-
TMS570LS31x5/21x5 16- and 32-Bit RISC Flash Microcontroller SPNS164C April 2012 – April 2015 TMS570LS2125 , TMS570LS2135 , TMS570LS2135-S , TMS570LS3135
PRODUCTION DATA.
-
TMS570LS31x5/21x5 16- and 32-Bit RISC Flash Microcontroller
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Device Comparison
-
4Terminal Configuration and Functions
- 4.1 PGE QFP Package Pinout (144-Pin)
- 4.2 ZWT BGA Package Ball-Map (337-Ball Grid Array)
- 4.3
Terminal Functions
- 4.3.1
PGE Package
- 4.3.1.1 Multibuffered Analog-to-Digital Converters (MibADCs)
- 4.3.1.2 Enhanced High-End Timer (N2HET) Modules
- 4.3.1.3 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 4.3.1.4 FlexRay Interface Controller (FlexRay)
- 4.3.1.5 Controller Area Network Controllers (DCANs)
- 4.3.1.6 Local Interconnect Network Interface Module (LIN)
- 4.3.1.7 Standard Serial Communication Interface (SCI)
- 4.3.1.8 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface Module (I2C)
- 4.3.1.9 Standard Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 4.3.1.10 Multibuffered Serial Peripheral Interface Modules (MibSPI)
- 4.3.1.11 System Module Interface
- 4.3.1.12 Clock Inputs and Outputs
- 4.3.1.13 Test and Debug Modules Interface
- 4.3.1.14 Flash Supply and Test Pads
- 4.3.1.15 Supply for Core Logic: 1.2-V Nominal
- 4.3.1.16 Supply for I/O Cells: 3.3-V Nominal
- 4.3.1.17 Ground Reference for All Supplies Except VCCAD
- 4.3.2
ZWT Package
- 4.3.2.1 Multibuffered Analog-to-Digital Converters (MibADCs)
- 4.3.2.2 Enhanced High-End Timer (N2HET) Modules
- 4.3.2.3 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
- 4.3.2.4 FlexRay Interface Controller (FlexRay)
- 4.3.2.5 Controller Area Network Controllers (DCANs)
- 4.3.2.6 Local Interconnect Network Interface Module (LIN)
- 4.3.2.7 Standard Serial Communication Interface (SCI)
- 4.3.2.8 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface Module (I2C)
- 4.3.2.9 Standard Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
- 4.3.2.10 Multibuffered Serial Peripheral Interface Modules (MibSPI)
- 4.3.2.11 External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- 4.3.2.12 Embedded Trace Macrocell for Cortex-R4F CPU (ETM-R4F)
- 4.3.2.13 RAM Trace Port (RTP)
- 4.3.2.14 Data Modification Module (DMM)
- 4.3.2.15 System Module Interface
- 4.3.2.16 Clock Inputs and Outputs
- 4.3.2.17 Test and Debug Modules Interface
- 4.3.2.18 Flash Supply and Test Pads
- 4.3.2.19 No Connects
- 4.3.2.20 Supply for Core Logic: 1.2-V Nominal
- 4.3.2.21 Supply for I/O Cells: 3.3-V Nominal
- 4.3.2.22 Ground Reference for All Supplies Except VCCAD
- 4.3.1
PGE Package
-
5Specifications
- 5.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 5.2 ESD Ratings
- 5.3 Power-On Hours (POH)
- 5.4 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 5.5 Switching Characteristics for Clock Domains
- 5.6 Wait States Required
- 5.7 Power Consumption
- 5.8 Input/Output Electrical Characteristics
- 5.9 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 5.10 Output Buffer Drive Strengths
- 5.11 Input Timings
- 5.12 Output Timings
- 5.13 Low-EMI Output Buffers
-
6System Information and Electrical Specifications
- 6.1 Device Power Domains
- 6.2 Voltage Monitor Characteristics
- 6.3 Power Sequencing and Power On Reset
- 6.4 Warm Reset (nRST)
- 6.5 ARM-R4F CPU Information
- 6.6 Clocks
- 6.7 Clock Monitoring
- 6.8 Glitch Filters
- 6.9 Device Memory Map
- 6.10 Flash Memory
- 6.11 Tightly Coupled RAM (TCRAM) Interface Module
- 6.12 Parity Protection for Peripheral RAMs
- 6.13 On-Chip SRAM Initialization and Testing
- 6.14 External Memory Interface (EMIF)
- 6.15 Vectored Interrupt Manager
- 6.16 DMA Controller
- 6.17 Real Time Interrupt Module
- 6.18 Error Signaling Module
- 6.19 Reset / Abort / Error Sources
- 6.20 Digital Windowed Watchdog
- 6.21
Debug Subsystem
- 6.21.1 Block Diagram
- 6.21.2 Debug Components Memory Map
- 6.21.3 JTAG Identification Code
- 6.21.4 Debug ROM
- 6.21.5 JTAG Scan Interface Timings
- 6.21.6 Advanced JTAG Security Module
- 6.21.7 Embedded Trace Macrocell (ETM-R4)
- 6.21.8 RAM Trace Port (RTP)
- 6.21.9 Data Modification Module (DMM)
- 6.21.10 Boundary Scan Chain
-
7Peripheral Information and Electrical Specifications
- 7.1 Peripheral Legend
- 7.2 Multibuffered 12-Bit Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 7.3 General-Purpose Input/Output
- 7.4 Enhanced High-End Timer (N2HET)
- 7.5 FlexRay Interface
- 7.6 Controller Area Network (DCAN)
- 7.7 Local Interconnect Network Interface (LIN)
- 7.8 Serial Communication Interface (SCI)
- 7.9 Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- 7.10 Multibuffered / Standard Serial Peripheral Interface
- 8Device and Documentation Support
- 9Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
- IMPORTANT NOTICE
TMS570LS31x5/21x5 16- and 32-Bit RISC Flash Microcontroller
1 Device Overview
1.1 Features
- High-Performance Automotive-Grade Microcontroller for Safety-Critical Applications
- Dual CPUs Running in Lockstep
- ECC on Flash and RAM Interfaces
- Built-In Self-Test (BIST) for CPU and On-chip RAMs
- Error Signaling Module With Error Pin
- Voltage and Clock Monitoring
- ARM®Cortex®-R4F 32-Bit RISC CPU
- Efficient 1.66 DMIPS/MHz With 8-Stage Pipeline
- FPU With Single- and Double-Precision
- 12-Region Memory Protection Unit (MPU)
- Open Architecture With Third-Party Support
- Operating Conditions
- System Clock up to 180 MHz
- Core Supply Voltage (VCC): 1.2 V Nominal
- I/O Supply Voltage (VCCIO): 3.3 V Nominal
- ADC Supply Voltage (VCCAD): 3.0 to 5.25 V
- Integrated Memory
- 3MB of Program Flash With ECC (LS3135)
- 2MB of Program Flash With ECC (LS2135/2125)
- 256KB of RAM With ECC (LS3135/2135)
- 192KB of RAM With ECC (LS2125)
- 64KB of Flash With ECC for Emulated EEPROM
- 16-Bit External Memory Interface
- Common Platform Architecture
- Consistent Memory Map Across Family
- Real-Time Interrupt (RTI) Timer OS Timer
- 96-Channel Vectored Interrupt Module (VIM)
- 2-Channel Cyclic Redundancy Checker (CRC)
- Direct Memory Access (DMA) Controller
- 16 Channels and 32 Control Packets
- Parity Protection for Control Packet RAM
- DMA Accesses Protected by Dedicated MPU
- Frequency-Modulated Phase-Locked Loop (FMPLL) With Built-In Slip Detector
- Separate Nonmodulating PLL for FlexRay™
- Trace and Calibration Capabilities
- Embedded Trace Macrocell (ETM-R4)
- Data Modification Module (DMM)
- RAM Trace Port (RTP)
- Parameter Overlay Module (POM)
- Multiple Communication Interfaces
- FlexRay Controller With Two Channels
- 8KB of Message RAM With Parity Protection
- Dedicated Transfer Unit (FTU)
- Three CAN Controllers (DCANs)
- 64 Mailboxes, Each With Parity Protection
- Compliant to CAN Protocol Version 2.0B
- Standard Serial Communication Interface (SCI)
- Local Interconnect Network (LIN) Interface Controller
- Compliant to LIN Protocol Version 2.1
- Can be Configured as a Second SCI
- Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C)
- Three Multibuffered Serial Peripheral Interfaces (MibSPIs)
- 128 Words With Parity Protection Each
- Two Standard Serial Peripheral Interfaces (SPIs)
- FlexRay Controller With Two Channels
-
Two Next Generation High-End Timer (N2HET) Modules
- N2HET1: 32 Programmable Channels
- N2HET2: 18 Programmable Channels
- 160-Word Instruction RAM Each With Parity Protection
- Each N2HET Includes Hardware Angle Generator
- Dedicated High-End Transfer Unit (HTU) With MPU for Each N2HET
- Two 12-Bit Multibuffered ADC Modules
- ADC1: 24 Channels
- ADC2: 16 Channels Shared With ADC1
- 64 Result Buffers With Parity Protection Each
- General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO) Pins Capable of Generating Interrupts
- Sixteen Pins on the ZWT Package
- Four Pins on the PGE Package
- IEEE 1149.1 JTAG, Boundary Scan and ARM CoreSight™ Components
- JTAG Security Module
- Packages
- 144-Pin Quad Flatpack (PGE) [Green]
- 337-Ball Grid Array (ZWT) [Green]
1.2 Applications
- Braking Systems (Antilock Brake Systems and Electronic Stability Control)
- Electric Power Steering
- HEV and EV Inverter Systems
- Battery Management Systems
- Active Driver Assistance Systems
- Aerospace and Avionics
- Railway Communications
- Off-road Vehicles
1.3 Description
The TMS570LS31x5/21x5 device is a high-performance automotive-grade microcontroller family for safety systems. The safety architecture includes dual CPUs in lockstep, CPU and memory BIST logic, ECC on both the flash and the data SRAM, parity on peripheral memories, and loopback capability on peripheral I/Os.
The TMS570LS31x5/21x5 device integrates the ARM Cortex-R4F Floating-Point CPU. The CPU offers an efficient 1.66 DMIPS/MHz, and has configurations that can run up to 180 MHz, providing up to 298 DMIPS. The device supports the word-invariant big-endian [BE32] format.
The TMS570LS3135 device has 3MB of integrated flash and 256KB of data RAM. The TMS570LS2135 device has 2MB of integrated flash and 256KB of data RAM. The TMS570LS2125 device has 2MB of integrated flash and 192KB of data RAM. Both the flash and RAM have single-bit error correction and double-bit error detection. The flash memory on this device is a nonvolatile, electrically erasable, and programmable memory implemented with a 64-bit-wide data bus interface. The flash operates on a 3.3-V supply input (same level as I/O supply) for all read, program, and erase operations. When in pipeline mode, the flash operates with a system clock frequency of up to 180 MHz. The SRAM supports single-cycle read and write accesses in byte, halfword, word, and double-word modes.
The TMS570LS31x5/21x5 device features peripherals for real-time control-based applications, including two Next Generation High-End Timer (N2HET) timing coprocessors and two 12-bit Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) supporting up to 24 inputs.
The N2HET is an advanced intelligent timer that provides sophisticated timing functions for real-time applications. The timer is software-controlled, using a reduced instruction set, with a specialized timer micromachine and an attached I/O port. The N2HET can be used for pulse-width-modulated outputs, capture or compare inputs, or GPIO. The N2HET is especially well suited for applications requiring multiple sensor information and drive actuators with complex and accurate time pulses. A High-End Timer Transfer Unit (HTU) can perform DMA-type transactions to transfer N2HET data to or from main memory. A Memory Protection Unit (MPU) is built into the HTU.
The device has two 12-bit-resolution MibADCs with 24 channels and 64 words of parity-protected buffer RAM each. The MibADC channels can be converted individually or can be grouped by software for sequential conversion sequences. Sixteen channels are shared between the two MibADCs. There are three separate groupings. Each sequence can be converted once when triggered or configured for continuous conversion mode. The MibADC has a 10-bit mode for use when compatibility with older devices or faster conversion time is desired.
The device has multiple communication interfaces: three MibSPIs, two SPIs, one LIN, one SCI, three DCANs, one I2C module, and one FlexRay controller. The SPIs provide a convenient method of serial high-speed communication between similar shift-register type devices. The LIN supports the Local Interconnect standard 2.0 and can be used as a UART in full-duplex mode using the standard Non-Return-to-Zero (NRZ) format.
The DCAN supports the CAN 2.0 (A and B) protocol standard and uses a serial, multimaster communication protocol that efficiently supports distributed real-time control with robust communication rates of up to 1 Mbps. The DCAN is ideal for systems operating in noisy and harsh environments (for example, automotive vehicle networking and industrial fieldbus) that require reliable serial communication or multiplexed wiring.
The FlexRay controller uses a dual-channel serial, fixed time base multimaster communication protocol with communication rates of 10 Mbps per channel. A FlexRay Transfer Unit (FTU) enables autonomous transfers of FlexRay data to and from the CPU main memory. Transfers are protected by a dedicated, built-in MPU.
The I2C module is a multimaster communication module providing an interface between the microcontroller and an I2C-compatible device through the I2C serial bus. The I2C supports speeds of 100 and 400 Kbps.
The Frequency-Modulated Phase-Locked Loop (FMPLL) clock module is used to multiply the external frequency reference to a higher frequency for internal use. There are two FMPLL modules on this device. These modules, when enabled, provide two of the seven possible clock source inputs to the Global Clock Module (GCM). The GCM manages the mapping between the available clock sources and the device clock domains.
The device also has an External Clock Prescaler (ECP) module that when enabled, outputs a continuous external clock on the ECLK pin (or ball). The ECLK frequency is a user-programmable ratio of the peripheral interface clock (VCLK) frequency. This low-frequency output can be monitored externally as an indicator of the device operating frequency.
The DMA controller has 16 channels, 32 control packets, and parity protection on its memory. An MPU is built into the DMA to limit the DMA to prescribed areas of memory and to protect the rest of the memory system from any malfunction of the DMA.
The Error Signaling Module (ESM) monitors all device errors and determines whether an interrupt is generated or the external ERROR pin is toggled when a fault is detected. The ERROR pin can be monitored externally as an indicator of a fault condition in the microcontroller.
The External Memory Interface (EMIF) provides off-chip expansion capability with the ability to interface to synchronous DRAM (SDRAM) devices, asynchronous memories, peripherals or FPGA devices.
Several interfaces are implemented to enhance the debugging capabilities of application code. In addition to the built-in ARM Cortex-R4F CoreSight debug features, an External Trace Macrocell (ETM) provides instruction and data trace of program execution. For instrumentation purposes, a RAM Trace Port (RTP) module is implemented to support high-speed tracing of RAM and peripheral accesses by the CPU or any other master. A Data Modification Module (DMM) gives the ability to write external data into the device memory. Both the RTP and DMM have no or only minimum impact on the program execution time of the application code. A Parameter Overlay Module (POM) can reroute flash accesses to internal memory or to the EMIF. This rerouting allows the dynamic calibration against production code of parameters and tables without rebuilding the code to explicitly access RAM or halting the processor to reprogram the data flash.
With integrated safety features and a wide choice of communication and control peripherals, the TMS570LS31x5/21x5 device is an ideal solution for high-performance real-time control applications with safety-critical requirements.
Device Information(1)
| PART NUMBER | PACKAGE | BODY SIZE |
|---|---|---|
| TMS570LS2125ZWT | NFBGA (337) | 16.0 mm × 16.0 mm |
| TMS570LS2125PGE | LQFP (144) | 20.0 mm × 20.0 mm |
| TMS570LS2135ZWT | NFBGA (337) | 16.0 mm × 16.0 mm |
| TMS570LS2135PGE | LQFP (144) | 20.0 mm × 20.0 mm |
| TMS570LS3135ZWT | NFBGA (337) | 16.0 mm × 16.0 mm |
| TMS570LS3135PGE | LQFP (144) | 20.0 mm × 20.0 mm |
1.4 Functional Block Diagram
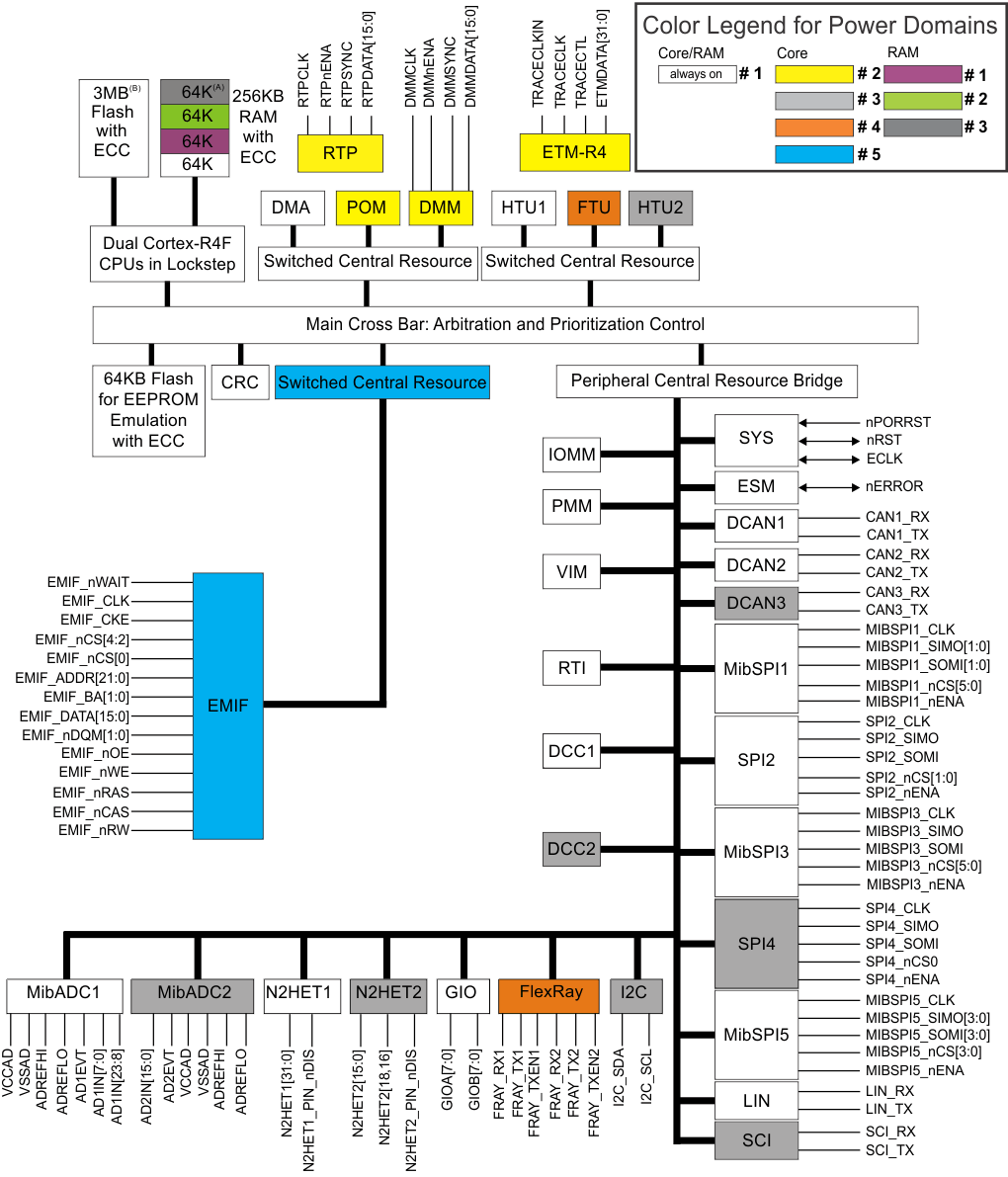
2 Revision History
This data manual revision history highlights the technical changes made to the SPNS164B device-specific data manual to make it an SPNS164C revision.
Scope: Applicable updates to the Hercules™ TMS570 MCU device family, specifically relating to the TMS570LS31x5/21x5 devices, which are now in the production data (PD) stage of development have been incorporated.
Changes from August 1, 2013 to April 30, 2015 (from B Revision (July 2013) to C Revision)
- Section 1 (Device Overview): Updated/Changed section title Go
- Updated/Changed the N2HET featureGo
- (Device Information): Added tableGo
- Added Section 3, Device ComparisonGo
- Section 4 (Terminal Configuration and Functions): Updated/Changed section titleGo
- Table 4-2 (PGE Enhanced High-End Timer Modules (N2HET1, N2HET2)): Updated/Changed N2HET1 time input capture or output compare pin descriptionGo
- Table 4-2: Added N2HET1_PIN_nDIS signal DESCRIPTIONGo
- Table 4-2: Updated/Changed N2HET2 time input capture or output compare pin descriptionGo
- Table 4-2: Added N2HET2_PIN_nDIS signal DESCRIPTIONGo
- Table 4-3 Updated description about using GIOB[2] on pin 55 Go
- Table 4-13 (PGE Test and Debug Modules Interface): Updated/Changed TEST pin descriptionGo
- Table 4-19 (ZWT Enhanced High-End Timer (N2HET) Modules): Updated/Changed N2HET1 time input capture or output compare pin descriptionGo
- Table 4-19 Added alternate terminals for N2HET1 pins 17, 19, 21, 23, 25, 27, 29 and 31Go
- Table 4-19: Added N2HET1_PIN_nDIS signal DESCRIPTIONGo
- Table 4-19: Updated/Changed N2HET2 time input capture or output compare pin descriptionGo
- Table 4-19: Added N2HET2_PIN_nDIS signal DESCRIPTIONGo
- Table 4-20 Updated description about using GIOB[2] on ball V10Go
- Table 4-28 (External Memory Interface (EMIF)): Global: Deleted EMIF_RNW pin function.Go
- Table 4-34 (ZWT Test and Debug Modules Interface): Updated/Changed TEST pin descriptionGo
- Table 4-36 (No Connects): Deleted NC pins A8, B8, and B9; supported on FlexRay Interface ControllerGo
- Section 5 (Specifications): Updated/Changed section titleGo
- Section 5.1 (Absolute Maximum Ratings): Reformatted tableGo
- Section 5.1 (Absolute Maximum Ratings): Updated/Changed VCCAD supply voltage range MAX value from "5.5" to "6.25" VGo
- Section 5.1: Updated/Changed ADC input pins input voltage range MAX value from "5.5" to "6.25" VGo
- Section 5.2 (ESD Ratings): Added table (new)Go
- Section 5.3 (Power-On Hours (POH)): Added table (new)Go
- Section 5.8 (Input/Output Electrical Characteristics): Updated/Changed Input Clamp Current from IIC to IIKGo
- Section 5.9 (Thermal Resistance Characteristics): Moved section and updated/changed subsection title.Go
- Table 5-2 (Thermal Resistance Characteristics (PGE Package)): Added test conditions and added ΨJT row for PGE packageGo
- Table 5-3 (Thermal Resistance Characteristics (ZWT Package)): Added test conditions and added ΨJT row for ZWT packageGo
- Clarified impact of SPI2PC9 register on drive strength of SPI2SOMI pin Go
- Updated/Changed the MIN value of tv(RST) to 2256tc(OSC) ns Go
- Section 6.6.1 (Clock Sources): Added Table 6-8, Available Clock Source cross-referencesGo
- Section 6.6.1.1 (Main Oscillator): Added Figure 6-4, Recommended Crystal/Clock Connection cross-referenceGo
- Table 6-10 Added limits for HF LPO after software trim Go
- Table 6-13 (Clock Domain Descriptions): Added missing "1" to the VCLKACON clock source selection register name for VCLKA3 rowGo
- Section 6.9.1 Added addititional device-specific memory mapGo
- Table 6-20 Corrected size of bank 7 OTP and bank 7 OTP ECCGo
- Figure 6-12 (TCRAM Block Diagram): Updated/Changed figure, deleted A TCMGo
- Table 6-25 Added table footnotes identifying the address ranges of the ESRAM PBIST groupsGo
- Table 6-25 Added RAM power domain information in the table notesGo
- Table 6-26(Memory Initialization): Updated/Changed N2HET2 RAM ending address from "0xFF57FFFF" to "0xFF45FFFF"Go
- Table 6-38 Corrected base JTAG ID Base Value From 0xnD8A002F to 0xnB8A002FGo
- Table 6-38 (JTAG ID Code): Added JTAG Identification Code for Silicon Revision "Rev D" Go
- Table 7-7 (MibADC Recommended Operating Conditions): Updated/Changed Analog input clamp current from IAIC to IAIKGo
- FlexRay Interface, Section 7.5.1 (Features): Updated/Changed "8KB of message ..." bullet for clarificationGo
- Controller Area Network (DCAN) Section 7.6.1 (Features): Updated/Changed TRM references to the correct document titles Go
- Table 7-24 (SPI Master Mode External Timing Parameters (CLOCK PHASE = 0, SPICLK = output, SPISIMO = output, and SPISOMI = input)): Updated/Changed table footnote to "... CLOCK PHASE bit (SPIFMTx.16) is cleared"Go
- Section 8 (Device and Documentation Support): Updated/Changed section to meet new requirements, including addition of several subsectionsGo
- Section 8.8 (Device Identification Code Register): Added Device ID code value for silicon Rev DGo
- Section 8.9 (Die Identification Registers): Updated/Changed the address of the two die identification registers (DIEIDL and DIEIDH) to point to the original registers at location 0xFFFFFF7C and 0xFFFFFF80 for this section.Go
- Table 8-3 (Die-ID Registers): Updated/Changed the BIT LOCATION column for all ITEM rowsGo
- Section 9 (Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information): Updated/Changed section titleGo
- Section 9.1 (Packaging Information): Updated/Changed the paragraphGo
3 Device Comparison
Table 3-1 lists the features of the TMS570LS2125/LS2135/LS3135 devices.
Table 3-1 TMS570LS2125, LS2135, LS3135 Device Comparison(2)(3)
| FEATURES | DEVICES | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Generic Part Number | TMS570LC4357ZWT(1) | TMS570LS3137ZWT(1) | TMS570LS3135ZWT | TMS570LS3135PGE | TMS570LS2135ZWT | TMS570LS2135PGE | TMS570LS2125ZWT | TMS570LS2125PGE | TMS570LS1227ZWT(1) |
| Package | 337 BGA | 337 BGA | 337 BGA | 144 QFP | 337 BGA | 144 QFP | 337 BGA | 144 QFP | 337 BGA |
| CPU | ARM Cortex-R5F | ARM Cortex-R4F | ARM Cortex-R4F | ARM Cortex-R4F | ARM Cortex-R4F | ARM Cortex-R4F | ARM Cortex-R4F | ARM Cortex-R4F | ARM Cortex-R4F |
| Frequency (MHz) | 300 | 180 | 180 | 160 | 180 | 160 | 180 | 160 | 180 |
| Cache (KB) | 32 I 32 D |
– | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| Flash (KB) | 4096 | 3072 | 3072 | 3072 | 2048 | 2048 | 2048 | 2048 | 1280 |
| RAM (KB) | 512 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 256 | 192 | 192 | 192 |
| Data Flash [EEPROM] (KB) | 128 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 64 | 64 |
| EMAC | 10/100 | 10/100 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 10/100 |
| FlexRay | 2-ch | 2-ch | 2-ch | 2-ch | 2-ch | 2-ch | 2-ch | 2-ch | 2-ch |
| CAN | 4 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| MibADC 12-bit (Ch) |
2 (41ch) | 2 (24ch) | 2 (24ch) | 2 (24ch) | 2 (24ch) | 2 (24ch) | 2 (24ch) | 2 (24ch) | 2 (24ch) |
| N2HET (Ch) | 2 (64) | 2 (44) | 2 (50) | 2 (50) | 2 (44) | 2 (40) | 2 (44) | 2 (40) | 2 (44) |
| ePWM Channels | 14 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 14 |
| eCAP Channels | 6 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 6 |
| eQEP Channels | 2 | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | 2 |
| MibSPI (CS) | 5 (4 x 6 + 2) | 3 (6 + 6 + 4) | 3 (6 + 6 + 4) | 3 (5 + 6 + 1) | 3 (6 + 6 + 4) | 3 (5 + 6 + 1) | 3 (6 + 6 + 4) | 3 (5 + 6 + 1) | 3 (6 + 6 + 4) |
| SPI (CS) | – | 2 (2 + 1) | 2 (2 + 1) | 1 (1) | 2 (2 + 1) | 1 (1) | 2 (2 + 1) | 1 (1) | 2 (2 + 1) |
| SCI (LIN) | 4 (2 with LIN) | 2 (1 with LIN) | 2 (1 with LIN) | 2 (1 with LIN) | 2 (1 with LIN) | 2 (1 with LIN) | 2 (1 with LIN) | 2 (1 with LIN) | 2 (1 with LIN) |
| I2C | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| GPIO (INT)(4) | 168 (with 16 interrupt capable) | 144 (with 16 interrupt capable) | 144 (with 16 interrupt capable) | 58 (with 4 interrupt capable) | 144 (with 16 interrupt capable) | 58 (with 4 interrupt capable) | 144 (with 16 interrupt capable) | 58 (with 4 interrupt capable) | 101 (with 16 interrupt capable) |
| EMIF | 16-bit data | 16-bit data | 16-bit data | – | 16-bit data | – | 16-bit data | – | 16-bit data |
| ETM (Trace) | 32-bit | 32-bit | 32-bit | – | 32-bit | – | 32-bit | – | – |
| RTP/DMM | 16/16 | 16/16 | 16/16 | – | 16/16 | – | 16/16 | – | – |
| Operating Temperature |
-40ºC to 125ºC | -40ºC to 125ºC | -40ºC to 125ºC | -40ºC to 125ºC | -40ºC to 125ºC | -40ºC to 125ºC | -40ºC to 125ºC | -40ºC to 125ºC | -40ºC to 125ºC |
| Core Supply (V) | 1.14 V – 1.32 V | 1.14 V – 1.32 V | 1.14 V – 1.32 V | 1.14 V – 1.32 V | 1.14 V – 1.32 V | 1.14 V – 1.32 V | 1.14 V – 1.32 V | 1.14 V – 1.32 V | 1.14 V – 1.32 V |
| I/O Supply (V) | 3.0 V – 3.6 V | 3.0 V – 3.6 V | 3.0 V – 3.6 V | 3.0 V – 3.6 V | 3.0 V – 3.6 V | 3.0 V – 3.6 V | 3.0 V – 3.6 V | 3.0 V – 3.6 V | 3.0 V – 3.6 V |
4 Terminal Configuration and Functions
4.1 PGE QFP Package Pinout (144-Pin)
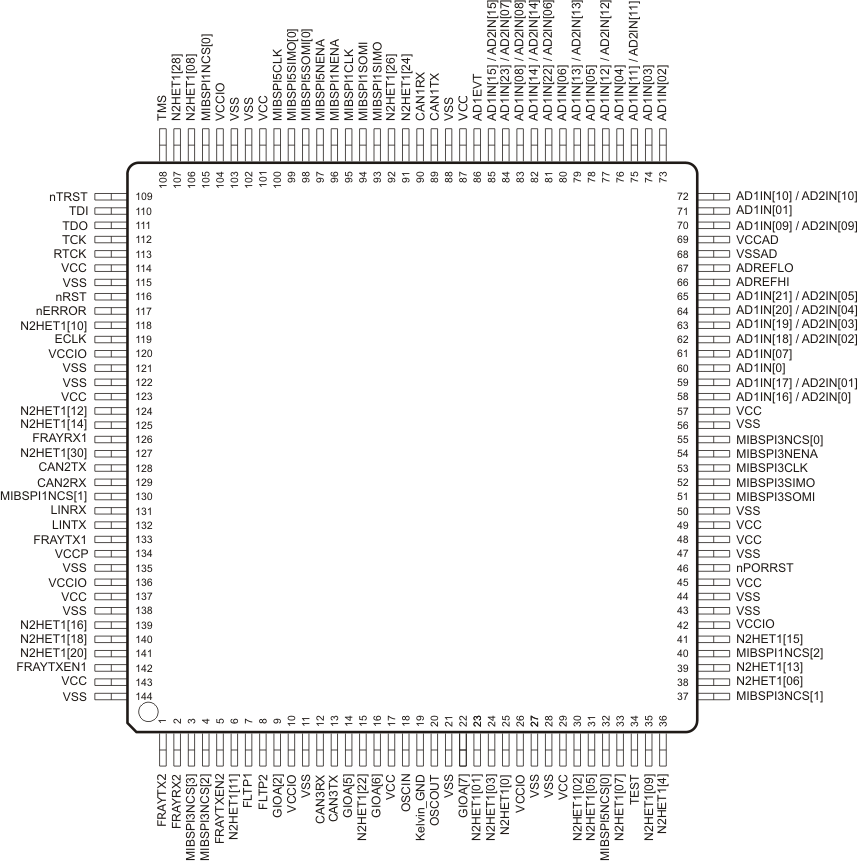
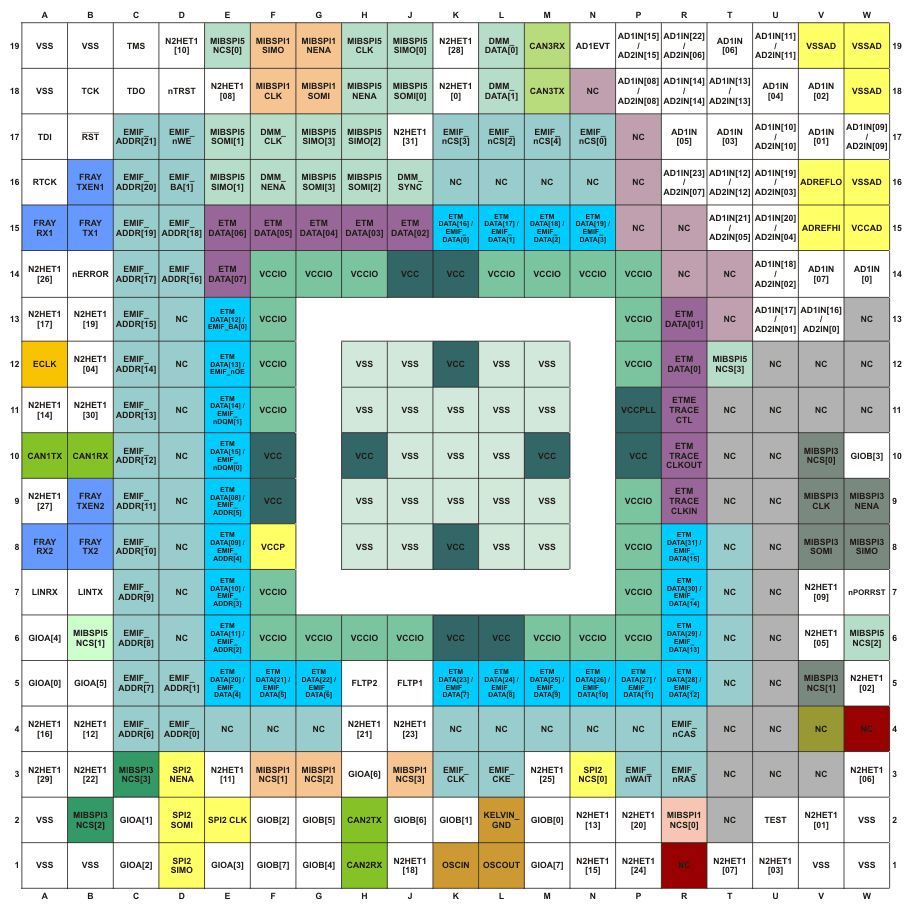
4.2 ZWT BGA Package Ball-Map (337-Ball Grid Array)
4.3 Terminal Functions
Section 4.3.1 and Section 4.3.2identify the external signal names, the associated pin or ball numbers along with the mechanical package designator, the pin or ball type (Input, Output, I/O, Power, or Ground), whether the pin or ball has any internal pullup or pulldown, whether the pin or ball can be configured as a GPIO, and a functional pin or ball description. The first signal name listed is the primary function for that terminal. The signal name in bold is the function being described. For information on how to select between different multiplexed functions, see the TMS570LS31x/21x 16/32-Bit RISC Flash Microcontroller Technical Reference Manual (SPNU499) .
NOTE
In the Terminal Functions table below, the "Reset Pull State" is the state of the pull applied to the terminal while nPORRST is low and immediately after nPORRST goes High. The default pull direction may change when software configures the pin for an alternate function. The "Pull Type" is the type of pull asserted when the signal name in bold is enabled for the given terminal by the IOMM control registers.
All I/O signals except nRST are configured as inputs while nPORRST is low and immediately after nPORRST goes High. While nPORRST is low, the input buffers are disabled, and the output buffers are disabled with the default pulls enabled.
All output-only signals have the output buffer disabled and the default pull enabled while nPORRST is low, and are configured as outputs with the pulls disabled immediately after nPORRST goes High.
4.3.1 PGE Package
4.3.1.1 Multibuffered Analog-to-Digital Converters (MibADCs)
Table 4-1 PGE Multibuffered Analog-to-Digital Converters (MibADC1, MibADC2)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 144 PGE | ||||
| ADREFHI(1) | 66 | Input | N/A | None | ADC high reference supply |
| ADREFLO(1) | 67 | Input | ADC low reference supply | ||
| VCCAD(1) | 69 | Power | Operating supply for ADC | ||
| VSSAD(1) | 68 | Ground | |||
| AD1EVT | 86 | I/O | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | ADC1 event trigger input, or GPIO |
| MIBSPI3NCS[0]/AD2EVT/GIOB[2]/N2HET2_PIN_nDIS | 55 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | ADC2 event trigger input, or GPIO |
| AD1IN[0] | 60 | Input | N/A | None | ADC1 analog input |
| AD1IN[1] | 71 | ||||
| AD1IN[2] | 73 | ||||
| AD1IN[3] | 74 | ||||
| AD1IN[4] | 76 | ||||
| AD1IN[5] | 78 | ||||
| AD1IN[6] | 80 | ||||
| AD1IN[7] | 61 | ||||
| AD1IN[8] / AD2IN[8] | 83 | Input | N/A | None | ADC1/ADC2 shared analog inputs |
| AD1IN[9] / AD2IN[9] | 70 | ||||
| AD1IN[10] / AD2IN[10] | 72 | ||||
| AD1IN[11] / AD2IN[11] | 75 | ||||
| AD1IN[12] / AD2IN[12] | 77 | ||||
| AD1IN[13] / AD2IN[13] | 79 | ||||
| AD1IN[14] / AD2IN[14] | 82 | ||||
| AD1IN[15] / AD2IN[15] | 85 | ||||
| AD1IN[16] / AD2IN[0] | 58 | ||||
| AD1IN[17] / AD2IN[1] | 59 | ||||
| AD1IN[18] / AD2IN[2] | 62 | ||||
| AD1IN[19] / AD2IN[3] | 63 | ||||
| AD1IN[20] / AD2IN[4] | 64 | ||||
| AD1IN[21] / AD2IN[5] | 65 | ||||
| AD1IN[22] / AD2IN[6] | 81 | ||||
| AD1IN[23] / AD2IN[7] | 84 | ||||
4.3.1.2 Enhanced High-End Timer (N2HET) Modules
Table 4-2 PGE Enhanced High-End Timer Modules (N2HET1, N2HET2)
4.3.1.3 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
Table 4-3 PGE General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
4.3.1.4 FlexRay Interface Controller (FlexRay)
Table 4-4 FlexRay Interface Controller (FlexRay)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 144 PGE | ||||
| FRAYRX1 | 126 | Input | Pullup | Fixed 100 µA Pullup |
FlexRay data receive (channel 1) |
| FRAYTX1 | 133 | Output | N/A | None | FlexRay data transmit (channel 1) |
| FRAYTXEN1 | 142 | Output | FlexRay transmit enable (channel 1) | ||
| FRAYRX2 | 2 | Input | Pullup | Fixed 100 µA Pullup |
FlexRay data receive (channel 2) |
| FRAYTX2 | 1 | Output | N/A | None | FlexRay data transmit (channel 2) |
| FRAYTXEN2 | 5 | Output | FlexRay transmit enable (channel 2) | ||
4.3.1.5 Controller Area Network Controllers (DCANs)
Table 4-5 PGE Controller Area Network Controllers (DCAN)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 144 PGE | ||||
| CAN1RX | 90 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | CAN1 receive, or GPIO |
| CAN1TX | 89 | CAN1 transmit, or GPIO | |||
| CAN2RX | 129 | CAN2 receive, or GPIO | |||
| CAN2TX | 128 | CAN2 transmit, or GPIO | |||
| CAN3RX | 12 | CAN3 receive, or GPIO | |||
| CAN3TX | 13 | CAN3 transmit, or GPIO | |||
4.3.1.6 Local Interconnect Network Interface Module (LIN)
Table 4-6 PGE Local Interconnect Network Interface Module (LIN)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 144 PGE | ||||
| LINRX | 131 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | LIN receive, or GPIO |
| LINTX | 132 | LIN transmit, or GPIO | |||
4.3.1.7 Standard Serial Communication Interface (SCI)
Table 4-7 PGE Standard Serial Communication Interface (SCI)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 144 PGE | ||||
| N2HET1[6]/SCIRX | 38 | I/O | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | SCI receive, or GPIO |
| N2HET1[13]/SCITX | 39 | SCI transmit, or GPIO | |||
4.3.1.8 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface Module (I2C)
Table 4-8 PGE Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface Module (I2C)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 144 PGE | ||||
| MIBSPI3NCS[2]/I2C_SDA/N2HET1[27] | 4 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | I2C serial data, or GPIO |
| MIBSPI3NCS[3]/I2C_SCL/N2HET1[29] | 3 | I2C serial clock, or GPIO | |||
4.3.1.9 Standard Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
Table 4-9 PGE Standard Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 144 PGE | ||||
| N2HET1[0]/SPI4CLK | 25 | I/O | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | SPI4 clock, or GPIO |
| N2HET1[3]/SPI4NCS[0]/N2HET2[10] | 24 | SPI4 chip select, or GPIO | |||
| N2HET1[1]/SPI4NENA/N2HET2[8] | 23 | SPI4 enable, or GPIO | |||
| N2HET1[2]/SPI4SIMO[0] | 30 | SPI4 slave-input master-output, or GPIO | |||
| N2HET1[5]/SPI4SOMI[0]/N2HET2[12] | 31 | SPI4 slave-output master-input, or GPIO | |||
4.3.1.10 Multibuffered Serial Peripheral Interface Modules (MibSPI)
Table 4-10 PGE Multibuffered Serial Peripheral Interface Modules (MibSPI)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 144 PGE | ||||
| MIBSPI1CLK | 95 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI1 clock, or GPIO |
| MIBSPI1NCS[0]/MIBSPI1SOMI[1] | 105 | MibSPI1 chip select, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI1NCS[1]/N2HET1[17] | 130 | ||||
| MIBSPI1NCS[2]/N2HET1[19] | 40 | ||||
| N2HET1[15]/MIBSPI1NCS[4] | 41 | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI1 chip select, or GPIO | |
| N2HET1[24]/MIBSPI1NCS[5] | 91 | ||||
| MIBSPI1NENA/N2HET1[23] | 96 | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI1 enable, or GPIO | |
| MIBSPI1SIMO[0] | 93 | MibSPI1 slave-in master-out, or GPIO | |||
| N2HET1[8]/MIBSPI1SIMO[1] | 106 | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI1 slave-in master-out, or GPIO | |
| MIBSPI1SOMI[0] | 94 | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI1 slave-out master-in, or GPIO | |
| MIBSPI1NCS[0]/MIBSPI1SOMI[1] | 105 | ||||
| MIBSPI3CLK | 53 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI3 clock, or GPIO |
| MIBSPI3NCS[0]/AD2EVT/GIOB[2]/N2HET2_PIN_nDIS | 55 | MibSPI3 chip select, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI3NCS[1]/N2HET1[25]/MDCLK | 37 | ||||
| MIBSPI3NCS[2]/I2C_SDA/N2HET1[27] | 4 | ||||
| MIBSPI3NCS[3]/I2C_SCL/N2HET1[29] | 3 | ||||
| N2HET1[11]/MIBSPI3NCS[4]/N2HET2[18] | 6 | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI3 chip select, or GPIO | |
| MIBSPI3NENA /MIBSPI3NCS[5]/N2HET1[31] | 54 | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI3 chip select, or GPIO | |
| MIBSPI3NENA/MIBSPI3NCS[5]/N2HET1[31] | 54 | MibSPI3 enable, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI3SIMO[0] | 52 | MibSPI3 slave-in master-out, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI3SOMI[0] | 51 | MibSPI3 slave-out master-in, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI5CLK | 100 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI5 clock, or GPIO |
| MIBSPI5NCS[0] | 32 | MibSPI5 chip select, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI5NENA | 97 | MibSPI5 enable, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI5SIMO[0] | 99 | MibSPI5 slave-in master-out, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI5SOMI[0] | 98 | MibSPI5 slave-out master-in, or GPIO | |||
4.3.1.11 System Module Interface
Table 4-11 PGE System Module Interface
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 144 PGE | ||||
| nPORRST | 46 | Input | Pulldown | Fixed 100 µA Pulldown |
Power-on reset, cold reset External power supply monitor circuitry must drive nPORRST low when any of the supplies to the microcontroller fall out of the specified range. This terminal has a glitch filter. See Section 6.8. |
| nRST | 116 | I/O | Pullup | Fixed 100 µA Pullup |
System reset, warm reset, bidirectional. The internal circuitry indicates any reset condition by driving nRST low. The external circuitry can assert a system reset by driving nRST low. To ensure that an external reset is not arbitrarily generated, TI recommends that an external pullup resistor is connected to this terminal. This terminal has a glitch filter. See Section 6.8. |
| nERROR | 117 | I/O | Pulldown | Fixed 20 µA Pulldown |
ESM Error Signal Indicates error of high severity. See Section 6.18. |
4.3.1.12 Clock Inputs and Outputs
Table 4-12 PGE Clock Inputs and Outputs
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 144 PGE | ||||
| OSCIN | 18 | Input | N/A | None | From external crystal/resonator, or external clock input |
| KELVIN_GND | 19 | Input | Kelvin ground for oscillator | ||
| OSCOUT | 20 | Output | To external crystal/resonator | ||
| ECLK | 119 | I/O | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | External prescaled clock output, or GIO. |
| GIOA[5]/EXTCLKIN/N2HET1_PIN_nDIS | 14 | Input | Pulldown | 20 µA | External clock input #1 |
4.3.1.13 Test and Debug Modules Interface
Table 4-13 PGE Test and Debug Modules Interface
4.3.1.14 Flash Supply and Test Pads
Table 4-14 PGE Flash Supply and Test Pads
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 144 PGE | ||||
| VCCP | 134 | 3.3-V Power | N/A | None | Flash pump supply |
| FLTP1 | 7 | N/A | None | Flash test pads. These terminals are reserved for TI use only. For proper operation these terminals must connect only to a test pad or not be connected at all [no connect (NC)]. | |
| FLTP2 | 8 | ||||
4.3.1.15 Supply for Core Logic: 1.2-V Nominal
Table 4-15 PGE Supply for Core Logic: 1.2-V Nominal
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 144 PGE | ||||
| VCC | 17 | 1.2-V Power | N/A | None | 1.2-V Core supply |
| VCC | 29 | ||||
| VCC | 45 | ||||
| VCC | 48 | ||||
| VCC | 49 | ||||
| VCC | 57 | ||||
| VCC | 87 | ||||
| VCC | 101 | ||||
| VCC | 114 | ||||
| VCC | 123 | ||||
| VCC | 137 | ||||
| VCC | 143 | ||||
4.3.1.16 Supply for I/O Cells: 3.3-V Nominal
Table 4-16 PGE Supply for I/O Cells: 3.3-V Nominal
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 144 PGE | ||||
| VCCIO | 10 | 3.3-V Power | N/A | None | 3.3-V Operating supply for I/Os |
| VCCIO | 26 | ||||
| VCCIO | 42 | ||||
| VCCIO | 104 | ||||
| VCCIO | 120 | ||||
| VCCIO | 136 | ||||
4.3.1.17 Ground Reference for All Supplies Except VCCAD
Table 4-17 PGE Ground Reference for All Supplies Except VCCAD
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 144 PGE | ||||
| VSS | 11 | Ground | N/A | None | Ground reference |
| VSS | 21 | ||||
| VSS | 27 | ||||
| VSS | 28 | ||||
| VSS | 43 | ||||
| VSS | 44 | ||||
| VSS | 47 | ||||
| VSS | 50 | ||||
| VSS | 56 | ||||
| VSS | 88 | ||||
| VSS | 102 | ||||
| VSS | 103 | ||||
| VSS | 115 | ||||
| VSS | 121 | ||||
| VSS | 122 | ||||
| VSS | 135 | ||||
| VSS | 138 | ||||
| VSS | 144 | ||||
4.3.2 ZWT Package
4.3.2.1 Multibuffered Analog-to-Digital Converters (MibADCs)
Table 4-18 ZWT Multibuffered Analog-to-Digital Converters (MibADC1, MibADC2)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| ADREFHI(1) | V15 | Input | N/A | None | ADC high reference supply |
| ADREFLO(1) | V16 | Input | ADC low reference supply | ||
| VCCAD(1) | W15 | Power | Operating supply for ADC | ||
| VSSAD | V19 | Ground | N/A | None | ADC supply power |
| VSSAD | W16 | ||||
| VSSAD | W18 | ||||
| VSSAD | W19 | ||||
| AD1EVT | N19 | I/O | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | ADC1 event trigger input, or GPIO |
| MIBSPI3NCS[0]/AD2EVT/GIOB[2]/N2HET2_PIN_nDIS | V10 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | ADC2 event trigger input, or GPIO |
| AD1IN[0] | W14 | Input | N/A | None | ADC1 analog input |
| AD1IN[1] | V17 | ||||
| AD1IN[2] | V18 | ||||
| AD1IN[3] | T17 | ||||
| AD1IN[4] | U18 | ||||
| AD1IN[5] | R17 | ||||
| AD1IN[6] | T19 | ||||
| AD1IN[7] | V14 | ||||
| AD1IN[8] / AD2IN[8] | P18 | Input | N/A | None | ADC1/ADC2 shared analog inputs |
| AD1IN[9] / AD2IN[9] | W17 | ||||
| AD1IN[10] / AD2IN[10] | U17 | ||||
| AD1IN[11] / AD2IN[11] | U19 | ||||
| AD1IN[12] / AD2IN[12] | T16 | ||||
| AD1IN[13] / AD2IN[13] | T18 | ||||
| AD1IN[14] / AD2IN[14] | R18 | ||||
| AD1IN[15] / AD2IN[15] | P19 | ||||
| AD1IN[16] / AD2IN[0] | V13 | ||||
| AD1IN[17] / AD2IN[1] | U13 | ||||
| AD1IN[18] / AD2IN[2] | U14 | ||||
| AD1IN[19] / AD2IN[3] | U16 | ||||
| AD1IN[20] / AD2IN[4] | U15 | ||||
| AD1IN[21] / AD2IN[5] | T15 | ||||
| AD1IN[22] / AD2IN[6] | R19 | ||||
| AD1IN[23] / AD2IN[7] | R16 | ||||
4.3.2.2 Enhanced High-End Timer (N2HET) Modules
Table 4-19 ZWT Enhanced High-End Timer (N2HET) Modules
4.3.2.3 General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
Table 4-20 ZWT General-Purpose Input/Output (GPIO)
4.3.2.4 FlexRay Interface Controller (FlexRay)
Table 4-21 FlexRay Interface Controller (FlexRay)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| FRAYRX1 | A15 | Input | Pullup | Fixed 100 µA Pullup |
FlexRay data receive (channel 1) |
| FRAYTX1 | B15 | Output | None | None | FlexRay data transmit (channel 1) |
| FRAYTXEN1 | B16 | Output | FlexRay transmit enable (channel 1) | ||
| FRAYRX2 | A8 | Input | Pullup | Fixed 100 µA Pullup |
FlexRay data receive (channel 2) |
| FRAYTX2 | B8 | Output | None | None | FlexRay data transmit (channel 2) |
| FRAYTXEN2 | B9 | Output | FlexRay transmit enable (channel 2) | ||
4.3.2.5 Controller Area Network Controllers (DCANs)
Table 4-22 ZWT Controller Area Network Controllers (DCANs)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| CAN1RX | B10 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | CAN1 receive, or GPIO |
| CAN1TX | A10 | CAN1 transmit, or GPIO | |||
| CAN2RX | H1 | CAN2 receive, or GPIO | |||
| CAN2TX | H2 | CAN2 transmit, or GPIO | |||
| CAN3RX | M19 | CAN3 receive, or GPIO | |||
| CAN3TX | M18 | CAN3 transmit, or GPIO | |||
4.3.2.6 Local Interconnect Network Interface Module (LIN)
Table 4-23 ZWT Local Interconnect Network Interface Module (LIN)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| LINRX | A7 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | LIN receive, or GPIO |
| LINTX | B7 | LIN transmit, or GPIO | |||
4.3.2.7 Standard Serial Communication Interface (SCI)
Table 4-24 ZWT Standard Serial Communication Interface (SCI)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| N2HET1[6]/SCIRX | W3 | I/O | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | SCI receive, or GPIO |
| N2HET1[13]/SCITX | N2 | SCI transmit, or GPIO | |||
4.3.2.8 Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface Module (I2C)
Table 4-25 ZWT Inter-Integrated Circuit Interface Module (I2C)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| MIBSPI3NCS[2]/I2C_SDA/N2HET1[27] | B2 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | I2C serial data, or GPIO |
| MIBSPI3NCS[3]/I2C_SCL/N2HET1[29] | C3 | I2C serial clock, or GPIO | |||
4.3.2.9 Standard Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
Table 4-26 ZWT Standard Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| SPI2CLK | E2 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | SPI2 clock, or GPIO |
| SPI2NCS[0] | N3 | SPI2 chip select, or GPIO | |||
| SPI2NENA/SPI2NCS[1] | D3 | SPI2 chip select, or GPIO | |||
| SPI2NENA/SPI2NCS[1] | D3 | SPI2 enable, or GPIO | |||
| SPI2SIMO[0] | D1 | SPI2 slave-input master-output, or GPIO | |||
| SPI2SOMI[0] | D2 | SPI2 slave-output master-input, or GPIO | |||
| N2HET1[0]/SPI4CLK | K18 | I/O | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | SPI4 clock, or GPIO |
| N2HET1[3]/SPI4NCS[0]/N2HET2[10] | U1 | SPI4 chip select, or GPIO | |||
| N2HET1[1]/SPI4NENA/N2HET2[8] | V2 | SPI4 enable, or GPIO | |||
| N2HET1[2]/SPI4SIMO[0] | W5 | SPI4 slave-input master-output, or GPIO | |||
| N2HET1[5]/SPI4SOMI[0]/N2HET2[12] | V6 | SPI4 slave-output master-input, or GPIO | |||
4.3.2.10 Multibuffered Serial Peripheral Interface Modules (MibSPI)
Table 4-27 ZWT Multibuffered Serial Peripheral Interface Modules (MibSPI)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| MIBSPI1CLK | F18 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI1 clock, or GPIO |
| MIBSPI1NCS[0]/MIBSPI1SOMI[1] | R2 | MibSPI1 chip select, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI1NCS[1]/N2HET1[17] | F3 | ||||
| MIBSPI1NCS[2]/N2HET1[19] | G3 | ||||
| MIBSPI1NCS[3]/N2HET1[21] | J3 | ||||
| N2HET1[15]/MIBSPI1NCS[4] | N1 | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI1 chip select, or GPIO | |
| N2HET1[24]/MIBSPI1NCS[5] | P1 | ||||
| MIBSPI1NENA/N2HET1[23] | G19 | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI1 enable, or GPIO | |
| MIBSPI1SIMO[0] | F19 | MibSPI1 slave-in master-out, or GPIO | |||
| N2HET1[8]/MIBSPI1SIMO[1] | E18 | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI1 slave-in master-out, or GPIO | |
| MIBSPI1SOMI[0] | G18 | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI1 slave-out master-in, or GPIO | |
| MIBSPI1NCS[0]/MIBSPI1SOMI[1] | R2 | ||||
| MIBSPI3CLK | V9 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI3 clock, or GPIO |
| MIBSPI3NCS[0]/AD2EVT/GIOB[2]/N2HET2_PIN_nDIS | V10 | MibSPI3 chip select, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI3NCS[1]/N2HET1[25]/MDCLK | V5 | ||||
| MIBSPI3NCS[2]/I2C_SDA/N2HET1[27] | B2 | ||||
| MIBSPI3NCS[3]/I2C_SCL/N2HET1[29] | C3 | ||||
| N2HET1[11]/MIBSPI3NCS[4]/N2HET2[18] | E3 | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI3 chip select, or GPIO | |
| MIBSPI3NENA/MIBSPI3NCS[5]/N2HET1[31] | W9 | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI3 chip select, or GPIO | |
| MIBSPI3NENA/MIBSPI3NCS[5]/N2HET1[31] | W9 | MibSPI3 enable, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI3SIMO[0] | W8 | MibSPI3 slave-in master-out, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI3SOMI[0] | V8 | MibSPI3 slave-out master-in, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI5CLK/DMM_DATA[4] | H19 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | MibSPI5 clock, or GPIO |
| MIBSPI5NCS[0]/DMM_DATA[5] | E19 | MibSPI5 chip select, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI5NCS[1]/DMM_DATA[6] | B6 | ||||
| MIBSPI5NCS[2]/DMM_DATA[2] | W6 | ||||
| MIBSPI5NCS[3]/DMM_DATA[3] | T12 | ||||
| MIBSPI5NENA/DMM_DATA[7] | H18 | MibSPI5 enable, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI5SIMO[0]/DMM_DATA[8] | J19 | MibSPI5 slave-in master-out, or GPIO | |||
| MIBSPI5SIMO[1]/DMM_DATA[9] | E16 | ||||
| MIBSPI5SIMO[2]/DMM_DATA[10] | H17 | ||||
| MIBSPI5SIMO[3]/DMM_DATA[11] | G17 | ||||
| MIBSPI5SOMI[0]/DMM_DATA[12] | J18 | ||||
| MIBSPI5SOMI[1]/DMM_DATA[13] | E17 | ||||
| MIBSPI5SOMI[2]/DMM_DATA[14] | H16 | ||||
| MIBSPI5SOMI[3]/DMM_DATA[15] | G16 | ||||
4.3.2.11 External Memory Interface (EMIF)
Table 4-28 External Memory Interface (EMIF)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| EMIF_CKE | L3 | Output | Pulldown | None | EMIF Clock Enable |
| EMIF_CLK | K3 | I/O | None | EMIF clock. This is an output signal in functional mode. It is gated off by default, so that the signal is tri-stated. PINMUX29[8] must be cleared to enable this output. | |
| ETMDATA[13]/EMIF_nOE | E12 | Pulldown | None | EMIF Output Enable | |
| EMIF_nWAIT | P3 | I/O | Pullup | Fixed 20 µA Pullup |
EMIF Extended Wait Signal |
| EMIF_nWE | D17 | Output | Pullup | None | EMIF Write Enable. |
| EMIF_nCAS | R4 | Output | EMIF column address strobe | ||
| EMIF_nRAS | R3 | Output | EMIF row address strobe | ||
| EMIF_nCS[0]/RTP_DATA[15]/N2HET2[7] | N17 | Output | Pulldown | EMIF chip select, SDRAM | |
| EMIF_nCS[2] | L17 | Output | Pullup | EMIF chip selects, asynchronous This applies to chip selects 2, 3, and 4 |
|
| EMIF_nCS[3]/RTP_DATA[14]/N2HET2[9] | K17 | Output | Pulldown | ||
| EMIF_nCS[4]/RTP_DATA[7] | M17 | Output | Pullup | ||
| ETMDATA[15]/EMIF_nDQM[0] | E10 | Output | Pulldown | EMIF Data Mask or Write Strobe. Data mask for SDRAM devices, write strobe for connected asynchronous devices. |
|
| ETMDATA[14]/EMIF_nDQM[1] | E11 | Output | |||
| ETMDATA[12]/EMIF_BA[0] | E13 | Output | EMIF bank address or address line | ||
| EMIF_BA[1]/N2HET2[5] | D16 | Output | EMIF bank address or address line | ||
| EMIF_ADDR[0]/N2HET2[1] | D4 | Output | EMIF address | ||
| EMIF_ADDR[1]/N2HET2[3] | D5 | Output | |||
| ETMDATA[11]/EMIF_ADDR[2] | E6 | Output | |||
| ETMDATA[10]/EMIF_ADDR[3] | E7 | Output | |||
| ETMDATA[9]/EMIF_ADDR[4] | E8 | Output | |||
| ETMDATA[8]/EMIF_ADDR[5] | E9 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[6]/RTP_DATA[13]/N2HET2[11] | C4 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[7]/RTP_DATA[12]/N2HET2[13] | C5 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[8]/RTP_DATA[11]/N2HET2[15] | C6 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[9]/RTP_DATA[10] | C7 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[10]/RTP_DATA[9] | C8 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[11]/RTP_DATA[8] | C9 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[12]/RTP_DATA[6] | C10 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[13]/RTP_DATA[5] | C11 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[14]/RTP_DATA[4] | C12 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[15]/RTP_DATA[3] | C13 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[16]/RTP_DATA[2] | D14 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[17]/RTP_DATA[1] | C14 | Output | Pulldown | ||
| EMIF_ADDR[18]/RTP_DATA[0] | D15 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[19]/RTP_nENA | C15 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[20]/RTP_nSYNC | C16 | Output | |||
| EMIF_ADDR[21]/RTP_CLK | C17 | Output | |||
| ETMDATA[16]/EMIF_DATA[0] | K15 | I/O | Pulldown | Fixed 20 µA Pullup |
EMIF Data |
| ETMDATA[17]/EMIF_DATA[1] | L15 | I/O | |||
| ETMDATA[18]/EMIF_DATA[2] | M15 | I/O | |||
| ETMDATA[19]/EMIF_DATA[3] | N15 | I/O | |||
| ETMDATA[20]/EMIF_DATA[4] | E5 | I/O | |||
| ETMDATA[21]/EMIF_DATA[5] | F5 | I/O | |||
| ETMDATA[22]/EMIF_DATA[6] | G5 | I/O | |||
| ETMDATA[23]/EMIF_DATA[7] | K5 | I/O | |||
| ETMDATA[24]/EMIF_DATA[8] | L5 | I/O | |||
| ETMDATA[25]/EMIF_DATA[9] | M5 | I/O | |||
| ETMDATA[26]/EMIF_DATA[10] | N5 | I/O | |||
| ETMDATA[27]/EMIF_DATA[11] | P5 | I/O | |||
| ETMDATA[28]/EMIF_DATA[12] | R5 | I/O | |||
| ETMDATA[29]/EMIF_DATA[13] | R6 | I/O | |||
| ETMDATA[30]/EMIF_DATA[14] | R7 | I/O | |||
| ETMDATA[31]/EMIF_DATA[15] | R8 | I/O | |||
4.3.2.12 Embedded Trace Macrocell for Cortex-R4F CPU (ETM-R4F)
Table 4-29 Embedded Trace Macrocell for Cortex-R4F CPU (ETM-R4F)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| ETMTRACECLKIN/EXTCLKIN2 | R9 | Input | Pulldown | Fixed 20 µA Pullup |
ETM Trace Clock Input |
| ETMTRACECLKOUT | R10 | Output | Pulldown | None | ETM Trace Clock Output |
| ETMTRACECTL | R11 | ETM trace control | |||
| ETMDATA[0] | R12 | ETM data | |||
| ETMDATA[1] | R13 | ||||
| ETMDATA[2] | J15 | ||||
| ETMDATA[3] | H15 | ||||
| ETMDATA[4] | G15 | ||||
| ETMDATA[5] | F15 | ||||
| ETMDATA[6] | E15 | ||||
| ETMDATA[7] | E14 | ||||
| ETMDATA[8]/EMIF_ADDR[5] | E9 | ||||
| ETMDATA[9]/EMIF_ADDR[4] | E8 | ||||
| ETMDATA[10]/EMIF_ADDR[3] | E7 | ||||
| ETMDATA[11]/EMIF_ADDR[2] | E6 | ||||
| ETMDATA[12]/EMIF_BA[0] | E13 | ||||
| ETMDATA[13]/EMIF_nOE | E12 | ||||
| ETMDATA[14]/EMIF_nDQM[1] | E11 | ||||
| ETMDATA[15]/EMIF_nDQM[0] | E10 | ||||
| ETMDATA[16]/EMIF_DATA[0] | K15 | ||||
| ETMDATA[17]/EMIF_DATA[1] | L15 | ||||
| ETMDATA[18]/EMIF_DATA[2] | M15 | ||||
| ETMDATA[19]/EMIF_DATA[3] | N15 | ||||
| ETMDATA[20]/EMIF_DATA[4] | E5 | ||||
| ETMDATA[21]/EMIF_DATA[5] | F5 | ||||
| ETMDATA[22]/EMIF_DATA[6] | G5 | ||||
| ETMDATA[23]/EMIF_DATA[7] | K5 | ||||
| ETMDATA[24]/EMIF_DATA[8] | L5 | ||||
| ETMDATA[25]/EMIF_DATA[9] | M5 | ||||
| ETMDATA[26]/EMIF_DATA[10] | N5 | ||||
| ETMDATA[27]/EMIF_DATA[11] | P5 | ||||
| ETMDATA[28]/EMIF_DATA[12] | R5 | ||||
| ETMDATA[29]/EMIF_DATA[13] | R6 | ||||
| ETMDATA[30]/EMIF_DATA[14] | R7 | ||||
| ETMDATA[31]/EMIF_DATA[15] | R8 | ||||
4.3.2.13 RAM Trace Port (RTP)
Table 4-30 RAM Trace Port (RTP)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| EMIF_ADDR[21]/RTP_CLK | C17 | I/O | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | RTP packet clock, or GPIO |
| EMIF_ADDR[19]/RTP_nENA | C15 | I/O | RTP packet handshake, or GPIO | ||
| EMIF_ADDR[20]/RTP_nSYNC | C16 | I/O | RTP synchronization, or GPIO | ||
| EMIF_ADDR[18]/RTP_DATA[0] | D15 | I/O | RTP packet data, or GPIO | ||
| EMIF_ADDR[17]/RTP_DATA[1] | C14 | ||||
| EMIF_ADDR[16]/RTP_DATA[2] | D14 | ||||
| EMIF_ADDR[15]/RTP_DATA[3] | C13 | ||||
| EMIF_ADDR[14]/RTP_DATA[4] | C12 | ||||
| EMIF_ADDR[13]/RTP_DATA[5] | C11 | ||||
| EMIF_ADDR[12]/RTP_DATA[6] | C10 | ||||
| EMIF_nCS[4]/RTP_DATA[7] | M17 | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | ||
| EMIF_ADDR[11]/RTP_DATA[8] | C9 | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | ||
| EMIF_ADDR[10]/RTP_DATA[9] | C8 | ||||
| EMIF_ADDR[9]/RTP_DATA[10] | C7 | ||||
| EMIF_ADDR[8]/RTP_DATA[11]/N2HET2[15] | C6 | ||||
| EMIF_ADDR[7]/RTP_DATA[12]/N2HET2[13] | C5 | ||||
| EMIF_ADDR[6]/RTP_DATA[13]/N2HET2[11] | C4 | ||||
| EMIF_nCS[0]/RTP_DATA[15]/N2HET2[7] | N17 | ||||
| EMIF_nCS[3]/RTP_DATA[14]/N2HET2[9] | K17 | ||||
4.3.2.14 Data Modification Module (DMM)
Table 4-31 Data Modification Module (DMM)
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| DMM_CLK | F17 | I/O | Pullup | Programmable, 20 µA | DMM clock, or GPIO |
| DMM_nENA | F16 | DMM handshake, or GPIO | |||
| DMM_SYNC | J16 | DMM synchronization, or GPIO | |||
| DMM_DATA[0] | L19 | DMM data, or GPIO | |||
| DMM_DATA[1] | L18 | ||||
| MIBSPI5NCS[2]/DMM_DATA[2] | W6 | ||||
| MIBSPI5NCS[3]/DMM_DATA[3] | T12 | ||||
| MIBSPI5CLK/DMM_DATA[4] | H19 | ||||
| MIBSPI5NCS[0]/DMM_DATA[5] | E19 | ||||
| MIBSPI5NCS[1]/DMM_DATA[6] | B6 | ||||
| MIBSPI5NENA/DMM_DATA[7] | H18 | ||||
| MIBSPI5SIMO[0]/DMM_DATA[8] | J19 | ||||
| MIBSPI5SIMO[1]/DMM_DATA[9] | E16 | ||||
| MIBSPI5SIMO[2]/DMM_DATA[10] | H17 | ||||
| MIBSPI5SIMO[3]/DMM_DATA[11] | G17 | ||||
| MIBSPI5SOMI[0]/DMM_DATA[12] | J18 | ||||
| MIBSPI5SOMI[1]/DMM_DATA[13] | E17 | ||||
| MIBSPI5SOMI[2]/DMM_DATA[14] | H16 | ||||
| MIBSPI5SOMI[3]/DMM_DATA[15] | G16 | ||||
4.3.2.15 System Module Interface
Table 4-32 ZWT System Module Interface
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| nPORRST | W7 | Input | Pulldown | Fixed 100 µA Pulldown |
Power-on reset, cold reset External power supply monitor circuitry must drive nPORRST low when any of the supplies to the microcontroller fall out of the specified range. This terminal has a glitch filter. See Section 6.8. |
| nRST | B17 | I/O | Pullup | Fixed 100 µA Pullup |
System reset, warm reset, bidirectional. The internal circuitry indicates any reset condition by driving nRST low. The external circuitry can assert a system reset by driving nRST low. To ensure that an external reset is not arbitrarily generated, TI recommends that an external pullup resistor is connected to this terminal. This terminal has a glitch filter. See Section 6.8. |
| nERROR | B14 | I/O | Pulldown | Fixed 20 µA Pulldown |
ESM Error Signal Indicates error of high severity. See Section 6.18. |
4.3.2.16 Clock Inputs and Outputs
Table 4-33 ZWT Clock Inputs and Outputs
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| OSCIN | K1 | Input | N/A | None | From external crystal/resonator, or external clock input |
| KELVIN_GND | L2 | Input | Kelvin ground for oscillator | ||
| OSCOUT | L1 | Output | To external crystal/resonator | ||
| ECLK | A12 | I/O | Pulldown | Programmable, 20 µA | External prescaled clock output, or GIO. |
| GIOA[5]/EXTCLKIN/N2HET1_PIN_nDIS | B5 | Input | Pulldown | Fixed 20 µA Pulldown |
External clock input #1 |
| ETMTRACECLKIN/EXTCLKIN2 | R9 | Input | External clock input #2 | ||
| VCCPLL | P11 | 1.2-V Power | N/A | None | Dedicated core supply for PLLs |
4.3.2.17 Test and Debug Modules Interface
Table 4-34 ZWT Test and Debug Modules Interface
4.3.2.18 Flash Supply and Test Pads
Table 4-35 ZWT Flash Supply and Test Pads
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| VCCP | F8 | 3.3-V Power | N/A | None | Flash pump supply |
| FLTP1 | J5 | – | N/A | None | Flash test pads. These terminals are reserved for TI use only. For proper operation these terminals must connect only to a test pad or not be connected at all [no connect (NC)]. |
| FLTP2 | H5 | ||||
4.3.2.19 No Connects
Table 4-36 No Connects
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE | RESET PULL STATE | PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| NC | D6 | – | N/A | None | No Connects. These balls are not connected to any internal logic and can be connected to the PCB ground without affecting the functionality of the device. |
| NC | D7 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | D8 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | D9 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | D10 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | D11 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | D12 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | D13 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | E4 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | F4 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | G4 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | K4 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | K16 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | L4 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | L16 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | M4 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | M16 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | N4 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | N16 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | N18 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | P4 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | P15 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | P16 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | P17 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | R1 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | R14 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | R15 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | T2 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | T3 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | T4 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | T5 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | T6 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | T7 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | T8 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | T9 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | T10 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | T11 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | T13 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | T14 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | U3 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | U4 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | U5 | – | N/A | None | No Connects. These balls are not connected to any internal logic and can be connected to the PCB ground without affecting the functionality of the device. |
| NC | U6 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | U7 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | U8 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | U9 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | U10 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | U11 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | U12 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | V3 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | V4 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | V11 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | V12 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | W4 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | W11 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | W12 | – | N/A | None | |
| NC | W13 | – | N/A | None | |
4.3.2.20 Supply for Core Logic: 1.2-V Nominal
Table 4-37 ZWT Supply for Core Logic: 1.2-V Nominal
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE | RESET PULL STATE | PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| VCC | F9 | 1.2-V Power | N/A | None | Core supply |
| VCC | F10 | ||||
| VCC | H10 | ||||
| VCC | J14 | ||||
| VCC | K6 | ||||
| VCC | K8 | ||||
| VCC | K12 | ||||
| VCC | K14 | ||||
| VCC | L6 | ||||
| VCC | M10 | ||||
| VCC | P10 | ||||
4.3.2.21 Supply for I/O Cells: 3.3-V Nominal
Table 4-38 ZWT Supply for I/O Cells: 3.3-V Nominal
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE | RESET PULL STATE | PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| VCCIO | F6 | 3.3-V Power | N/A | None | Operating supply for I/Os |
| VCCIO | F7 | ||||
| VCCIO | F11 | ||||
| VCCIO | F12 | ||||
| VCCIO | F13 | ||||
| VCCIO | F14 | ||||
| VCCIO | G6 | ||||
| VCCIO | G14 | ||||
| VCCIO | H6 | ||||
| VCCIO | H14 | ||||
| VCCIO | J6 | ||||
| VCCIO | L14 | ||||
| VCCIO | M6 | ||||
| VCCIO | M14 | ||||
| VCCIO | N6 | ||||
| VCCIO | N14 | ||||
| VCCIO | P6 | ||||
| VCCIO | P7 | ||||
| VCCIO | P8 | ||||
| VCCIO | P9 | ||||
| VCCIO | P12 | ||||
| VCCIO | P13 | ||||
| VCCIO | P14 | ||||
4.3.2.22 Ground Reference for All Supplies Except VCCAD
Table 4-39 ZWT Ground Reference for All Supplies Except VCCAD
| TERMINAL | SIGNAL TYPE |
RESET PULL STATE |
PULL TYPE | DESCRIPTION | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIGNAL NAME | 337 ZWT | ||||
| VSS | A1 | Ground | N/A | None | Ground reference |
| VSS | A2 | ||||
| VSS | A18 | ||||
| VSS | A19 | ||||
| VSS | B1 | ||||
| VSS | B19 | ||||
| VSS | H8 | ||||
| VSS | H9 | ||||
| VSS | H11 | ||||
| VSS | H12 | ||||
| VSS | J8 | ||||
| VSS | J9 | ||||
| VSS | J10 | ||||
| VSS | J11 | ||||
| VSS | J12 | ||||
| VSS | K9 | ||||
| VSS | K10 | ||||
| VSS | K11 | ||||
| VSS | L8 | ||||
| VSS | L9 | ||||
| VSS | L10 | ||||
| VSS | L11 | ||||
| VSS | L12 | ||||
| VSS | M8 | ||||
| VSS | M9 | ||||
| VSS | M11 | ||||
| VSS | M12 | ||||
| VSS | V1 | ||||
| VSS | W1 | ||||
| VSS | W2 | ||||