TIDUCJ0G November 2016 – April 2020
1 System Description
Three-phase power is used by equipment operating at high power in industrial applications. To improve grid power quality and reduce the harmonic currents drawn, power factor correction is needed as many of the forward loads are DC. For example, in an offboard, fast EV charger, operating at 20 KW, the input is a three-phase AC connection from the grid and the output is DC to the battery.
Though many topologies exist for active three-phase power factor conversion, a Vienna rectifier is popular due to its operation in continuous conduction mode (CCM), inherent multilevel switching (three level), and reduced voltage stress on the power devices. Traditionally, hysteresis-based controllers have been used for Vienna rectifiers. Only recently have sine triangle-based PWM been shown to work for Vienna Rectifier control. This control can be quite challenging to design. Several variants of Vienna rectifiers exist, Figure 1 shows the variant of the Vienna rectifier chosen in this design along with the key voltages and currents being sensed.
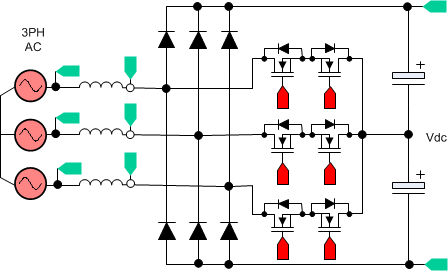
A Y-connection Vienna rectifier is implemented in this design guide. With this design, the purpose is to provide an example of how to control a Vienna rectifier and how to tune the different loops using the C2000 MCU.