SCEA123 October 2022 LSF0102 , SN74LXC2T45 , SN74LXC8T245 , TXB0104 , TXS0102 , TXS0104E , TXU0204 , TXU0304
Enabling Smart Solar Inverter Designs with Level Translation
Green energy has become a critical component of the overall energy strategy for governments, corporations, and individuals. At the heart of green energy is the growing impact of solar power generation. Solar panel or photovoltaic (PV) installations have increased dramatically over the past few years as advancements in technology has significantly reduced the cost of photovoltaic cells that make up solar panels. One technology that has contributed to the increase in solar installations is the availability of low cost and efficient string (see Figure 1-1) and micro inverter technologies that help address efficiency and scalability concerns often associated with investing in solar power generation. Solar inverter technology is essential for synchronizing a solar installation with the grid so that maximum utility can be realized from the generated power. Solar inverters perform the critical function of converting the Direct Current (DC) generated by solar panels to usable Alternating Current (AC) which can be used on site for home and commercial uses or synchronized back to the grid enabling cost savings through net metering. As solar power generation continues to grow, string and micro inverters have become enabling technologies. Robust and efficient inverter designs have become critical to the PV ecosystem. Inverter systems designers now need to make their designs smarter to improve efficiency and take advantage of power saving algorithms that are being incorporated with other PV system components such as power optimizers. To make inverters smarter, system designers need to use more advanced and capable microcontrollers in their designs. The latest microcontrollers and processors are designed to be low power and extremely efficient. One of the design challenges faced by systems designers as they incorporate these new microcontrollers in their designs is having to align the lower I/O voltage levels of the microcontroller with the higher I/O voltage levels of the peripheral devices of the signal chain such as the wireless communications modules and components of the AC and DC power topologies on the inverter.
The I/O level mismatch between lower power processors and peripheral devices often involve multiple interface types and signaling standards. Interfaces such as I2C, SPI, SMBus, I2S, GPIO and many others often need to be level shifted between processors and peripheral devices. System designers are turning to level shifter integrated circuit devices to help resolve I/O level mismatches between devices in their designs in an easy, efficient, and cost-effective manner without having to sacrifice system performance. One example where level translation devices are often needed within inverter designs is the interface between the microcontroller and the wireless communication module. The MCU to wireless interface is implemented with a UART interface that often needs to be level shifted. The example in figure two shows level translation between an MCU operating at 1.8 V and a wireless module operating at 3.3 V. Level translators like TXU0204 enable design engineers to implement low power level shifting between core components for interfaces such as, UART, GPIO and virtually any other multi-bit interface as well as the low voltage I/O levels associated with low power modes of these devices. Other interfaces that might need level shifting within an inverter signal chain includes interfaces with the AC and DC power topologies as well as various sensors that can be used on a design. For common interface types such as SPI, UART and JTAG push-pull level translation devices from TI’s SN74AXC, SN74LXC , and TXU families can provide solutions that are easy to implement with industry standard footprints. For open drain interfaces like I2C and SMBus, TI’s TXS and LSF level translation families provide cost effective solutions that are available in a wide variety of channel counts and industry standard packages and pinouts. For a list of recommended level translation devices for common interface types please see table one. For More information on all of TI’s level translation solutions please visit TI’s Level Translation Landing Page.
| Interface | TI Recommended Device | |
|---|---|---|
| 3.6 V maximum | 5.5 V maximum | |
| FET Replacement | 2N7001T-Q1 | SN74LXC1T45-Q1 |
| 1 Bit GPIO/Clock Signal | SN74AXC1T45-Q1 | SN74LXC1T45-Q1 |
| 2 Bit GPIO | SN74AXC2T245-Q1 | SN74LXC2T45-Q1 / TXU0102-Q1/TXU0202-Q1 |
| 2-Pin JTAG/UART | SN74AXC2T45-Q1 | SN74LXC2T45-Q1 /TXU0102-Q1/TXU0202-Q1 |
| I2C/MDIO/SMBus | TXS0102-Q1 / LSF0102-Q1 | TXS0102-Q1 / LSF0102-Q1 |
| 4 Bit GPIO | SN74AXC4T245-Q1 | TXB0104-Q1 / TXU0104-Q1 |
| UART | SN74AXC4T245-Q1 | TXB0104-Q1 / TXU0204-Q1 |
| SPI | SN74AXC4T774-Q1 / TXB0104-Q1 | TXB0104-Q1 / TXU0304-Q1 |
| JTAG | SN74AXC4T774-Q1 / TXB0104-Q1 | TXB0104-Q1 / TXU0204-Q1 |
| I2S/PCM | SN74AXC4T774-Q1 / TXB0104-Q1 | TXB0104-Q1 / TXU0204-Q1 |
| Quad-SPI | TXB0106-Q1 | TXB0106-Q1 |
| SDIO/SD/MMC | TXS0206 or TWL1200 | N/A |
| 8 Bit GPIO/RGMII | SN74AXC8T245-Q1 | SN74LXC8T245-Q1 |
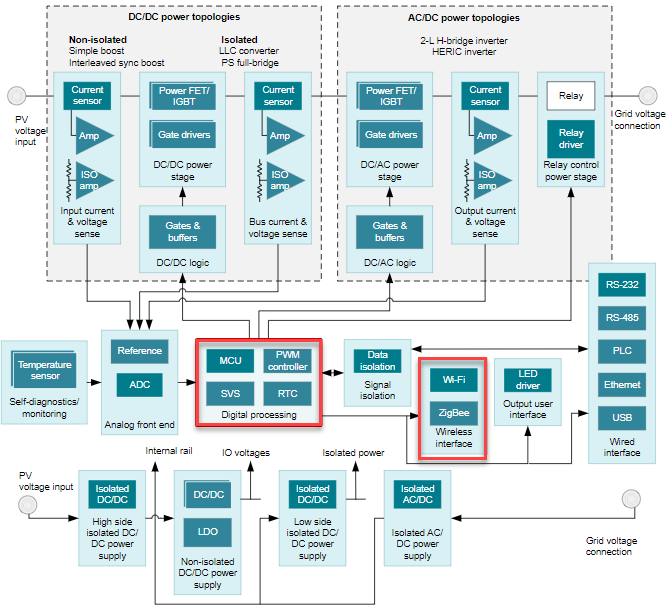 Figure 1-1 Solar Inverter System Reference Diagram
Figure 1-1 Solar Inverter System Reference Diagram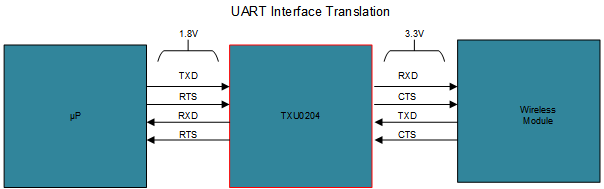 Figure 1-2 Level Translation Use Case for UART Interface
Figure 1-2 Level Translation Use Case for UART Interface