SWCS048G March 2010 – September 2014 TPS65921
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1Device Overview
- 2Revision History
- 3Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
4Specifications
- 4.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 4.2 Handling Ratings
- 4.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 4.4 Thermal Resistance Characteristics for ZQZ Package
- 4.5 Crystal Oscillator
- 4.6 Clock Slicer
- 4.7 32KCLKOUT Output Clock
- 4.8 HFCLKOUT Output Clock
- 4.9 VDD1 DC-DC Converter
- 4.10 VDD2 DC-DC Converter
- 4.11 VIO DC-DC Converter
- 4.12 VMMC1 Low Dropout Regulator
- 4.13 VDAC Low Dropout Regulator
- 4.14 VAUX2 Low Dropout Regulator
- 4.15 VPLL1 Low Dropout Regulator
- 4.16 Internal LDOs
- 4.17 Voltage References
- 4.18 Battery Threshold Levels
- 4.19 Power Consumption
- 4.20 USB Charge Pump
- 4.21 Hot-Die Detection and Thermal Shutdown
- 4.22 USB
- 4.23 MADC
- 4.24 TPS65921 Interface Target Frequencies
- 4.25 JTAG Interfaces
- 5Detailed Description
- 6Device and Documentation Support
- 7Mechanical Packaging and Orderable Information
封装选项
机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
散热焊盘机械数据 (封装 | 引脚)
订购信息
1 Device Overview
1.1 Features
-
Three Step-Down Converters:
- Up to 1.2 A of Output Current for VDD1
- TPS65921B Supports VDD1 up to 1.2 A
- TPS65921B1 Supports VDD1 up to 1.4 A (Necessary for 1-GHz Operation)
- SmartReflex™ Dynamic Voltage Management
- 3.2-MHz Fixed Frequency Operation
- VIN Range from 2.7 to 4.5 V
- Typical 30 µA Quiescent per Converter
- Up to 1.2 A of Output Current for VDD1
- Four General-Purpose Configurable LDOs:
- Dynamic Voltage Scaling
- 220-mA Maximum Current for One LDO
- VIN Range from 2.7 to 4.5 V
- 2 LDOs With Low Noise and High PSRR
- RTC With Alarm Wake-Up Mechanism
- Clock Management
- 32-kHz Crystal Oscillator
- Clock Slicer for 26, 19.2, and 38.4 MHz
- HF Clock Output Buffer
- USB:
- USB HS 2.0 Transceiver
- USB 1.3 OTG-Compliant
- 12-Bit ULPI 1.1 Interface
- USB Power Supply (5-V CP for VBUS)
- Control
- High-Speed I2C Interface
- All Resource Configurable by I2C
- Keypad Interface up to 8 × 8
- 10-Bit A/D Converter
- Hot-Die, Thermal Shutdown Protection
- µ*BGA 120 Balls ZQZ
1.2 Applications
- Mobile Phones and Smart Phones
- MP3 Players
- Handheld Devices
- E-Books
- OMAP™ and Low-Power DSP Supply
1.3 Description
The TPS65921 device is a highly integrated power-management circuit (IC) that supports the power and peripheral requirements of the OMAP application processors. The device contains power management, a universal serial bus (USB) high-speed (HS) transceiver, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC), a real-time clock (RTC), a keypad interface, and an embedded power control (EPC). The power portion of the device contains three buck converters, two controllable by a dedicated SmartReflex class-3 interface, multiple low-dropout (LDO) regulators, an EPC to manage the power-sequencing requirements of OMAP, and an RTC module. The USB module provides an HS 2.0 transceiver suitable for direct connection to the OMAP universal transceiver macrocell interface (UTMI) + low pin interface (ULPI) with an integrated charge pump (CP).
The device also provides auxiliary modules: ADC, keypad interface, and general-purpose inputs/outputs (GPIOs) muxed with the JTAG functions. The keypad interface implements a built-in scanning algorithm to decode hardware-based key presses and to reduce software use, with multiple additional GPIOs that can be used as interrupts when they are configured as inputs.
1.4 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 shows the functional block diagram of the device.
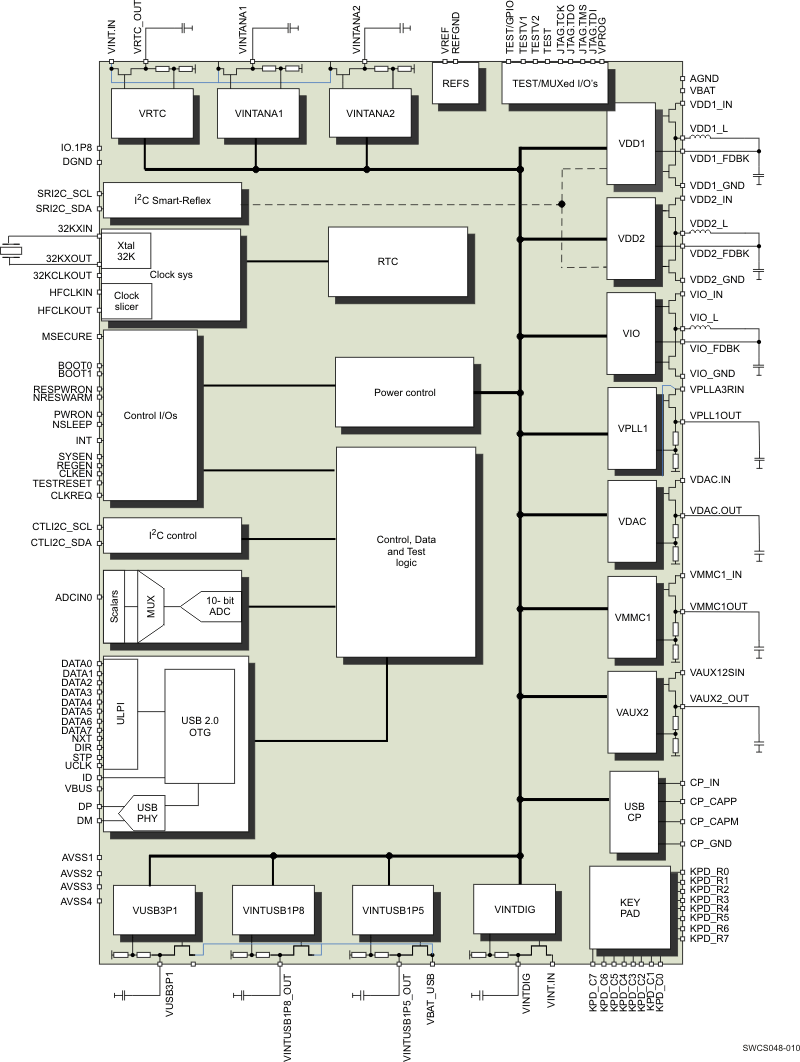 Figure 1-1 Functional Block Diagram
Figure 1-1 Functional Block Diagram