ZHCSJC9G September 2006 – Jaunuary 2020 LM5069
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Application
- 8.2.1
48-V, 10-A Hot Swap Design
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
48-V, 10-A Hot Swap Design
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
8.2.1.2.3 Select Power Limit
In general, a lower-power limit setting is preferred to reduce the stress on the MOSFET. However, when the LM5069 is set to a very low power limit setting, it has to regulate the FET current and hence the voltage across the sense resistor (VSNS) to a very low value. VSNS can be computed as shown in Equation 7.
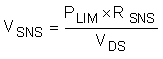
To avoid significant degradation of the power limiting accuracy, a VSNS of less than 5 mV is not recommended. Based on this requirement the minimum allowed power limit can be computed in Equation 8.
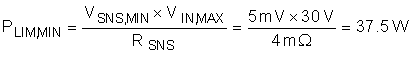
To avoid significant degradation of the power limiting accuracy a VSNS of less than 5 mV is not recommended. Based on this requirement, the minimum allowed power limit can be computed with Equation 9.
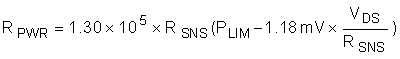
Note that the minimum RPWR would occur when VDS = VIN,MAX. We can then compute the minimum RPWR with Equation 10.
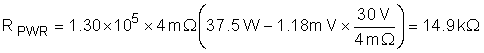
To obtain the smallest accurate power limit, the next largest available resistor must be selected. In this case a 15.8-kΩ resistor was chosen, which sets a 39.23-W power limit.