ZHCSD33A November 2014 – December 2014 MSP430FR5739-EP
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1器件概述
- 2修订历史记录
- 3Pin Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.3 Thermal Information
- 4.4 Active Mode Supply Current Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 4.5 Low-Power Mode Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 4.6 Schmitt-Trigger Inputs - General Purpose I/O (P1.0 to P1.7, P2.0 to P2.7, P3.0 to P3.7, P4.0 to P4.1, PJ.0 to PJ.5, RST/NMI)
- 4.7 Inputs - Ports P1 and P2 (P1.0 to P1.7, P2.0 to P2.7)
- 4.8 Leakage Current - General Purpose I/O (P1.0 to P1.7, P2.0 to P2.7, P3.0 to P3.7, P4.0 to P4.1, PJ.0 to PJ.5, RST/NMI)
- 4.9 Outputs - General Purpose I/O (P1.0 to P1.7, P2.0 to P2.7, P3.0 to P3.7, P4.0 to P4.1, PJ.0 to PJ.5)
- 4.10 Output Frequency - General Purpose I/O (P1.0 to P1.7, P2.0 to P2.7, P3.0 to P3.7, P4.0 to P4.1, PJ.0 to PJ.5)
- 4.11 Typical Characteristics - Outputs
- 4.12 Crystal Oscillator, XT1, Low-Frequency (LF) Mode
- 4.13 Crystal Oscillator, XT1, High-Frequency (HF) Mode
- 4.14 Internal Very-Low-Power Low-Frequency Oscillator (VLO)
- 4.15 DCO Frequencies
- 4.16 MODOSC
- 4.17 PMM, Core Voltage
- 4.18 PMM, SVS, BOR
- 4.19 Wake-Up from Low Power Modes
- 4.20 Timer_A
- 4.21 Timer_B
- 4.22 eUSCI (UART Mode) Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.23 eUSCI (UART Mode)
- 4.24 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode) Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.25 eUSCI (SPI Master Mode)
- 4.26 eUSCI (SPI Slave Mode)
- 4.27 eUSCI (I2C Mode)
- 4.28 10-Bit ADC, Power Supply and Input Range Conditions
- 4.29 10-Bit ADC, Timing Parameters
- 4.30 10-Bit ADC, Linearity Parameters
- 4.31 REF, External Reference
- 4.32 REF, Built-In Reference
- 4.33 REF, Temperature Sensor and Built-In VMID
- 4.34 Comparator_D
- 4.35 FRAM
- 4.36 JTAG and Spy-Bi-Wire Interface
-
5Detailed Description
- 5.1 Functional Block Diagram
- 5.2 CPU
- 5.3 Operating Modes
- 5.4 Interrupt Vector Addresses
- 5.5 Memory Organization
- 5.6 Bootstrap Loader (BSL)
- 5.7 JTAG Operation
- 5.8 FRAM
- 5.9 Memory Protection Unit (MPU)
- 5.10
Peripherals
- 5.10.1 Digital I/O
- 5.10.2 Oscillator and Clock System (CS)
- 5.10.3 Power Management Module (PMM)
- 5.10.4 Hardware Multiplier (MPY)
- 5.10.5 Real-Time Clock (RTC_B)
- 5.10.6 Watchdog Timer (WDT_A)
- 5.10.7 System Module (SYS)
- 5.10.8 DMA Controller
- 5.10.9 Enhanced Universal Serial Communication Interface (eUSCI)
- 5.10.10 TA0, TA1
- 5.10.11 TB0, TB1, TB2
- 5.10.12 ADC10_B
- 5.10.13 Comparator_D
- 5.10.14 CRC16
- 5.10.15 Shared Reference (REF)
- 5.10.16 Embedded Emulation Module (EEM)
- 5.10.17 Peripheral File Map
-
6Input/Output Schematics
- 6.1 Port P1, P1.0 to P1.2, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.2 Port P1, P1.3 to P1.5, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.3 Port P1, P1.6 to P1.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.4 Port P2, P2.0 to P2.2, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.5 Port P2, P2.3 to P2.4, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.6 Port P2, P2.5 to P2.6, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.7 Port P2, P2.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.8 Port P3, P3.0 to P3.3, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.9 Port P3, P3.4 to P3.6, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.10 Port P3, P3.7, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.11 Port P4, P4.0, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.12 Port P4, P4.1, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 6.13 Port J, J.0 to J.3 JTAG pins TDO, TMS, TCK, TDI/TCLK, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger or Output
- 6.14 Port PJ, PJ.4 and PJ.5 Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 7Device Descriptors (TLV)
- 8器件和文档支持
- 9机械封装和可订购信息
8 器件和文档支持
8.1 器件支持
8.1.1 开始使用
TI 还提供了立即入门必备的所有硬件平台和软件组件以及工具! 不仅如此,TI 还拥有众多辅助组件以满足您的需求。 要获得 MSP430™ MCU 产品线、可用开发工具和评估套件,以及高级开发资源,请访问 MSP430 入门网页。
8.1.2 Development Tools Support
All MSP430™ microcontrollers are supported by a wide variety of software and hardware development tools. Tools are available from TI and various third parties. See them all at www.ti.com/msp430tools.
8.1.2.1 Hardware Features
See the Code Composer Studio for MSP430 User's Guide (SLAU157) for details on the available features.
| MSP430 Architecture | 4-Wire JTAG | 2-Wire JTAG | Break- points (N) |
Range Break- points | Clock Control | State Sequencer | Trace Buffer | LPMx.5 Debugging Support |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSP430Xv2 | Yes | Yes | 3 | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
8.1.2.2 Recommended Hardware Options
8.1.2.2.1 Target Socket Boards
The target socket boards allow easy programming and debugging of the device using JTAG. They also feature header pin outs for prototyping. Target socket boards are orderable individually or as a kit with the JTAG programmer and debugger included. The following table shows the compatible target boards and the supported packages.
| Package | Target Board and Programmer Bundle | Target Board Only |
|---|---|---|
| 40-pin VQFN (RHA) | MSP-FET430U40A | MSP-TS430RHA40A |
8.1.2.2.2 Experimenter Boards
Experimenter Boards and Evaluation kits are available for some MSP430 devices. These kits feature additional hardware components and connectivity for full system evaluation and prototyping. See www.ti.com/msp430tools for details.
8.1.2.2.3 Debugging and Programming Tools
Hardware programming and debugging tools are available from TI and from its third party suppliers. See the full list of available tools at www.ti.com/msp430tools.
8.1.2.2.4 Production Programmers
The production programmers expedite loading firmware to devices by programming several devices simultaneously.
| Part Number | PC Port | Features | Provider |
|---|---|---|---|
| MSP-GANG | Serial and USB | Program up to eight devices at a time. Works with PC or standalone. | Texas Instruments |
8.1.2.3 Recommended Software Options
8.1.2.3.1 Integrated Development Environments
Software development tools are available from TI or from third parties. Open source solutions are also available.
This device is supported by Code Composer Studio™ IDE (CCS).
8.1.2.3.2 MSP430Ware
MSP430Ware is a collection of code examples, data sheets, and other design resources for all MSP430 devices delivered in a convenient package. In addition to providing a complete collection of existing MSP430 design resources, MSP430Ware also includes a high-level API called MSP430 Driver Library. This library makes it easy to program MSP430 hardware. MSP430Ware is available as a component of CCS or as a standalone package.
8.1.2.3.3 Command-Line Programmer
MSP430 Flasher is an open-source, shell-based interface for programming MSP430 microcontrollers through a FET programmer or eZ430 using JTAG or Spy-Bi-Wire (SBW) communication. MSP430 Flasher can be used to download binary files (.txt or .hex) files directly to the MSP430 microcontroller without the need for an IDE.
8.1.3 器件和开发工具命名规则
为了指明产品开发周期所处的阶段,TI 为所有 MSP430 MCU 器件和支持工具的产品型号分配了前缀。 每个 MSP430 MCU 商用系列产品成员具有以下三个前缀中的一个:MSP,PMS 或 XMS(例如,MSP430F5259)。 德州仪器 (TI) 建议为其支持的工具使用三个可能前缀指示符中的两个:MSP 和 MSPX。 这些前缀代表了产品从工程原型机(其中 XMS 针对器件,而 MSPX 针对工具)直到完全合格的生产器件和工具(其中 MSP 针对器件,而 MSP 针对工具)的产品开发进化阶段。
器件开发进化流程:
XMS - 试验器件不一定代表最终器件的电气技术规格
PMS - 最终的芯片模型符合器件的电气技术规格,但是未经完整的质量和可靠性验证
MSP - 完全合格的生产器件
支持工具开发进化流程:
MSPX - 还未经德州仪器 (TI) 完整内部质量测试的开发支持产品。
MSP – 完全合格的开发支持产品
XMS 和 PMS 器件和 MSPX 开发支持工具在供货时附带如下免责条款:
“开发的产品用于内部评估用途。”
MSP 器件和 MSP 开发支持工具已进行完全特性描述,并且器件的质量和可靠性已经完全论证。 TI 的标准保修证书适用。
预测显示原型器件(XMS 和 PMS)的故障率大于标准生产器件。 由于它们的预计的最终使用故障率仍未定义,德州仪器 (TI) 建议不要将这些器件用于任何生产系统。 只有合格的产品器件将被使用。
TI 器件的命名规则也包括一个带有器件系列名称的后缀。 这个后缀包括封装类型(例如,PZP)和温度范围(如,T)。Figure 8-1 提供了读取任一系列产品成员完整器件名称的图例。
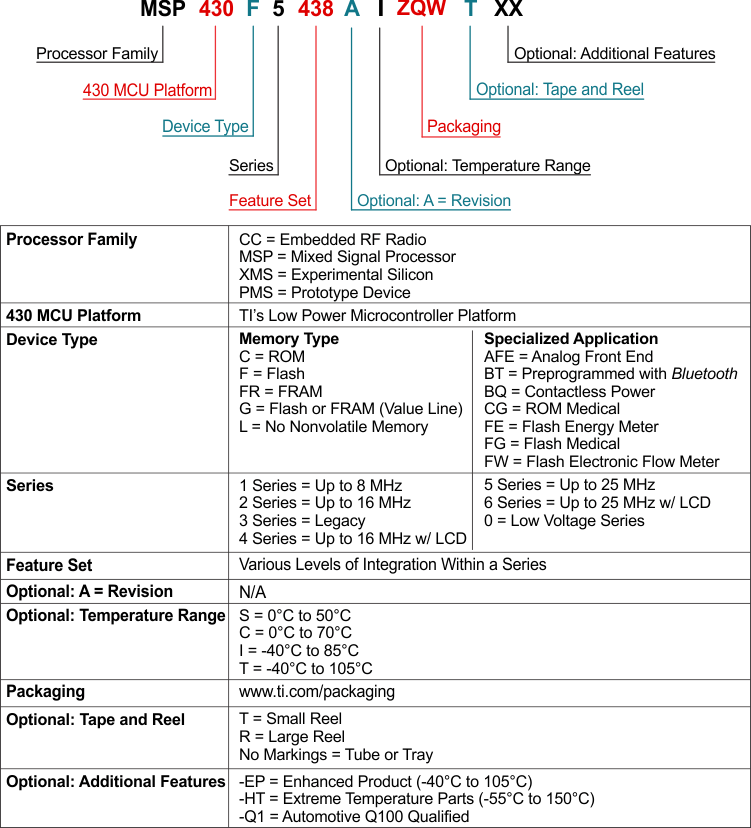 Figure 8-1 器件命名规则
Figure 8-1 器件命名规则
8.2 文档支持
以下文档描述了 MSP430FR5739-EP MCU。 www.ti.com.cn 网站上提供了这些文档的副本。
-
SLAU272MSP430FR57xx 系列用户指南。 这款器件系列内所提供的全部模块和外设的详细信息。
-
SLAZ392MSP430FR5739 器件勘误表。 描述了针对这款器件每个芯片修订版本功能技术规格的已知例外情况。
-
SLAZ391MSP430FR5738 器件勘误表。 描述了针对这款器件每个芯片修订版本功能技术规格的已知例外情况。
-
SLAZ390MSP430FR5737 器件勘误表。 描述了针对这款器件每个芯片修订版本功能技术规格的已知例外情况。
-
SLAZ389MSP430FR5736 器件勘误表。 描述了针对这款器件每个芯片修订版本功能技术规格的已知例外情况。
-
SLAZ388MSP430FR5735 器件勘误表。 描述了针对这款器件每个芯片修订版本功能技术规格的已知例外情况。
-
SLAZ387MSP430FR5734 器件勘误表。 描述了针对这款器件每个芯片修订版本功能技术规格的已知例外情况。
-
SLAZ386MSP430FR5733 器件勘误表。 描述了针对这款器件每个芯片修订版本功能技术规格的已知例外情况。
-
SLAZ385MSP430FR5732 器件勘误表。 描述了针对这款器件每个芯片修订版本功能技术规格的已知例外情况。
-
SLAZ384MSP430FR5731 器件勘误表。 描述了针对这款器件每个芯片修订版本功能技术规格的已知例外情况。
-
SLAZ383MSP430FR5730 器件勘误表。 描述了针对这款器件每个芯片修订版本功能技术规格的已知例外情况。
8.3 Community Resources
The following links connect to TI community resources. Linked contents are provided "AS IS" by the respective contributors. They do not constitute TI specifications and do not necessarily reflect TI's views; see TI's Terms of Use.
TI E2E™ Community
TI's Engineer-to-Engineer (E2E) Community. Created to foster collaboration among engineers. At e2e.ti.com, you can ask questions, share knowledge, explore ideas, and help solve problems with fellow engineers.
TI Embedded Processors Wiki
Texas Instruments Embedded Processors Wiki. Established to help developers get started with embedded processors from Texas Instruments and to foster innovation and growth of general knowledge about the hardware and software surrounding these devices.
8.4 商标
, MSP430, Code Composer Studio, E2E are trademarks of Texas Instruments.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
8.5 静电放电警告

ESD 可能会损坏该集成电路。德州仪器 (TI) 建议通过适当的预防措施处理所有集成电路。如果不遵守正确的处理措施和安装程序 , 可能会损坏集成电路。
ESD 的损坏小至导致微小的性能降级 , 大至整个器件故障。 精密的集成电路可能更容易受到损坏 , 这是因为非常细微的参数更改都可能会导致器件与其发布的规格不相符。