ZHCSDI9D January 2015 – January 2017 HD3SS460
PRODUCTION DATA.
1 特性
- 提供面向 USB Type-CTM 生态系统的 MUX 解决方案,其中包括交替模式 (AM)
- 提供多种通道选择选项,其中包括 USBSS、双通道 AM 和四通道 AM
- 与 5 Gbps USB3.1 第 1 代和包含 5.4 Gbps DisplayPort 1.2a 的 AM 兼容
- 与源设备/主机和接收设备/设备应用 兼容
- 针对低速 SBU 引脚提供交叉点 MUX
- 双向“复用/解复用”差动开关
- 支持 0V 至 2V 共模电压
- 功耗较低,关断电流和工作电流分别为 1μA 和 0.6mA
- 单电源电压 VCC:3.3V±10%
- 工业温度范围:–40°C 至 85°C
2 应用
- 可换向 USB Type-CTM 生态系统
- 平板电脑、笔记本电脑、监视器、电话
- USB 主机和设备
- 扩展坞
3 说明
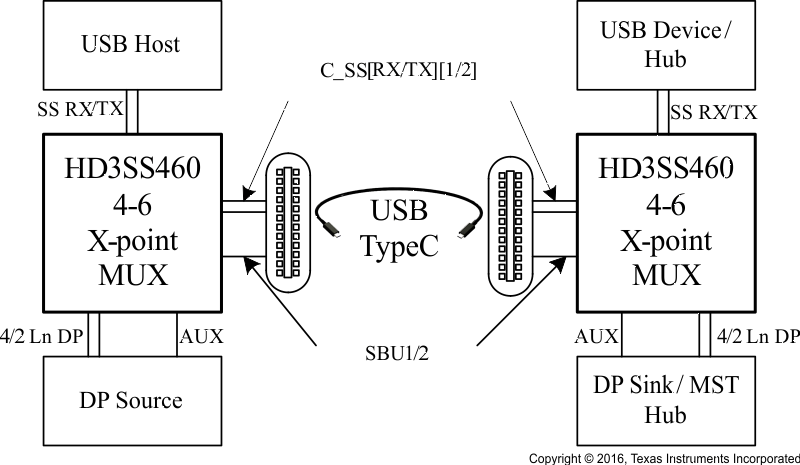
HD3SS460 是一款高速双向无源开关,可采用复用或解复用两种配置。该器件可通过负载点 (POL) 控制引脚进行切换,从而适应连接器换向。该器件还可通过 AMSEL 控制引脚来实现双通道数据/双通道视频与所有四通道视频的复用。
该器件还针对低速引脚提供了交叉点 MUX,可满足可换向连接器实现的需求。
HD3SS460 是一款通用模拟差分无源开关,适用于所有高速接口 应用, 前提条件是该应用在 0V 至 2V 共模电压范围内发生偏置并且具有幅值高达 1800 mVpp 的差分信令。该器件采用自适应跟踪,可确保信道在整个共模电压范围内保持不变。
该器件具有出色的动态特性,可在信号眼图衰减最小的情况下实现高速转换,并且附加抖动极少。该器件在工作模式下的功耗 < 2mW,关断模式下的功耗 < 5µW(可通过 EN 引脚切换模式)。
器件信息(1)
| 器件型号 | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|
| HD3SS460 | QFN (RHR) (28) | 3.50mm x 5.50mm |
| HD3SS460I | ||
| HD3SS460 | QFN (RNH) (30) | 2.50mm x 4.50mm |
| HD3SS460I |
- 要了解所有可用封装,请见数据表末尾的可订购产品附录。
sp
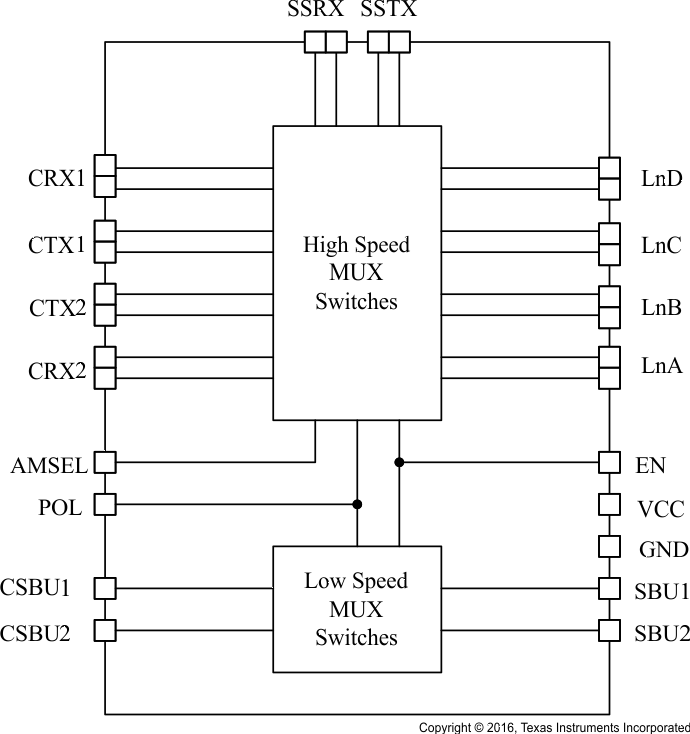
简化电路原理图
应用