ZHCSMJ2 March 2021 TPS92390
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 Revision History
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Control Interface
- 7.3.2 Function Setting
- 7.3.3 Device Supply (VDD)
- 7.3.4 Enable (EN)
- 7.3.5 Charge Pump
- 7.3.6 Boost Controller
- 7.3.7 LED Current Sinks
- 7.3.8 Brightness Control
- 7.3.9
Protection and Fault Detections
- 7.3.9.1 Supply Faults
- 7.3.9.2
Boost Faults
- 7.3.9.2.1 Boost Overvoltage Faults (BSTOVPL, BSTOVPH)
- 7.3.9.2.2 Boost Overcurrent Faults (BSTOCP)
- 7.3.9.2.3 LEDSET Resistor Missing Faults (LEDSET)
- 7.3.9.2.4 MODE Resistor Missing Faults (MODESEL)
- 7.3.9.2.5 FSET Resistor Missing Faults (FSET)
- 7.3.9.2.6 ISET Resistor Out of Range Faults (ISET)
- 7.3.9.2.7 Thermal Shutdown Faults (TSD)
- 7.3.9.3 LED Faults
- 7.3.9.4 Overview of the Fault and Protection Schemes
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5 Programming
- 7.6 Register Maps
-
8 Application and Implementation
- 8.1 Application Information
- 8.2
Typical Applications
- 8.2.1
Full Feature Application for Display Backlight
- 8.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.1.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.2 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.3 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.1.2.4 Charge Pump Output Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.5 Charge Pump Flying Capacitor
- 8.2.1.2.6 Output Diode
- 8.2.1.2.7 Switching FET
- 8.2.1.2.8 Boost Sense Resistor
- 8.2.1.2.9 Power-Line FET
- 8.2.1.2.10 Input Current Sense Resistor
- 8.2.1.2.11 Feedback Resistor Divider
- 8.2.1.2.12 Critical Components for Design
- 8.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.2 Application With Basic/Minimal Operation
- 8.2.3
SEPIC Mode Application
- 8.2.3.1 Design Requirements
- 8.2.3.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 8.2.3.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 8.2.3.2.2 Coupling Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.3.2.3 Output Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.3.2.4 Input Capacitor Selection
- 8.2.3.2.5 Charge Pump Output Capacitor
- 8.2.3.2.6 Charge Pump Flying Capacitor
- 8.2.3.2.7 Switching FET
- 8.2.3.2.8 Output Diode
- 8.2.3.2.9 Switching Sense Resistor
- 8.2.3.2.10 Power-Line FET
- 8.2.3.2.11 Input Current Sense Resistor
- 8.2.3.2.12 Feedback Resistor Divider
- 8.2.3.2.13 Critical Components for Design
- 8.2.3.3 Application Curves
- 8.2.1
Full Feature Application for Display Backlight
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11Device and Documentation Support
- 12Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
7.3.6.3.3 FB Divider Using External Compensation
The device has internal compensation network to keep the DC-DC control loop in good stability in most cases. However, an additional external compensation network could also be added on FB-pin to offer more flexibility in loop design or solving some extreme use-cases.
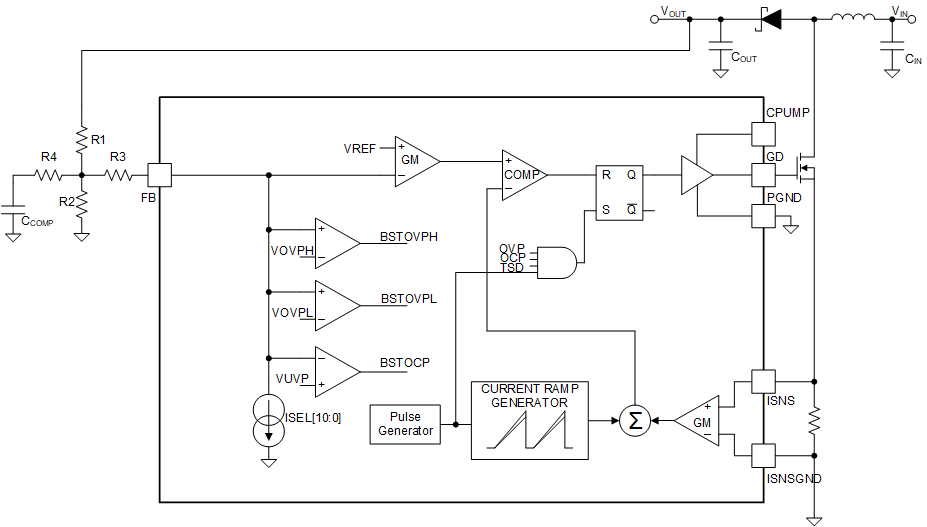 Figure 7-7 External Compensation Network
Figure 7-7 External Compensation NetworkThis network will create one additional pole and one additional zero in the loop.
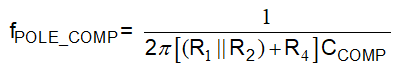
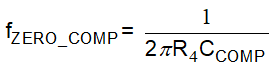
It could be noted that R3 doesn't take part in the compensation. So this external compensation network could be both used in two-divider netwrok and T-divider network with no equation change.
In real application, for example, when DC-DC loop has stability concern, putting the additional pole in 1 kHz and the additional zero in 2 kHz will suppress the loop gain by approximately 6 dB after 2 kHz. This will benefit gain margin and phase margin a lot.