ZHCSIW9I April 2004 – October 2018 LM5008
PRODUCTION DATA.
7.4.2 Active Mode
LM5008 is in active mode when the internal bias rail, VCC, is above its UV threshold. Depending on the load current, the device operates in either DCM or CCM mode.
Whenever the load current is reduced to a level less than half the peak-to-peak inductor ripple current, the device enters discontinuous conduction mode (DCM). Calculate the critical conduction boundary using Equation 6.
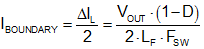
When the inductor current reaches zero, the SW node becomes high impedance. Resonant ringing occurs at SW as a result of the LC tank circuit formed by the buck inductor and the parasitic capacitance at the SW node. At light loads, several pulses may be skipped in between switching cycles, effectively reducing the switching frequency and further improving light-load efficiency.