SLUSFR7 August 2025 BQ24810
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1
- 1 Features
- 2 Applications
- 3 Description
- 4 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 5 Specifications
-
6 Detailed Description
- 6.1 Overview
- 6.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 6.3
Feature Description
- 6.3.1 Device Power Up
- 6.3.2 System Power Selection
- 6.3.3 Current and Power Monitor
- 6.3.4 Processor Hot Indication for CPU Throttling
- 6.3.5 Input Current Dynamic Power Management
- 6.3.6 Two-Level Adapter Current Limit (Peak Power Mode)
- 6.3.7 EMI Switching Frequency Adjust
- 6.3.8 Device Protections Features
- 6.4 Device Functional Modes
- 6.5 Programming
- 6.6
Register Maps
- 6.6.1 Battery-Charger Commands
- 6.6.2 Setting Charger Options
- 6.6.3 ChargeOption1 Register
- 6.6.4 ChargeOption2 Register
- 6.6.5 ChargeOption3 Register
- 6.6.6 ChargeOption4 Register
- 6.6.7 ProchotOption0 Register
- 6.6.8 ProchotOption1 Register
- 6.6.9 ProchotStatus Register
- 6.6.10 Charge Current Register
- 6.6.11 Charge Voltage Register
- 6.6.12 Discharge Current Register
- 6.6.13 Minimum System Voltage Register
- 6.6.14 Input Current Register
- 6.6.15 Register Exceptions
-
7 Application and Implementation
- 7.1 Application Information
- 7.2
Typical Applications
- 7.2.1
Typical System Schematic
- 7.2.1.1 Design Requirements
- 7.2.1.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 7.2.1.2.1 Adapter Current Sense Filter
- 7.2.1.2.2 Negative Output Voltage Protection
- 7.2.1.2.3 Reverse Input Voltage Protection
- 7.2.1.2.4 Reduce Battery Quiescent Current
- 7.2.1.2.5 CIN Capacitance
- 7.2.1.2.6 L1 Inductor Selection
- 7.2.1.2.7 CBATT Capacitance
- 7.2.1.2.8 Buck Charging Internal Compensation
- 7.2.1.2.9 CSYS Capacitance
- 7.2.1.2.10 Battery Only Boost Internal Compensation
- 7.2.1.2.11 Power MOSFETs Selection
- 7.2.1.2.12 Input Filter Design
- 7.2.1.3 Application Curves
- 7.2.2 Migration from Previous Devices (Does Not Support Battery Only Boost)
- 7.2.1
Typical System Schematic
- 7.3 Power Supply Recommendations
- 7.4 Layout
- 8 Device and Documentation Support
- 9 Revision History
- 10Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
6.4.3 Battery Only Boost Mode
When the system is powered from the battery with no adapter attached, a large system load will drop the system voltage significantly due to the battery's impedance. In order to provide the ability to handle large transients over the full operating range of the battery, the BQ24810 provides battery only boost mode. This mode uses the switching converter to boost the battery voltage to a regulated system output, providing additional headroom for system transients.
Unlike the hybrid power boost mode, which is expected to enter and exit frequently as supplemental current is required, battery only boost mode is entered once and maintained until either the adapter is plugged in, the battery reaches the BAT_DEPL_VTH (REG0x3B[15:14]) battery depletion threshold, or the mode is manually exited with the EN_BATT_BOOST (REG0x38[6]) bit. Entry into the mode may either be handled automatically, using the VSYSMIN threshold as set in VSysMin() (REG0x3E) register, or manually using the EN_BATT_BOOST bit. In order to use automatic entry, EN_BATT_BOOST is set to 1 while system voltage is above VSYSMIN. When the system voltage falls below VSYSMIN, the converter will enter battery only boost mode, regulating the system voltage to either 1.5V or 2.3V above VSYSMIN as set by the VBOOST (REG0x38[5]) bit.
All of the following conditions must be met in order to enter battery only boost mode:
- Battery only boost mode is enabled (REG0x38[6] = 1)
- Battery low power mode is disabled (REG0x12[15] = 0)
- System voltage (VACN) is below VSYSMIN
- ACOK is LOW
- Battery voltage (VSRN) is above depletion threshold in REG0x3B[15:14]
The time required to transition from direct-battery to regulated boost output is dependent on system conditions and generally requires between 1-5 msec. During this time, the battery via the body diode of the battery MOSFET holds up the system rail, resulting in a temporary voltage drop between the battery and system according to the forward voltage of the body diode. The VSysMin() entry should be set to a high enough threshold that the battery can support the transition under the worst case loading condition. A method for calculating this threshold is provided in Equation 4
VOP_MIN is the minimum operational voltage that will support the system. RBATT includes both the internal impedance of the battery as well as any resistance in the power path between the battery and the system. VBATFET_FD is the forward voltage drop of the BATFET body diode.
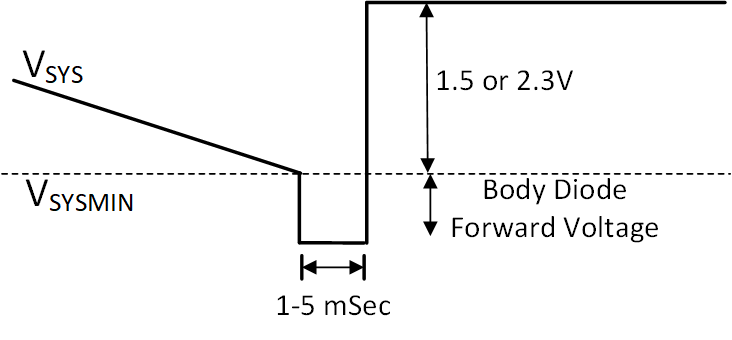 Figure 6-3 Entry Into Battery Only Boost Mode
Figure 6-3 Entry Into Battery Only Boost ModeFor systems where finer control is desired, entry into battery-only boost mode may be executed manually. For manual control, an external microcontroller is used to monitor the battery charge using a battery gas gauge IC or other method, and this information is used to determine the optimal point for entry into battery only boost mode. In order to manually enter battery only boost, VSYSMIN must be set below the current system voltage and then the REG0x38[6] enable bit set to 1. VSYSMIN may be adjusted after battery only boost is active in order to adjust the system regulation voltage. There is a delay of approximately 50 mSec (typical) between completion of the SMBUS command to enable battery only boost and entry into the mode.
One of the following conditions stops on-going battery only boost mode:
- Battery only boost mode is disabled (REG0x38[6] = 0)
- Battery low power mode is enabled (REG0x12[15] = 1)
- Adapter plugs in and ACOK goes HIGH
- Battery voltage (VSRN) is below depletion threshold in REG0x3B[15:14]
- Battery voltage (VSRN) rises to within 200 mV of system regulation voltage (measured at VACN)
- TSHUT IC temperature threshold is reached
- Short circuit is detected (see Inductor Short, MOSFET Short Protection for details)
- Watchdog timer expires if watchdog timer is enabled (see Charger Timeout for details)
In battery-only boost mode, the BQ24810 will regulate system voltage to either ( VSYSMIN + 1.5V ) or ( VSYSMIN + 2.3 V ) as set in REG0x38[5]. In order to properly transition during adapter insertion and removal, it is required that the minimum ACOK falling threshold for ACDET (2.30 V scaled by ACDET resistor divider) is above this regulation point. Once the device is in boost mode, status bit REG0x37[1] is set to 1 and BST_STAT pin goes LOW.
If the adapter is inserted while battery only boost mode is active, the system voltage will transition from the battery only boost regulation voltage to the adapter voltage, maintaining battery only boost mode for a deglitch time of AC_PLUG_EXIT_DEG (25ms/3ms/2ms/1ms), set in REG0x36[6:5]. Additionally, the ICRIT PROCHOT signal, if enabled, is automatically asserted, even if the adapter current never exceeds the ICRIT threshold. This may be used to preemptively slow the CPU during the transition.