SPRUJ22A November 2021 – March 2023 AWR2944
- Trademarks
- 1Getting Started
-
2Hardware
- 2.1 Block Diagram
- 2.2 PCB Handling Recommendations
- 2.3 Power Connections
- 2.4
Connectors
- 2.4.1 MIPI 60-Pin Connector (J19)
- 2.4.2 Debug Connector-60 pin (J7)
- 2.4.3 CAN-A Interface Connector (J3)
- 2.4.4 CAN-B Interface Connector (J2)
- 2.4.5 Ethernet Ports (J4 and J9)
- 2.4.6 USB Connectors (J8, J10)
- 2.4.7 OSC_CLKOUT Connector (J14)
- 2.4.8 PMIC SPI Connector (J16) (DNP)
- 2.4.9 Voltage Rails Ripple Measurement Connectors (J1, J5) (DNP)
- 2.5 Antenna
- 2.6 PMIC
- 2.7 On-Board Sensors
- 2.8 PC Connection
- 2.9 Connecting the AWR2944EVM to the DCA1000 EVM
- 2.10 Jumpers, Switches, and LEDs
- 3Design Files and Software Tools
- 4Revision History
2.5 Antenna
The AWR2944EVM includes onboard etched antennas for the four receivers and four transmitters, which enables tracking multiple objects with their distance and angle information. This antenna design enables estimation of both azimuth and elevation angles, which enable object detection in a 3-D plane (see Figure 2-14).
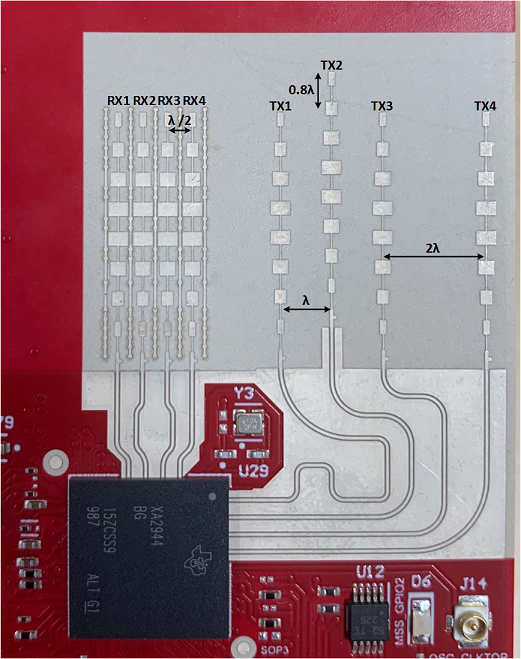 Figure 2-14 AWR2944EVM Antenna
Design
Figure 2-14 AWR2944EVM Antenna
DesignThe antenna placement shown in Figure 2-14 results in the virtual antenna array shown in Figure 2-15.
 Figure 2-15 Virtual Antenna Array
Figure 2-15 Virtual Antenna ArrayThe antenna peak gain is 13 dBi across the frequency band of 76 to 81 GHz. The radiation pattern of the antenna in the horizontal plan (H-plane) and elevation plan (E-plane) is as shown in Figure 2-16 and Figure 2-17, respectively.
The beamwidth of the antenna design can be determined from the radiation patterns provided below. For example, based on 3-dB drop in the gain as compared to bore sight, the horizontal 3dB-beamwidth is approximately ±30 degrees (see Figure 2-16), and elevation 3dB-beamwidth is approximately ±3 degrees (see Figure 2-17). Similarly, the horizontal 6 dB beamwidth is approximately ±45 degrees (see Figure 2-16) and the elevation 6dB-beamwidth is approximately ±5 degrees (see Figure 2-17).
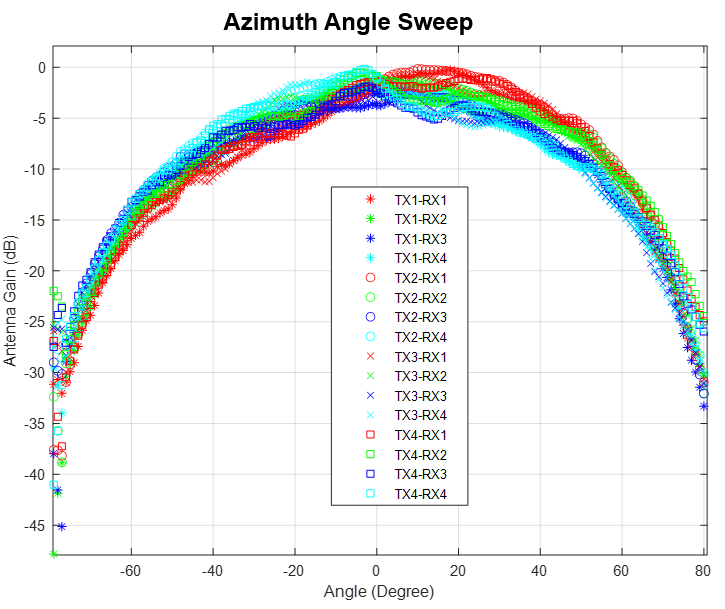 Figure 2-16 Azimuth Radiation Pattern
Figure 2-16 Azimuth Radiation Pattern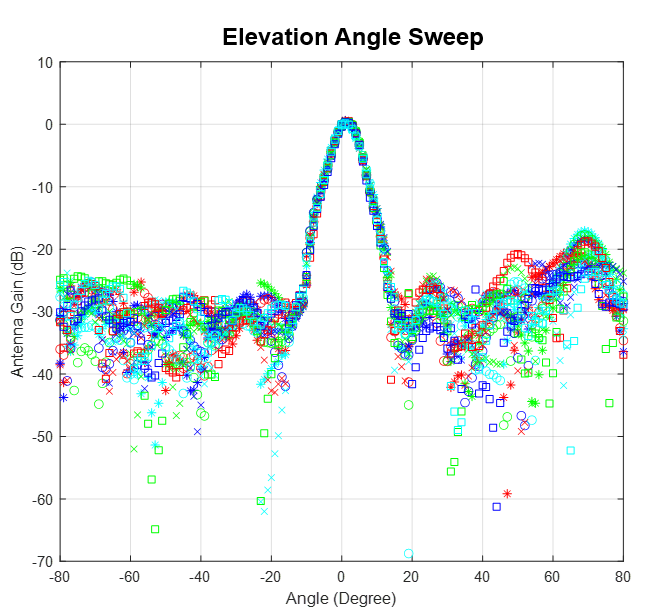 Figure 2-17 Elevation Radiation Pattern
Figure 2-17 Elevation Radiation Pattern