2.6 Enhanced Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) Module
- 6.2.7 Enhanced Controller Area Network (eCAN) Modules (eCAN-A and eCAN-B)
- 6.2.8 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Modules (SCI-A, SCI-B)
- 6.2.9 Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) Modules (SPI-A, SPI-B, SPI-C, SPI-D)
- 6.2.10 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 6.2.11 GPIO MUX
- 6.3 Memory Maps
- 6.4 Register Map
- 6.5 Interrupts
- 6.6 System Control
- 6.7 Low-Power Modes Block
- 6.1
Brief Descriptions
- 7Applications, Implementation, and Layout
- 8器件和文档支持
- 9机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
请参考 PDF 数据表获取器件具体的封装图。
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- PZ|100
- GBA|100
- NMF|100
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- PZ|100
订购信息
8.2 器件和开发支持工具命名规则
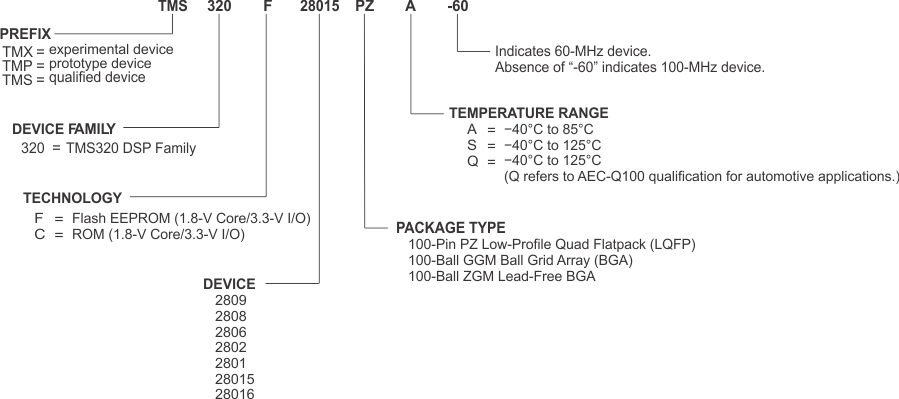
为了标明产品开发周期的阶段,TI 为所有 TMS320™DSP 器件和支持工具的部件号指定了前缀。每一个 TMS2808™ DSP 商用系列成员产品具有以下三个前缀中的一个:TMX,TMP,或者 TMS(例如,TMS320F2808)。德州仪器 (TI) 建议为其支持的工具使用三个可能前缀指示符中的两个:TMDX 和 TMDS。这些前缀代表了产品开发的发展阶段,即从工程原型 (TMX/TMDX) 直到完全合格的生产器件/工具 (TMS/TMDS)。
器件开发进化流程:
| TMX | 试验器件,不一定代表最终器件的电气规格 | |
| TMP | 最终硅片,符合器件的电气规格,但是未完成质量和可靠性验证 | |
| TMS | 完全合格的生产器件 |
支持工具开发发展流程:
| TMDX | 还未经完整的德州仪器 (TI) 内部质量测试的开发支持工具 | |
| TMDS | 完全合格的开发支持产品 |
TMX 和 TMP 器件和 TMDX 开发支持工具出货时带有如下的免责声明:
“开发产品用于内部评估用途。”
TMS 器件和 TMDS 开发支持工具已进行完全特性描述,并且器件的质量和可靠性已经完全论证。TI 的标准保修证书适用。
预测显示原型器件(TMX 或者 TMP)的故障率大于标准生产器件。由于它们的预计的最终使用故障率仍未定义,德州仪器建议不要将这些器件用于任何生产系统。只有合格的产品器件将被使用。
TI 器件的命名规则还包括一个带有器件系列名称的后缀。这个后缀表明封装类型(例如,PZ)和温度范围(如,S)。Figure 8-1 提供了解读任一系列产品成员的完整器件名称的图例。
有关器件部件号和详细的订购信息,请参阅封装选项附录、访问 TI 网站 (www.ti.com.cn) 或联系您的 TI 销售代表。
有关裸片器件命名规则标记的其他 说明 ,请参阅 TMS320F280x、TMS320C280x、TMS320F2801x DSP 器件勘误表。