SLLS804D March 2009 – August 2016 SN65HVDA540-5-Q1 , SN65HVDA540-Q1 , SN65HVDA541-5-Q1 , SN65HVDA541-Q1 , SN65HVDA542-5-Q1 , SN65HVDA542-Q1
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Parameter Measurement Information
- 8 Detailed Description
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Device and Documentation Support
- 13Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7 Parameter Measurement Information
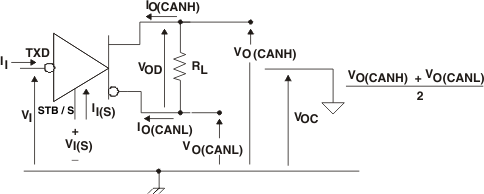 Figure 2. Driver Voltage, Current, and Test Definition
Figure 2. Driver Voltage, Current, and Test Definition
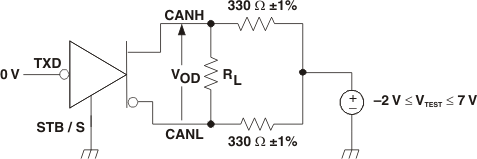 Figure 3. Driver VOD Test Circuit
Figure 3. Driver VOD Test Circuit
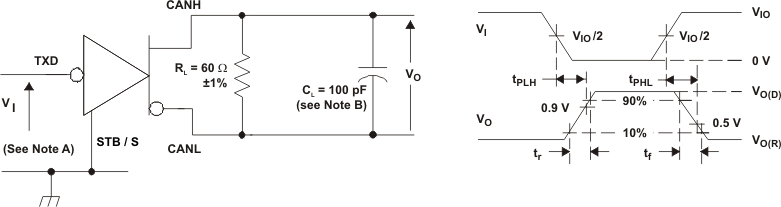
A. The input pulse is supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: PRR ≤ 125 kHz, 50% duty cycle, tr ≤ 6 ns, tf ≤ 6 ns, ZO = 50 Ω.
B. CL includes instrumentation and fixture capacitance within ±20%.
C. For HVDA54x-5 device versions, VIO = VCC.
Figure 4. Driver Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
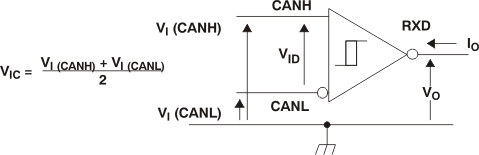 Figure 5. Receiver Voltage and Current Definitions
Figure 5. Receiver Voltage and Current Definitions
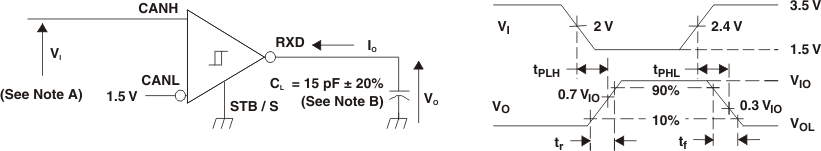
A. The input pulse is supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: PRR ≤ 125 kHz, 50% duty cycle, tr ≤ 6 ns, tf ≤ 6 ns, ZO = 50 Ω.
B. CL includes instrumentation and fixture capacitance within ±20%.
C. C. For HVDA54x-5 device versions VIO = VCC.
Figure 6. Receiver Test Circuit and Voltage Waveforms
Table 1. Differential Input Voltage Threshold Test
| INPUT | OUTPUT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCANH | VCANL | |VID| | R | |
| –11.1 V | –12 V | 900 mV | L | VOL |
| 12 V | 11.1 V | 900 mV | L | |
| –6 V | –12 V | 6 V | L | |
| 12 V | 6 V | 6 V | L | |
| –11.5 V | –12 V | 500 mV | H | VOH |
| 12 V | 11.5 V | 500 mV | H | |
| –12 V | –6 V | 6 V | H | |
| 6 V | 12 V | 6 V | H | |
| Open | Open | X | H | |
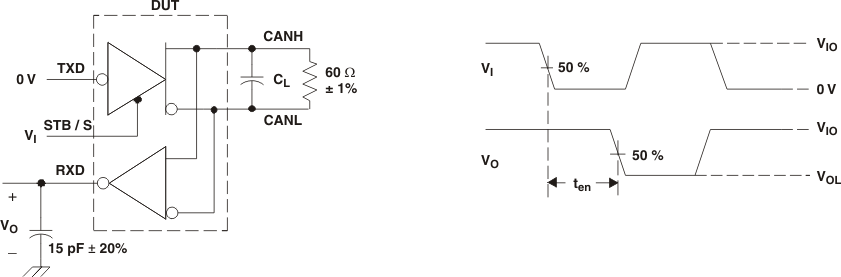
A. CL = 100 pF includes instrumentation and fixture capacitance within ±20%.
B. All VI input pulses are from 0 V to VIO and supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤ 6 ns. Pulse Repetition Rate (PRR) = 25 kHz, 50% duty cycle.
C. C. For HVDA54x-5 device versions VIO = VCC.
Figure 7. tEN Test Circuit and Waveforms
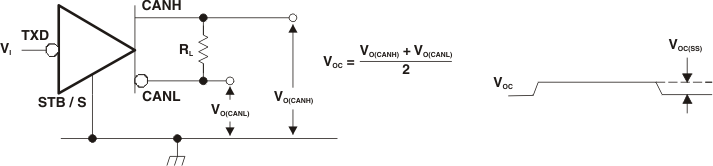
A. All VI input pulses are from 0 V to VIO and supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤ 6 ns. Pulse Repetition Rate (PRR) = 125 kHz, 50% duty cycle.
Figure 8. Common-Mode Output Voltage Test and Waveforms
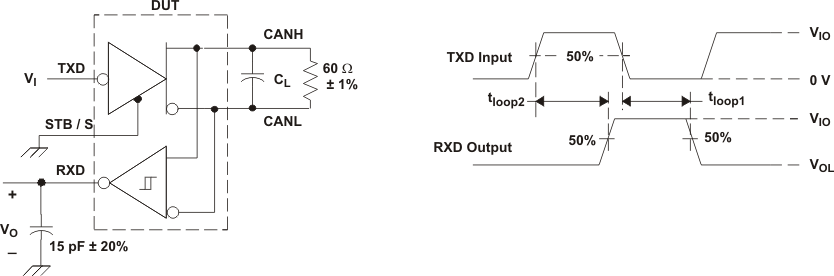
A. CL = 100 pF includes instrumentation and fixture capacitance within ±20%.
B. All VI input pulses are from 0 V to VIO and supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤ 6 ns. Pulse Repetition Rate (PRR) = 125 kHz, 50% duty cycle.
C. For HVDA54x-5 device versions, VIO = VCC.
Figure 9. tPROP(LOOP) Test Circuit and Waveform
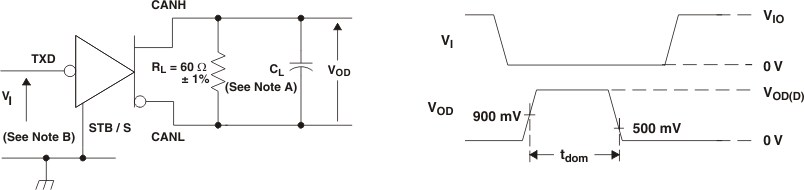
A. CL = 100 pF includes instrumentation and fixture capacitance within ±20%.
B. All VI input pulses are from 0 V to VIO and supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr or tf ≤ 6 ns. Pulse Repetition Rate (PRR) = 500 Hz, 50% duty cycle.
C. For HVDA54x-5 device versions, VIO = VCC.
Figure 10. TXD Dominant Time Out Test Circuit and Waveforms
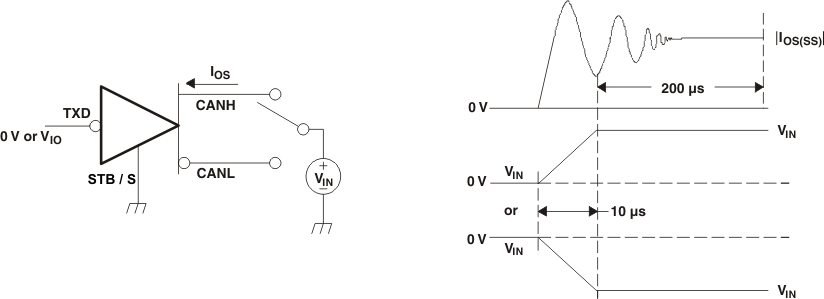
A. For HVDA54x-5 device versions VIO = VCC.
Figure 11. Driver Short-Circuit Current Test and Waveforms
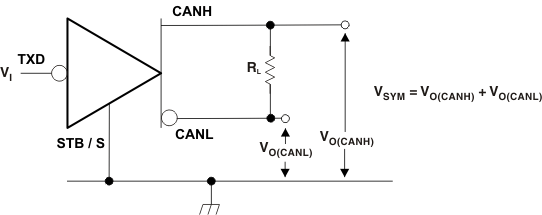
A. All VI input pulses are from 0 V to VIO and supplied by a generator having the following characteristics: tr/tf ≤ 6 ns, Pulse Repetition Rate (PRR) = 250 kHz, 50% duty cycle.
Figure 12. Driver Output Symmetry Test Circuit