ZHCSF53A April 2016 – June 2016
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 MP-A5 Coil Specification
- 8.3.2 High Voltage Dedicated Charging Port (HVDCP) Negotiation
- 8.3.3 Fast Charge Support
- 8.3.4 Option Select Pins
- 8.3.5 FOD and Parasitic Metal Object Detect (PMOD) Calibration
- 8.3.6 FOD Ping Calibration
- 8.3.7 Shut Down Through External Thermal Sensor or Trigger
- 8.3.8 Fault Handling and Indication
- 8.3.9 Power Transfer Start Signal
- 8.3.10 Power-On Reset
- 8.3.11 External Reset, RESET Pin
- 8.3.12 Trickle Charge and CS100
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
7 Specifications
7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings(1)
over operating free-air temperature (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage applied at V33D to DGND | –0.3 | 3.8 | V |
| Voltage applied at V33A to AGND | –0.3 | 3.8 | |
| Voltage applied to any pin(2) | –0.3 | 3.8 | |
| Storage temperature, Tstg | –40 | 150 | °C |
(1) Stresses beyond those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions beyond those indicated under Recommended Operating Conditions is not implied. Exposure to absolute-maximum-rated conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
(2) All voltages referenced to GND.
7.2 ESD Ratings
| MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V(ESD) | Electrostatic discharge | Human body model (HBM), per ANSI/ESDA/JEDEC JS-001, all pins(1) | ±2000 | V |
| Charged device model (CDM), per JEDEC specification JESD22-C101, all pins(2) | ±750 | |||
(1) JEDEC document JEP155 states that 500-V HBM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
(2) JEDEC document JEP157 states that 250-V CDM allows safe manufacturing with a standard ESD control process.
7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V | Supply voltage during operation, V33D, V33A | 3.0 | 3.3 | 3.6 | V |
| TA | Operating free-air temperature range | –40 | 85 | °C | |
| TJ | Junction temperature | 125 |
7.4 Thermal Information
| THERMAL METRIC(1) | bq501210 | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGC (VQFN) | |||
| 64 Pins | |||
| RθJA | Junction-to-ambient thermal resistance | 29.5 | °C/W |
| RθJC(top) | Junction-to-case (top) thermal resistance | 15.1 | °C/W |
| RθJB | Junction-to-board thermal resistance | 8.4 | °C/W |
| ψJT | Junction-to-top characterization parameter | 0.2 | °C/W |
| ψJB | Junction-to-board characterization parameter | 8.3 | °C/W |
| RθJC(bot) | Junction-to-case (bottom) thermal resistance | 1.2 | °C/W |
(1) For more information about traditional and new thermal metrics, see the Semiconductor and IC Package Thermal Metrics application report.
7.5 Electrical Characteristics
over operating free-air temperature range (unless otherwise noted)| PARAMETER | TEST CONDITIONS | MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SUPPLY CURRENT | ||||||||
| IV33A | Supply current | V33A = 3.3 V | 8 | 15 | mA | |||
| IV33D | V33D = 3.3 V | 44 | 55 | |||||
| ITotal | V33D = V33A = 3.3 V | 52 | 70 | |||||
| EXTERNALLY SUPPLIED 3.3 V POWER | ||||||||
| V33D | Digital 3.3-V power | TA = 25°C | 3 | 3.6 | V | |||
| V33A | Analog 3.3-V power | TA = 25°C | 3 | 3.6 | ||||
| V33Slew | 3.3-V slew rate | 3.3-V slew rate between 2.3 and 2.9 V, V33A = V33D |
0.25 | V/ms | ||||
| DIGITAL DEMODULATION INPUTS: COMM_A+, COMM_A–, COMM_B+, COMM_B–, COMM_C+, COMM_C– | ||||||||
| VCM | Common mode voltage each pin | –0.15 | 1.631 | V | ||||
| COMM+, COMM– | Modulation voltage digital resolution | 1 | mV | |||||
| REA | Input Impedance | Ground reference | 0.5 | 1.5 | 3 | MΩ | ||
| IOFFSET | Input offset current | 1-kΩ source impedance | –5 | 5 | µA | |||
| ANALOG INPUTS: V_SENSE, I_SENSE, T_SENSE, LED_MODE, CAL_INPUT, V_IN | ||||||||
| VADC_OPEN | Voltage indicating open pin | LED_MODE, CAL_INPUT open | 2.37 | V | ||||
| VADC_SHORT | Voltage indicating pin shorted to GND | LED_MODE, CAL_INPUT shorted to ground | 0.36 | |||||
| VADC_RANGE | Measurement range for voltage monitoring | All analog inputs | 0 | 2.5 | ||||
| INL | ADC integral nonlinearity | –2.5 | 2.5 | mV | ||||
| Ilkg | Input leakage current | 3 V applied to pin | 100 | nA | ||||
| RIN | Input impedance | Ground reference | 8 | MΩ | ||||
| CIN | Input capacitance | 10 | pF | |||||
| DIGITAL INPUTS/OUTPUTS | ||||||||
| VOL | Low-level output voltage | IOL = 6 mA , V33D = 3 V | DGND1 + 0.25 | V | ||||
| VOH | High-level output voltage | IOH = –6 mA , V33D = 3 V | V33D – 0.6 V | |||||
| VIH | High-level input voltage | V33D = 3 V | 2.1 | 3.6 | ||||
| VIL | Low-level input voltage | V33D = 3.5 V | 1.4 | |||||
| IOH(MAX) | Output high-source current | 4 | mA | |||||
| IOL(MAX) | Output low-sink current | 4 | ||||||
| SYSTEM PERFORMANCE | ||||||||
| VRESET | Voltage where device comes out of reset | V33D pin | 2.4 | V | ||||
| tRESET | Pulse duration needed for reset | RESET pin | 2 | µs | ||||
| ƒSW | Switching frequency (wireless power transfer) | System input power at startup | > 6 V | 130 | kHz | |||
| < 6 V | 110 | |||||||
| < 6 V, HVDCP to 9 or 12 V | 130 | |||||||
| tdetect | Time to detect presence of device requesting power | 0.5 | s | |||||
| Write_Cycles | Number of nonvolatile erase/write cycles | TJ = 25°C | 20 | k cycles | ||||
| PWM RAIL | ||||||||
| ƒSW_RAIL | Switching frequency | 4 * ƒSW | kHz | |||||
7.6 Typical Characteristics
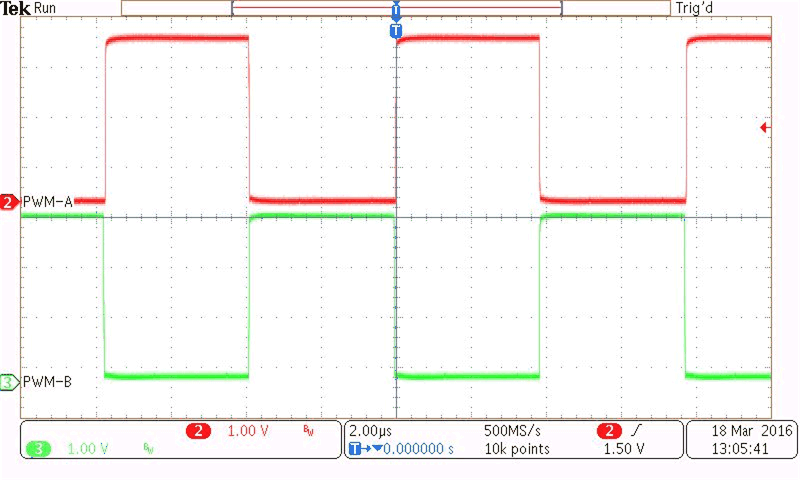
| CH2 = PWM-A (1 V / Division) | ||
| CH3 = PWM-B (1 V / Division) |
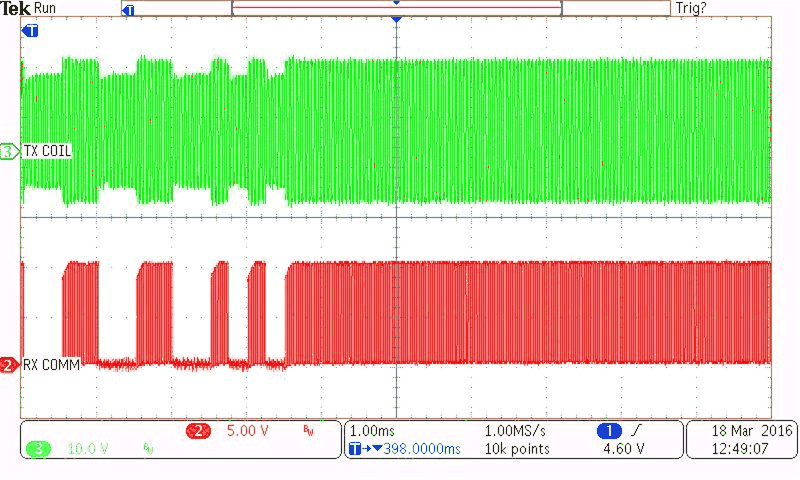
| CH2 = RX communication signal (5 V / Division) | ||||
| CH3 = TX coil voltage (10 V / Division) |
With RX 5-W Load
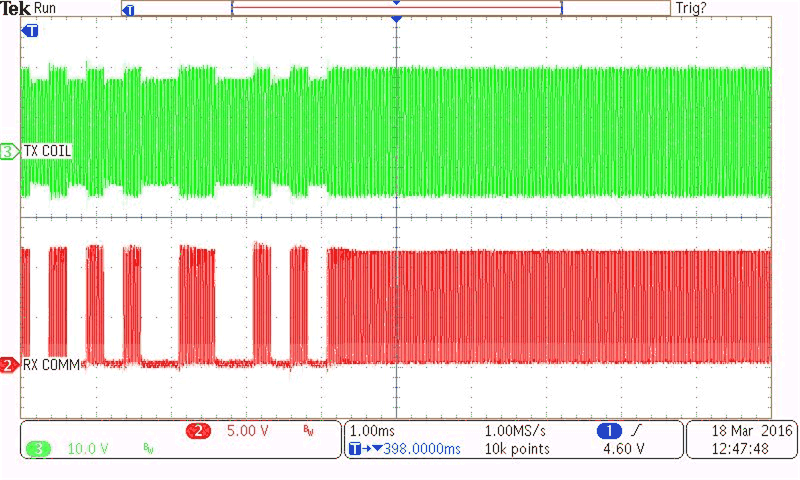
| CH2 = RX communication signal (5 V / Division) | ||
| CH3 = TX coil voltage (10 V / Division) |
With RX No Load
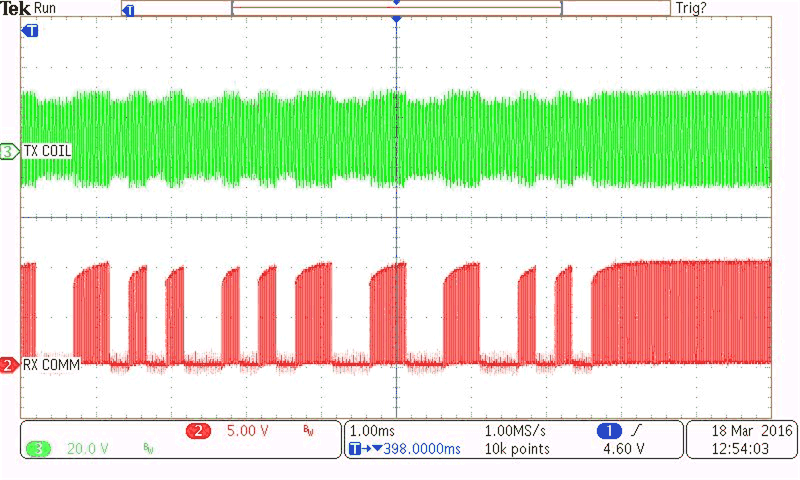
| CH2 = RX communication signal (5 V / Division) | ||||
| CH3 = TX coil voltage (20 V / Division) |
With RX 15-W Load