ZHCSAD3B January 2012 – December 2014 BQ24190 , BQ24192 , BQ24192I
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明 (续)
- 6 Device Comparison Table
- 7 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 8 Specifications
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 Overview
- 9.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 9.3
Feature Description
- 9.3.1
Device Power Up
- 9.3.1.1 Power-On-Reset (POR)
- 9.3.1.2 Power Up from Battery without DC Source
- 9.3.1.3
Power Up from DC Source
- 9.3.1.3.1 REGN LDO
- 9.3.1.3.2 Input Source Qualification
- 9.3.1.3.3 Input Current Limit Detection
- 9.3.1.3.4 D+/D- Detection Sets Input Current Limit in bq24190
- 9.3.1.3.5 PSEL/OTG Pins Set Input Current Limit in bq24192, bq24192I
- 9.3.1.3.6 HIZ State wth 100mA USB Host
- 9.3.1.3.7 Force Input Current Limit Detection
- 9.3.1.4 Converter Power-Up
- 9.3.1.5 Boost Mode Operation from Battery
- 9.3.2 Power Path Management
- 9.3.3 Battery Charging Management
- 9.3.4 Status Outputs (PG, STAT, and INT)
- 9.3.5 Protections
- 9.3.6 Serial Interface
- 9.3.1
Device Power Up
- 9.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9.5
Register Map
- 9.5.1
I2C Registers
- 9.5.1.1 Input Source Control Register REG00 (bq24190, bq24192 reset = 00110000, or 30; bq24192I reset = 00111000, or 38)
- 9.5.1.2 Power-On Configuration Register REG01 (reset = 00011011, or 1B)
- 9.5.1.3 Charge Current Control Register REG02 (bq24190, bq24192 reset = 01100000, or 60; bq24192I reset = 00100000, or 20)
- 9.5.1.4 Pre-Charge/Termination Current Control Register REG03 (reset = 00010001, or 11)
- 9.5.1.5 Charge Voltage Control Register REG04 (bq24190, bq241192 reset = 10110010, or B2; bq24192I reset = 10011010, or 9A)
- 9.5.1.6 Charge Termination/Timer Control Register REG05 (reset = 10011010, or 9A)
- 9.5.1.7 IR Compensation / Thermal Regulation Control Register REG06 (reset = 00000011, or 03)
- 9.5.1.8 Misc Operation Control Register REG07 (reset = 01001011, or 4B)
- 9.5.1.9 System Status Register REG08
- 9.5.1.10 Fault Register REG09
- 9.5.1.11 Vender / Part / Revision Status Register REG0A (bq24190 reset = 00100011, or 23; bq24192 reset = 00101011, or 2B; bq24192I reset = 00001011, or 0B)
- 9.5.1
I2C Registers
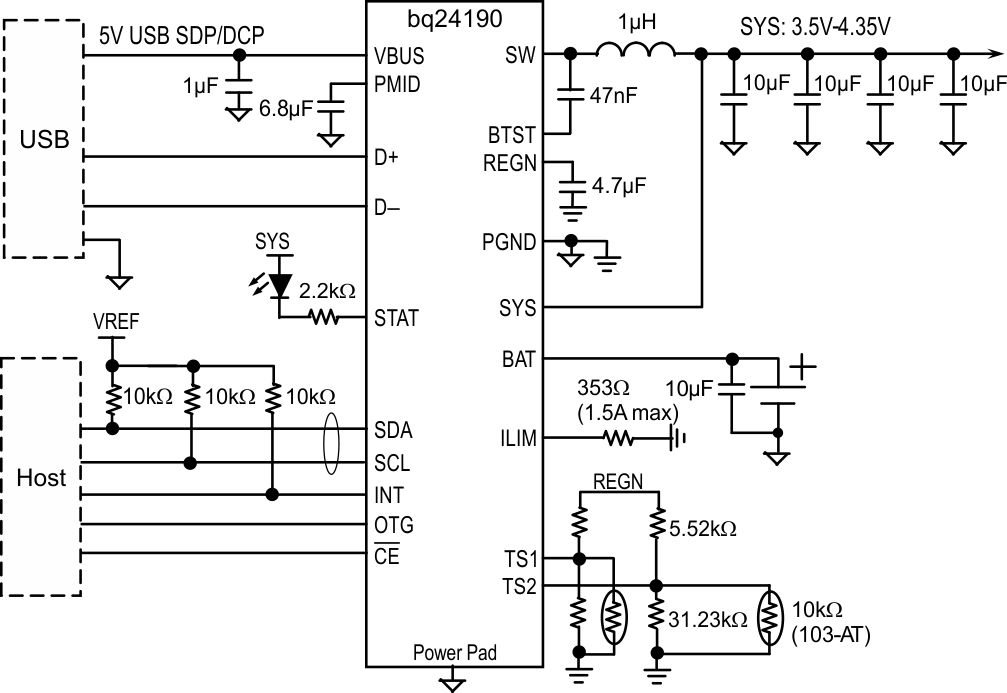
- 10Application and Implementation
- 11Power Supply Recommendations
- 12Layout
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
1 特性
- 高效 4.5A 开关模式充电器
- 2A 充电电流下的充电效率达 92%;4A 充电电流下的充电效率达 90%
- 通过电池路径阻抗补偿缩短充电时间
- 兼容 MaxLife 技术,与 bq27531 搭配使用时可实现快速充电
- 借助 12mΩ 电池放电金属氧化物半导体场效应晶体管 (MOSFET) 实现最高电池放电效率,放电电流高达 9A
- 单输入 USB 兼容/适配器充电器
- 与 USB 电池充电器技术规格 1.2 兼容的 USB 主机或充电端口 D+/D- 检测
- 输入电压和电流限制支持 USB 2.0 和 USB 3.0
- 输入电流限值:100mA、150mA、500mA、900mA、1.2A、1.5A、2A 和 3A
- 输入工作电压范围:3.9V 至 17V
- 通过输入电压动态电源管理 (DPM) 调节功能支持所有类型的适配器
- USB OTG 5V/1.3A 同步升压转换器操作
- 5V/1A 条件下的升压效率达 93%
- 窄 VDC (NVDC) 电源路径管理
- 与无电池或深度放电电池工作时可瞬时接通
- 电池管理模式中的理想二极管运行
- 薄型电感的开关频率为 1.5MHz
- 具有或不具有主机管理的自主电池充电
- 电池充电使能
- 电池充电预调节
- 充电终止和再充电
- 高精度(0°C 至 125°C)
- 充电电压调节范围为 ±0.5%
- 充电电流调节范围为 ±7%
- 输入电流调节范围为 ±7.5%
- 升压模式下输出调节范围 ±2%
- 高集成
- 电源路径管理
- 同步开关 MOSFET
- 集成电流感测
- 阴极负载二极管
- 内部环路补偿
- 安全性
- 电池温度感测和充电安全定时器
- 热调节和热关断
- 输入系统过压保护
- MOSFET 过流保护
- 针对 LED 或主机处理器的充电状态输出
- 低电池泄漏电流并支持关闭模式
- 4.00mm x 4.00mm 紧凑型超薄四方扁平无引线 (VQFN)-24 封装
2 应用
- 平板电脑和智能手机
- 便携式音频扬声器
- 便携式媒体播放器
- 互联网器件
3 说明
bq24190、bq24192 和 bq24192I 是高度集成的开关模式电池管理和系统电源路径管理器件,适用于各类、平板电脑和其他便携式设备的单节锂离子和锂聚合物电池。
器件信息(1)
| 产品型号 | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|
| bq24190 | VQFN (24) | 4.00mm x 4.00mm |
| bq24192 | ||
| bq24192I |
- 如需了解所有可用封装,请见数据表末尾的可订购产品附录。
4 修订历史记录
Changes from A Revision (October 2012) to B Revision
- 已统一 整篇数据表 中的封装说明Go
- Added ESD 额定值,特性 描述,器件功能模式,应用和实施,电源相关建议,布局,器件和文档支持以及机械、封装和可订购信息。Go
- Added 特性:兼容 MaxLife 技术,与 bq27531 搭配使用时可实现快速充电Go
- Changed VSLEEPZ, VBAT_DPL_HY, VBATGD , ICHG_20pct, VSHORT, IADPT_DPM, KILIM, VBTST_REFRESH in Electrical CharacteristicsGo
- Added –40°C to 85° to IBAT Test ConditionGo
- Added REG00[6:3] = 0110 (4.36 V) or 1011 (4.76 V) to VINDPM_REG_ACC Test ConditionsGo
- Added Typical input current of 1.5 A based on KLIM to IADPT_DPM Test ConditionsGo
- Added a MIN value of 435 to KILIMGo
- Deleted TJunction_REG MIN and MAXGo
- Added rising to VHTF parameter Go
- Deleted VREGN, VVBUS = 5 V, IREGN = 20 mA MAX valueGo
- Changed Functional Block DiagramGo
- Changed Charging Current in Table 4Go
- Changed REG09[5:4] to REG08[5:4] in Charging Termination sectionGo
- Added or when FORCE_20PCT (REG02[0]) bit is set, to Charging Safety Timer descriptionGo
- Added last paragraph to Charging Safety Timer descriptionGo
- Added twice to Host Mode and Default Mode descriptionGo
- Changed REG05[5:4]=11 to REG05[5:4]=00 in Host Mode and Default Mode descriptionGo
- Changed Charge Current Control Register REG02 Bit 0 descriptionGo
- Changed Charge Current Control Register REG02 Bit 0 noteGo
- Changed REG05 Bit 0 from JEITA ISET (0°C-10°C) to ReservedGo
- Changed REG07 Bit 4 from JEITA_VSET (45°C to 60°C) to ReservedGo
- Changed BOOT to BTST in Figure 38Go
- Changed BOOT to BTST in Figure 39Go
- Changed bq24193 to bq24192 in Figure 42Go