ZHCS171C June 2011 – May 2015 ADS4229
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison Table
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
-
7 Specifications
- 7.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 7.2 ESD Ratings
- 7.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 7.4 Thermal Information
- 7.5 Electrical Characteristics: ADS4229 (250 MSPS)
- 7.6 Electrical Characteristics: General
- 7.7 Digital Characteristics
- 7.8 LVDS and CMOS Modes Timing Requirements
- 7.9 LVDS Timings at Lower Sampling Frequencies
- 7.10 CMOS Timings at Lower Sampling Frequencies
- 7.11 Serial Interface Timing Characteristics
- 7.12 Reset Timing (Only when Serial Interface is Used)
- 7.13 Typical Characteristics
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
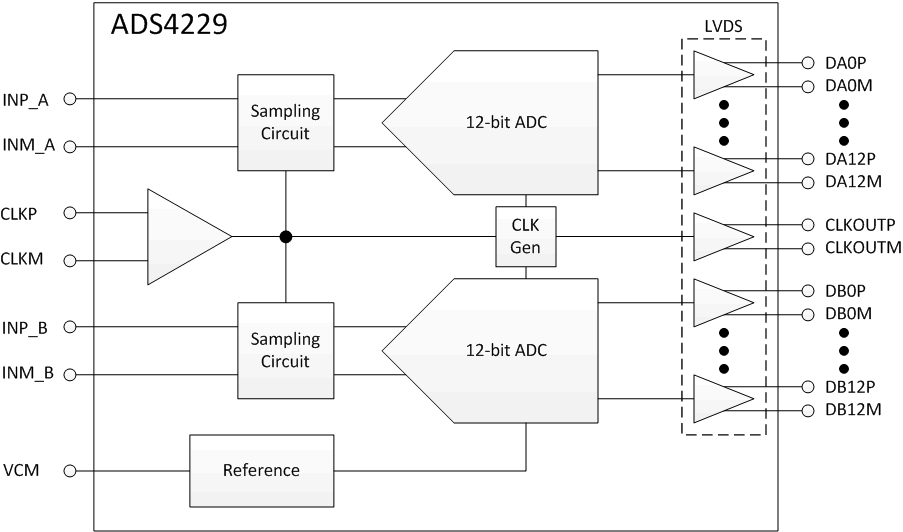
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3 Feature Description
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 8.6
Register Maps
- 8.6.1 Serial Register Map
- 8.6.2
Description of Serial Registers
- 8.6.2.1 Register Address 00h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.2 Register Address 01h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.3 Register Address 03h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.4 Register Address 25h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.5 Register Address 29h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.6 Register Address 2Bh (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.7 Register Address 3Dh (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.8 Register Address 3Fh (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.9 Register Address 40h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.10 Register Address 41h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.11 Register Address 42h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.12 Register Address 45h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.13 Register Address 4Ah (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.14 Register Address 58h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.15 Register Address BFh (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.16 Register Address C1h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.17 Register Address CFh (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.18 Register Address EFh (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.19 Register Address F1h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.20 Register Address F2h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.21 Register Address 2h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.22 Register Address D5h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.23 Register Address D7h (Default = 00h)
- 8.6.2.24 Register Address DBh (Default = 00h)
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
1 特性
2 应用
- 无线通信基础设施
- 由软件定义的无线电
- 功率放大器线性化
3 说明
ADS4229 是 ADS42xx 双通道,12 位和 14 位模数转换器 (ADC) 超低功耗系列产品。 采用创新设计技术实现高动态性能,而同时功耗极低(采用一个 1.8 V 电源)。 该拓扑使 ADS4229 非常适合多载波、宽带宽通信应用。
ADS4229 具有可被用于在较低满量程输入范围内改进无杂散动态范围 (SFDR) 性能的增益选项。 这个器件还包括一个 dc 偏移校正环路,此环路可被用于消除 ADC 偏移。 双数据速率 (DDR) 低压差分信令 (LVDS) 和并行互补金属氧化物半导体 (CMOS) 数字输出接口采用一个紧凑型 QFN-64 PowerPAD™ 封装。
此器件包含内部基准,而删除了传统基准引脚和相关的去耦合电容器。 ADS4229 可在工业温度范围(-40°C 至 +85°C)内工作。
器件信息(1)
| 器件型号 | 封装 | 封装尺寸(标称值) |
|---|---|---|
| ADS4229 | VQFN (64) | 9.00mm x 9.00mm |
- 如需了解所有可用封装,请见数据表末尾的可订购产品附录。
ADS4229 框图