ZHCSF80B May 2016 – September 2017 TPS22975
PRODUCTION DATA.
1 特性
- 集成单通道负载开关
- 输入电压范围:0.6V 至 VBIAS
- VBIAS 电压范围:2.5V 至 5.7V
- 导通电阻 (RON)
- RON = 16m(VIN = 0.6V 到 5.7V,
VBIAS = 5.7V 时的典型值)
- RON = 16m(VIN = 0.6V 到 5.7V,
- 6A 最大持续开关电流
- 低静态电流
- 37µA(VIN = VBIAS = 5V 时的典型值)
- 低控制输入阈值支持使用
1.2V、1.8V、2.5V、3.3V 逻辑器件 - 可配置的上升时间
- 热关断
- 快速输出放电 (QOD)(可选)
- 带有散热焊盘的小外形尺寸无引线 (SON) 8 引脚封装
- 经测试,静电放电 (ESD) 性能符合 JESD 22 规范
- 2000V 人体模型 (HBM) 和 1000V 带电器件模型 (CDM)
2 应用
- Ultrabook™
- 笔记本电脑和上网本
- 平板电脑
- 消费类电子产品
- 机顶盒和家庭网关
- 电信系统
- 固态硬盘 (SSD)
3 说明
TPS22975 产品系列包含两个器件:TPS22975 和 TPS22975N。每个器件都是一款单通道负载开关,可提供可配置的上升时间来尽量减小浪涌电流。此器件包括一个 N 通道金属氧化物半导体场效应晶体管 (MOSFET),可在 0.6 V 至 5.7V 的输入电压范围内运行并可支持 6A 的最大持续电流。此开关由一个开/关输入 (ON) 控制,此输入能够直接连接低电压控制信号。TPS22975 包含一个可选 230Ω 片上负载电阻,用于在此开关关断时进行快速输出放电。
TPS22975 采用小型,节省空间的 2mm × 2mm 8 引脚 SON 封装 (DSG),集成的散热焊盘允许该器件产生较高的功率耗散。该器件在自然通风环境下的额定运行温度范围为 –40°C 至 +105°C。
器件信息(1)
| 器件型号 | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|
| TPS22975 TPS22975N |
WSON (8) | 2.00mm x 2.00mm |
- 要了解所有可用封装,请参阅数据表末尾的可订购产品附录。
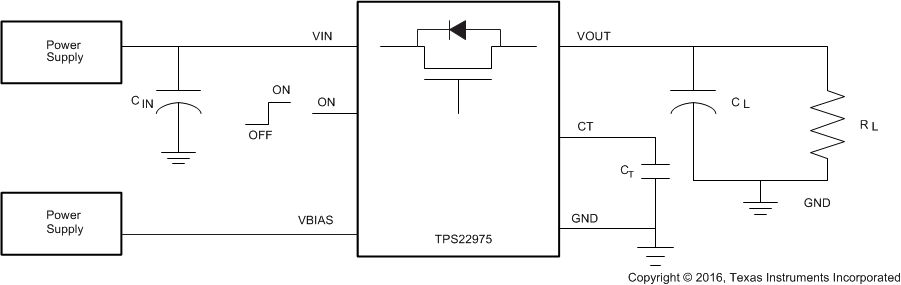
简化电路原理图
导通电阻与输入电压间的关系
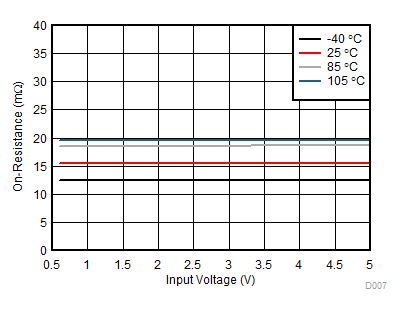
VBIAS = 5V,IVOUT = –200mA