SBVA093 December 2022 LP2992 , TPS786 , TPS7A30 , TPS7A3001-EP , TPS7A33 , TPS7A39 , TPS7A4501-SP , TPS7A47 , TPS7A47-Q1 , TPS7A4701-EP , TPS7A49 , TPS7A52 , TPS7A52-Q1 , TPS7A53 , TPS7A53-Q1 , TPS7A53A-Q1 , TPS7A53B , TPS7A54 , TPS7A54-Q1 , TPS7A57 , TPS7A7100 , TPS7A7200 , TPS7A7300 , TPS7A80 , TPS7A8300 , TPS7A83A , TPS7A84 , TPS7A84A , TPS7A85 , TPS7A85A , TPS7A87 , TPS7A89 , TPS7A90 , TPS7A91 , TPS7A92 , TPS7A94 , TPS7A96 , TPS7B7702-Q1 , TPS7H1111-SEP , TPS7H1111-SP , TPS7H1210-SEP
3 Current Sharing and Load Voltage Analysis for n Parallel LDO's
A model of the parallel LDO's can be developed, and used to provide a universal equation for current sharing in n parallel converters (Figure 3-1). Using mesh current analysis, we can derive the output current for any n number of parallel LDO's:
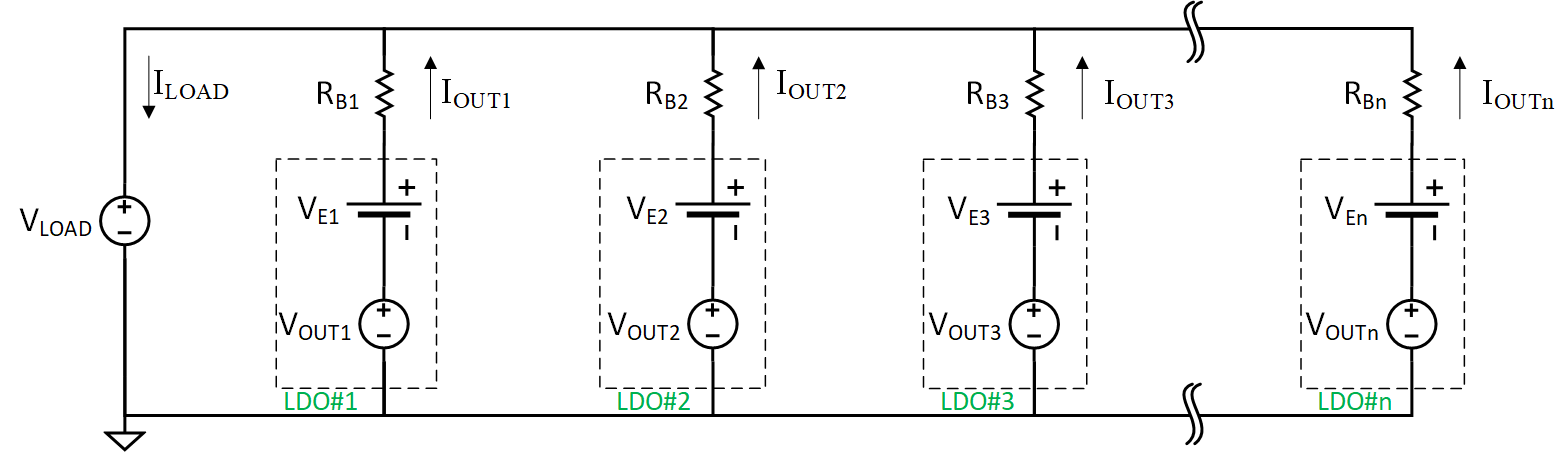 Figure 3-1 Equivalent Model for n Parallel LDO's
Using Ballast Resistors.
Figure 3-1 Equivalent Model for n Parallel LDO's
Using Ballast Resistors.The total load current is equal to the summation of current provided by each individual LDO. Thus:
In addition to deriving the current sharing of each LDO, we wish to compute the voltage on the load. Equation 5 can be rearranged to calculate VLOAD.
The universal equations for the current sharing and load voltage analysis are summarized in Equation 4, Equation 5 and Equation 6 for any n number of parallel LDO's using ballast resistors.
Equation 5 can be used to determine the maximum current provided by any LDO in a parallel system. This occurs when the error term for one LDO is the most positive while the error terms for the other LDO's are the most negative. In this worst-case scenario, IOUTn raises to its maximum possible value using Equation 4. This analysis provides the maximum current that each LDO must be designed to, and should be used in power dissipation analysis and thermal analysis for the parallel LDO's.