ZHCSF35A October 2014 – June 2016 PGA300
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
6 Specifications
- 6.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 6.2 ESD Ratings
- 6.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 6.4 Thermal Information
- 6.5 Electrical Characteristics - Reverse Voltage Protection
- 6.6 Electrical Characteristics - Regulators
- 6.7 Electrical Characteristics - Internal Reference
- 6.8 Electrical Characteristics - Bridge Sensor Supply
- 6.9 Electrical Characteristics - Temperature Sensor Supply
- 6.10 Electrical Characteristics - Internal Temperature Sensor
- 6.11 Electrical Characteristics - P Gain (Chopper Stabilized)
- 6.12 Electrical Characteristics - P Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 6.13 Electrical Characteristics - T Gain (Chopper Stabilized)
- 6.14 Electrical Characteristics - T Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 6.15 Electrical Characteristics - One-Wire Interface
- 6.16 Electrical Characteristics - DAC Output
- 6.17 Electrical Characteristics - DAC Gain
- 6.18 Electrical Characteristics - Non-Volatile Memory
- 6.19 Electrical Characteristics - Diagnostics
- 6.20 Operating Characteristics
- 6.21 Typical Characteristics
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
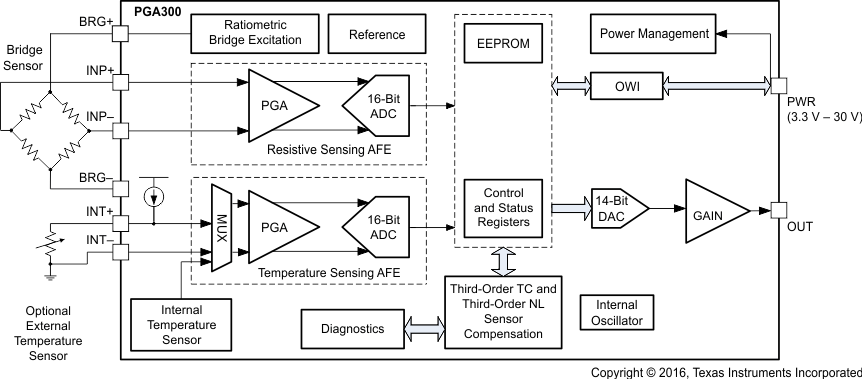
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Reverse-Voltage Protection Block
- 7.3.2 Linear Regulators
- 7.3.3 Internal Reference
- 7.3.4 BRG+ to BRG- Supply for the Resistive Bridge
- 7.3.5 ITEMP Supply for the Temperature Sensor
- 7.3.6 Internal Temperature Sensor
- 7.3.7 P Gain
- 7.3.8 P Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 7.3.9 T Gain
- 7.3.10 T Analog-to-Digital Converter
- 7.3.11 P GAIN and T GAIN Calibration
- 7.3.12 One-Wire Interface (OWI)
- 7.3.13 DAC Output
- 7.3.14 DAC Gain
- 7.3.15 Memory
- 7.3.16 Diagnostics
- 7.3.17 Digital Compensation and Filter
- 7.3.18 Filter Coefficients
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5
Register Maps
- 7.5.1 Register Settings
- 7.5.2
Control and Status Registers
- 7.5.2.1 DAC_CONFIG
- 7.5.2.2 OP_STAGE_CTRL
- 7.5.2.3 BRDG_CTRL
- 7.5.2.4 P_GAIN_SELECT
- 7.5.2.5 T_GAIN_SELECT
- 7.5.2.6 TEMP_CTRL
- 7.5.2.7 TEMP_SE
- 7.5.2.8 DIAG_ENABLE
- 7.5.2.9 AFEDIAG_CFG
- 7.5.2.10 AFEDIAG_MASK
- 7.5.2.11 COMPENSATION_CONTROL
- 7.5.2.12 EEPROM_LOCK
- 7.5.2.13 EEPROM_PAGE_ADDRESS
- 7.5.2.14 EEPROM_CTRL
- 7.5.2.15 EEPROM_CRC
- 7.5.2.16 EEPROM_STATUS
- 7.5.2.17 EEPROM_CRC_STATUS
- 7.5.2.18 EEPROM_CRC_VALUE
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
1 特性
- 模拟 特性
- 适用于阻性桥式传感器的模拟前端
- 传感器灵敏度可调节范围:1mV/V 至 135mV/V
- 片上温度传感器
- 可编程增益
- 适用于信号通道的 16 位 Σ-Δ 模数转换器
- 适用于温度通道的 16 位 Σ-Δ 模数转换器
- 14 位输出数模转换器 (DAC)
- 数字 特性
- 整个温度范围内的 FSO 精度 < 0.1%
- 系统响应时间 < 220µs
- 三阶偏移、增益和非线性温度补偿
- 诊断功能
- 集成 EEPROM 用于存储器件操作、校准数据和用户数据
- 外设 特性
- 单线接口,可通过电源引脚进行通信,无需额外使用线路
- 4mA 至 20mA 电流回路接口
- 比例电压输出和绝对电压输出
- 电源管理控制
- 模拟低压检测
- 通用 特性
- 工业温度范围:–40°C 至 150°C
- 电源:
- 片上电源管理,支持 3.3V 至 30V 的宽电源电压范围
- 集成反向保护电路
2 应用
- 压力传感器发送器和换能器
- 液位计、流量计
- 阻性现场发送器
3 说明
PGA300 器件提供了一个适用于压阻式和应力计压感元件的接口。该器件具有可编程模拟前端 (AFE)、模数转换器 (ADC) 和数字信号处理功能。这是一套完整的片上系统 (SoC) 解决方案,可直接连接传感元件。此外,PGA300 器件还集成了稳压器和振荡器,最大程度地减少了外部组件数。该器件采用三阶温度和非线性补偿实现高精度。凭借单线制串行接口 (OWI),可以通过电源引脚实现外部通信,从而简化系统校准过程。集成 DAC 支持绝对电压、比例电压以及 4mA 至 20mA 的电流回路输出。
器件信息(1)
| 器件型号 | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|
| PGA300 | VQFN (36) | 6.00mm x 6.00mm |
- 要了解所有可用封装,请参见数据表末尾的可订购产品附录。
PGA300 简化框图