ZHCSCH4H June 2013 – November 2016 TPS65132
UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED, this document contains PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用范围
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
- 8 Detailed Description
-
9 Application and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Applications
- 9.2.1
Low-current Applications (≤ 40 mA)
- 9.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.1.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.2
Mid-current Applications (≤ 80 mA)
- 9.2.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2.2 Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.3 Application Curves
- 9.2.3 High-current Applications (≤ 150 mA)
- 9.2.1
Low-current Applications (≤ 40 mA)
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
- RVC|20
订购信息
1 特性
- 输入电压范围:2.5V 至 5.5V
- VPOS 升压转换器:
由 4V 转换为 6V(步长为 0.1V) - VNEG 反相降压-升压转换器:
由 -6V 转换为 -4V(步长为 0.1V) - 最大输出电流:
80mA 或 150mA - 出色的综合效率
- > 85%(IOUT > 10mA)
- > 90%(IOUT > 40 mA)
- 性能优异
- 出色的瞬态响应
- 在整个温度范围内保持 1% 的输出电压精度
- I2C 接口
- 可编程上电/掉电
序列选项 - 灵活的输出电压编程
- 可编程有源输出放电
- > 1000x 的可编程非易失性存储器
- 可编程上电/掉电
- 欠压锁定和过热保护
- 两种封装选项
- 15 焊球芯片尺寸封装 (CSP)
- 20 引脚四方扁平无引线 (QFN) 封装
2 应用范围
- 小型、中型双极液晶显示屏 (LCD)
- 智能手机、平板电脑
- 摄像头、全球定位系统 (GPS)
- 家庭自动化、销售点
- 可穿戴设备(智能手表、活动追踪器)
- 通用分离轨电源
- 差分音频、耳机放大器
- 仪表、运算放大器、比较器
- 数模转换器/模数转换器 (DAC/ADC)
3 说明
TPS65132 系列设计用于支持正/负驱动 应用。该器件的两路输出均采用单电感方案,为用户提供尺寸最小的解决方案,在简化物料清单的同时保持高效。该器件可在低噪声条件下提供最佳线路和负载调节能力。凭借 2.5V 至 5.5V 的输入电压范围,该器件针对由单节电池(锂离子电池、锂镍电池和锂聚合物电池)供电的产品以及固定电压为 3.3V 和 5V 的电源轨进行了优化。TPS656132 系列器件提供 80mA 和 150mA 输出电流选项,可通过编程设定为 40mA。提供 CSP 和 QFN 两种封装选项。
器件信息 (1)
| 器件型号 | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|
| TPS65132 -B、-L、-T、-S |
DSBGA (15) | 2.11mm × 1.51mm |
| TPS65132W | WQFN (20) | 4.00mm × 3.00mm |
- 如需了解所有可用封装,请见数据表末尾的可订购产品附录。
空白
空白
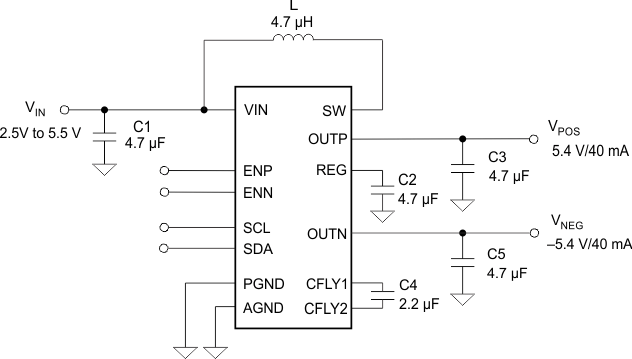
典型应用
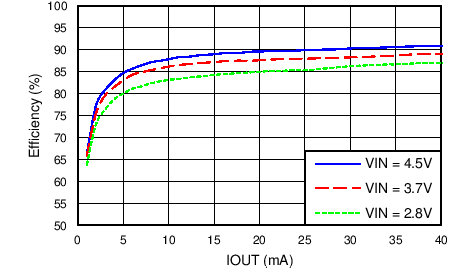
效率与输出电流间的关系