ZHCS862E March 2012 – May 2017 TPS62125
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
- 7 Detailed Description
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
1 特性
2 应用
- 嵌入式处理
- 由 4 节碱性电池、1 至 4 节锂离子电池供电的 应用
- 9V 至 15V 待机电源
- 能量采集
- 逆变器(负 VOUT)
3 说明
TPS62125 器件是一款高效同步降压转换器,针对低功耗/超低功耗 应用 进行了优化,输出电流高达 300mA。该器件的宽输入电压范围为 3V 至 17V,可支持由 4 节碱性电池、1 至 4 节锂离子电池串联配置以及 9V 至 15V 电压供电的 应用的输出电流传感电阻器和运算放大器而得以实现。该器件具备一个精密的低功耗使能比较器,其可用作输入电源电压监视器 (SVS),以满足系统特定的上电和断电要求。该使能比较器仅消耗 6µA 静态电流并 具备 典型值为 1.2V 的精确阈值以及可调节迟滞。借助此特性,该转换器能够从由太阳能板或者电流回路等高阻抗源供电的储能电容中提取电能,以生成电源轨。凭借其 DCS-Control 机制,该转换器可在节能模式下运行,从而在整个负载电流范围内保持最高效率。在轻载条件下,该转换器能够以脉频调制 (PFM) 模式运行并在负载电流较大时自动无缝转换至脉宽调制 (PWM) 模式。该 DCS-Control™机制已针对 PFM 模式下的低输出纹波电压进行了优化,从而最大限度地降低输出噪声 并 获得优异的交流负载稳压性能。开漏电源正常输出表示正在对输出电压进行稳压。
器件信息(1)
| 器件型号 | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|
| TPS62125 | WSON (8) | 2.00mm x 2.00mm |
- 如需了解所有可用封装,请参阅数据表末尾的可订购产品附录。
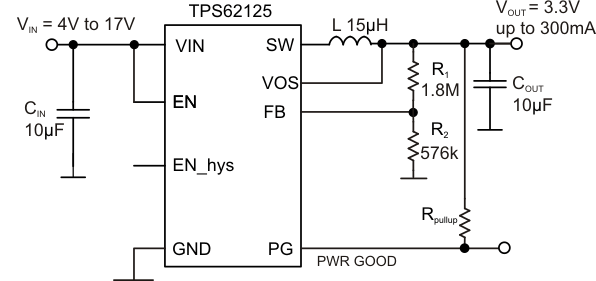
典型应用电路原理图
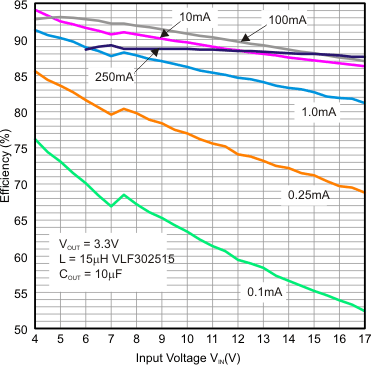
效率与输入电压间的关系