SLIS142D December 2012 – September 2016 TLC6C598-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6 Specifications
6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)(1)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Logic supply voltage | –0.3 | 8 | V |
| VI | Logic input-voltage range | –0.3 | 8 | V |
| VDS | Power DMOS drain-to-source voltage | –0.3 | 42 | V |
| Continuous total dissipation | See Thermal Information | |||
| TA | Operating ambient temperature | –40 | 125 | °C |
| TJ | Operating junction temperature range | –40 | 150 | °C |
| Tstg | Storage temperature range | –55 | 165 | °C |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only, and do not imply functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
6.2 ESD Ratings
| VALUE | UNIT | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per AEC Q100-002(1) | ±2000 | V | |
| Charged device model (CDM), per AEC Q100-011 | All pins | ±750 | |||
| Corner pins (1, 8, 9, and 16) | ±750 | ||||
(1) AEC Q100-002 indicates HBM stressing is done in accordance with the ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001 specification.
6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage | 3 | 5.5 | V |
| VIH | High-level input voltage | 2.4 | V | |
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | 0.7 | V | |
| TA | Operating ambient temperature | –40 | 125 | °C |
6.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | TLC6C598-Q1 | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PW (TSSOP) | D (SOIC) | |||
| 16 PINS | 16 PINS | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 129.4 | 100 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 55.4 | 45 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 65.8 | 40 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 9.9 | 10 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 65.2 | 40 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | NA | NA | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report (SPRA953).
6.5 Electrical Characteristics
VCC = 5 V, TC = 25°C (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DRAIN0 to DRAIN7. Drain-to-source voltage | 40 | V | |||||
| VOH | High-level output voltage, SER OUT | IOH = –20 μA | VCC = 5 V | 4.9 | 4.99 | V | |
| IOH = −4 mA | 4.5 | 4.69 | V | ||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage, SER OUT | IOH = 20 μA | VCC = 5 V | 0.001 | 0.01 | V | |
| IOH = 4 mA | 0.25 | 0.4 | V | ||||
| IIH | High-level input current | VCC = 5 V, VI = VCC | 0.2 | μA | |||
| IIL | Low-level input current | VCC = 5 V, VI = 0 | –0.2 | μA | |||
| ICC | Logic supply current | VCC = 5 V, no clock signal | All outputs off | 0.1 | 1 | μA | |
| All outputs on | 88 | 160 | |||||
| ICC(FRQ) | Logic supply current at frequency | fSRCK = 5 MHz, CL = 30 pF | All outputs on | 200 | μA | ||
| IDSX | Off-state drain current | VDS = 30 V | VCC = 5 V | 0.1 | μA | ||
| VDS = 30 V, TC = 125°C | VCC = 5 V | 0.15 | 0.3 | ||||
| rDS(on) | Static drain-source on-state resistance | ID = 20 mA, VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C, Single channel ON |
6 | 7.41 | 8.6 | Ω | |
| ID = 20 mA, VCC = 5 V, TA = 25°C, All channels ON |
6.7 | 8.3 | 9.6 | ||||
| ID = 20 mA, VCC = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, Single channel ON |
7.9 | 9.34 | 11.2 | ||||
| ID = 20 mA, VCC = 3.3 V, TA = 25°C, All channels ON |
8.7 | 10.25 | 12.3 | ||||
| ID = 20 mA, VCC = 5 V, TA = 125°C, Single channel ON |
9.1 | 11.13 | 12.9 | ||||
| ID = 20 mA, VCC = 5 V, TA = 125°C, All channels ON |
10.3 | 12.28 | 14.5 | ||||
| ID = 20 mA, VCC = 3.3 V, TA = 125°C, Single channel ON |
11.6 | 13.69 | 16.4 | ||||
| ID = 20 mA, VCC = 3.3 V, TA = 125°C, All channels ON |
12.8 | 14.89 | 18.2 | ||||
| TSHUTDOWN | Thermal shutdown trip point | 150 | 175 | 200 | ºC | ||
| Thys | Hysteresis | 15 | ºC | ||||
6.6 Timing Requirements
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tsu | Setup time, SER IN high before SRCK↑ | 15 | ns | ||
| th | Hold time, SER IN high after SRCK↑ | 15 | ns | ||
| tw | SER IN pulse duration | 40 | ns | ||
6.7 Switching Characteristics
VCC = 5 V, TJ = 25°C| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| tPLH | Propagation delay time, low-to-high-level output from G | CL = 30 pF, ID = 48 mA | 220 | ns | ||
| tPHL | Propagation delay time, high-to-low-level output from G | 75 | ns | |||
| tr | Rise time, drain output | 210 | ns | |||
| tf | Fall time, drain output | 128 | ns | |||
| tpd | Propagation delay time, SRCK↓ to SER OUT | CL = 30 pF, ID = 48 mA | 49.4 | ns | ||
| tor | SER OUT rise time (10% to 90%) | CL = 30 pF | 20 | ns | ||
| tof | SER OUT fall time (90% to 10%) | CL = 30 pF | 20 | ns | ||
| f(SRCK) | Serial clock frequency | CL = 30 pF, ID = 20 mA | 10 | MHz | ||
| tSRCK_WH | SRCK pulse duration, high | 30 | ns | |||
| tSRCK_WL | SRCK pulse duration, low | 30 | ns | |||
6.8 Timing Waveforms
Figure 1 shows the SER IN to SER OUT waveform. The output signal appears on the falling edge of the shift register clock (SRCK) because there is a phase inverter at SER OUT (see Figure 13). As a result, it takes seven and a half periods of SRCK for data to transfer from SER IN to SER OUT.
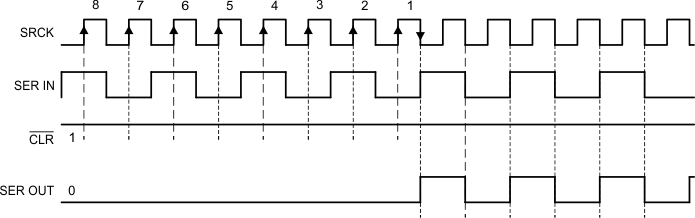 Figure 1. SER IN to SER OUT Waveform
Figure 1. SER IN to SER OUT Waveform
Figure 2 shows the switching times and voltage waveforms. Tests for all these parameters took place using the test circuit shown in Figure 11.
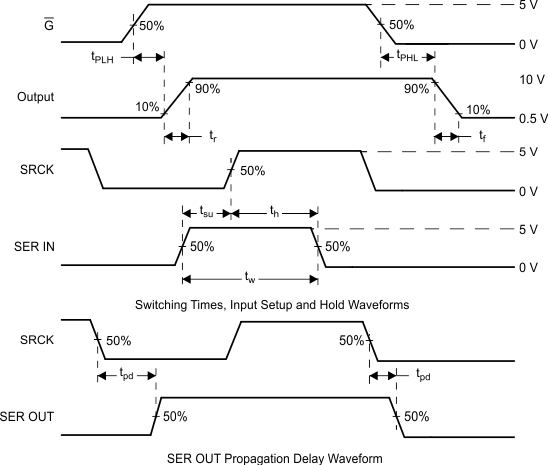 Figure 2. Switching Times and Voltage Waveforms
Figure 2. Switching Times and Voltage Waveforms
6.9 Typical Characteristics
Conditions for Figure 5 and Figure 6: Single channel on, conditions for Figure 7, Figure 8 and Figure 9: All channels on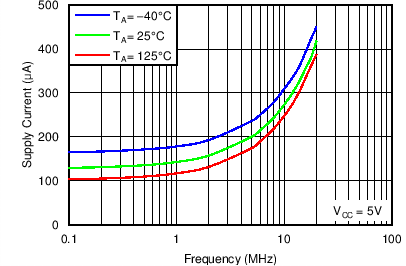 Figure 3. Supply Current vs Frequency
Figure 3. Supply Current vs Frequency
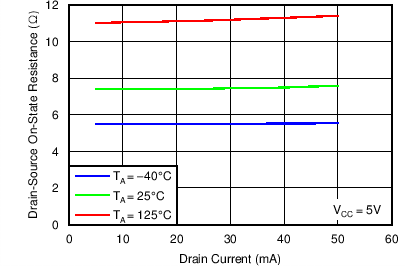 Figure 5. Drain-to-Source On-State Resistance vs Drain Current
Figure 5. Drain-to-Source On-State Resistance vs Drain Current
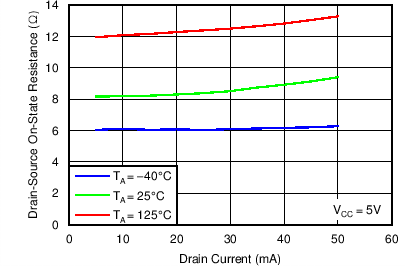 Figure 7. Drain-to-Source On-State Resistance vs Drain Current
Figure 7. Drain-to-Source On-State Resistance vs Drain Current
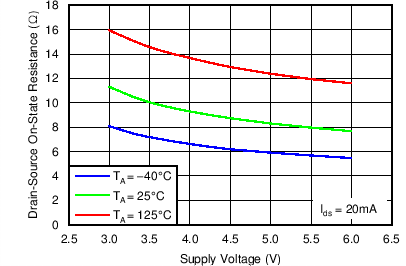 Figure 9. Drain-to-Source On-State Resistance vs Drain Current
Figure 9. Drain-to-Source On-State Resistance vs Drain Current
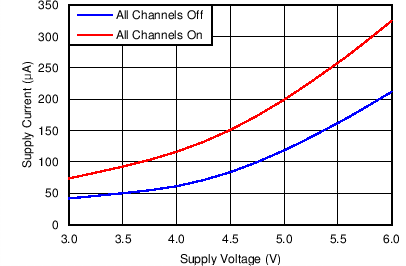 Figure 4. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage
Figure 4. Supply Current vs Supply Voltage
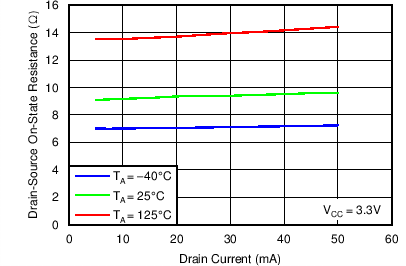 Figure 6. Drain-to-Source On-State Resistance vs Drain Current
Figure 6. Drain-to-Source On-State Resistance vs Drain Current
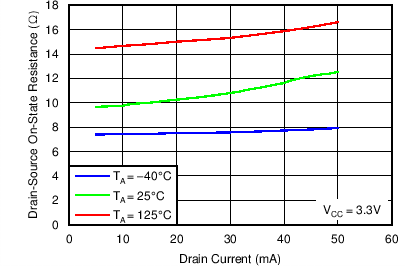 Figure 8. Drain-to-Source On-State Resistance vs Drain Current
Figure 8. Drain-to-Source On-State Resistance vs Drain Current
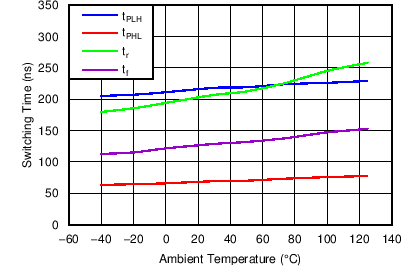 Figure 10. Switching Time vs Ambient Temperature
Figure 10. Switching Time vs Ambient Temperature