ZHCS446A September 2011 – December 2014 UCC28063
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 说明(继续)
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Principles of Operation
- 8.3.2 Natural Interleaving
- 8.3.3 On-Time Control, Maximum Frequency Limiting, and Restart Timer
- 8.3.4 Distortion Reduction
- 8.3.5 Zero-Current Detection and Valley Switching
- 8.3.6 Phase Management and Light-Load Operation
- 8.3.7 External Disable
- 8.3.8 Improved Error Amplifier
- 8.3.9 Soft Start
- 8.3.10 Brownout Protection
- 8.3.11 Dropout Detection
- 8.3.12 VREF
- 8.3.13 VCC
- 8.3.14 Control of Downstream Converter
- 8.3.15
System Level Protections
- 8.3.15.1 Failsafe OVP - Output Overvoltage Protection
- 8.3.15.2 Overcurrent Protection
- 8.3.15.3 Open-Loop Protection
- 8.3.15.4 VCC Undervoltage Lock-Out (UVLO) Protection
- 8.3.15.5 Phase-Fail Protection
- 8.3.15.6 CS-Open, TSET-Open and -Short Protection
- 8.3.15.7 Thermal Shutdown Protection
- 8.3.15.8 AC-Line Brownout and Dropout Protections
- 8.3.15.9 Fault Logic Diagram
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
-
9 Applications and Implementation
- 9.1 Application Information
- 9.2
Typical Application
- 9.2.1 Design Requirements
- 9.2.2
Detailed Design Procedure
- 9.2.2.1 Inductor Selection
- 9.2.2.2 ZCD Resistor Selection (RZA, RZB)
- 9.2.2.3 HVSEN
- 9.2.2.4 Output Capacitor Selection
- 9.2.2.5 Selecting (RS) For Peak Current Limiting
- 9.2.2.6 Power Semiconductor Selection (Q1, Q2, D1, D2)
- 9.2.2.7 Brownout Protection
- 9.2.2.8 Converter Timing
- 9.2.2.9 Programming VOUT
- 9.2.2.10 Voltage Loop Compensation
- 9.2.3 Application Curves
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12器件和文档支持
- 13机械、封装和可订购信息
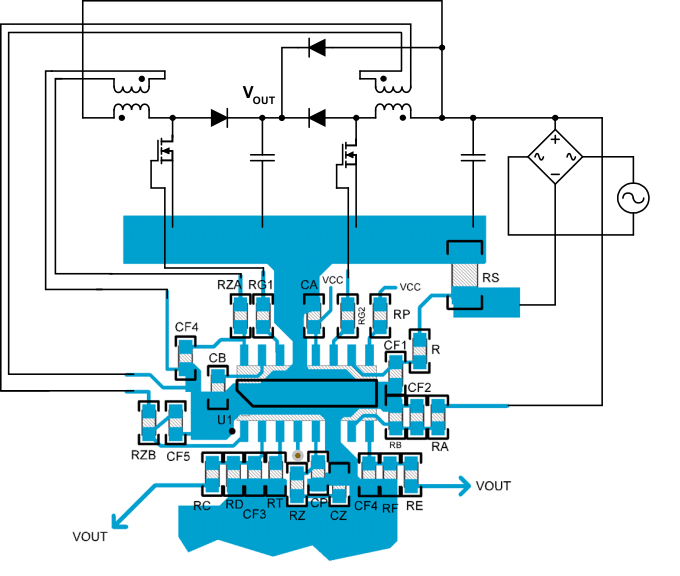
11 Layout
11.1 Layout Guidelines
Interleaved transition-mode PFC system architecture dramatically reduces input and output ripple current, allowing the circuit to use smaller and less expensive filters. To maximize the benefits of interleaving, the input and output filter capacitors should be located after the two phase currents are combined together. Similar to other power management devices, when laying out the printed circuit board (PCB) it is important to use star grounding techniques and keep filter capacitors as close to device ground as possible. To minimize the interference caused by capacitive coupling from the boost inductor, the device should be located at least 1 in (25.4 mm) away from the boost inductor. It is also recommended that the device not be placed underneath magnetic elements. Because of the precise timing requirement, timing-setting resistor RT should be placed as close as possible to the TSET pin and returned to the analog ground pin with the shortest possible path. See Figure 39 for a recommended component placement and layout.
11.2 Layout Example