ZHCSAC2C August 2012 – October 2018 PCM5121 , PCM5122
PRODUCTION DATA.
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Device Comparison
- 6 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 7 Specifications
-
8 Detailed Description
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 8.3
Feature Description
- 8.3.1 Terminology
- 8.3.2 Audio Data Interface
- 8.3.3 XSMT Pin (Soft Mute / Soft Un-Mute)
- 8.3.4 Audio Processing
- 8.3.5 DAC Outputs
- 8.3.6
Reset and System Clock Functions
- 8.3.6.1 Clocking Overview
- 8.3.6.2 Clock Slave Mode With Master and System Clock (SCK) Input (4 Wire I2S)
- 8.3.6.3 Clock Slave Mode With BCK PLL to Generate Internal Clocks (3-Wire PCM)
- 8.3.6.4 Clock Generation Using the PLL
- 8.3.6.5 PLL Calculation
- 8.3.6.6 Clock Master Mode from Audio Rate Master Clock
- 8.3.6.7 Clock Master from a Non-Audio Rate Master Clock
- 8.4 Device Functional Modes
- 8.5 Programming
- 9 Application and Implementation
- 10Power Supply Recommendations
- 11Layout
- 12Register Maps
- 13器件和文档支持
- 14机械、封装和可订购信息
10.3 External Power Sense Undervoltage Protection Mode
NOTE
External Power Sense Undervoltage Protection Mode is supported only when
DVDD = 3.3 V.
The XSMT pin can also be used to monitor a system voltage, such as the 24-VDC LCD TV backlight, or 12-VDC system supply using a voltage divider created with two resistors. (See Figure 81.)
- If the XSMT pin makes a transition from 1 to 0 over 6 ms or more, the device switches into external undervoltage protection mode. This mode uses two trigger levels:
- When the XSMT pin level reaches 2 V, soft mute process begins.
- When the XSMT pin level reaches 1.2 V, analog mute engages, regardless of digital audio level, and analog shutdown begins. (DAC and related circuitry powers down).
If XSMT is moved from 1 to 0 in 20 ns or less, then the device will interpret it as a digital controlled request to mute. It will perform a soft mute, then move to standby.
A timing diagram to show this is shown in Figure 82.
NOTE
The XSMT input pin voltage range is from –0.3 V to DVDD + 0.3 V. The ratio of external resistors must produce a voltage within this input range. Any increase in power supply (such as power supply positive noise or ripple) can pull the XSMT pin higher than DVDD + 0.3 V.
For example, if the PCM512x is monitoring a 12-V input, and dividing the voltage by 4, then the voltage at XSMT during ideal power supply conditions is 3.3 V. A voltage spike higher than 14.4 V causes a voltage greater than 3.6 V (DVDD + 0.3) on the XSMT pin, potentially damaging the device.
Providing the divider is set appropriately, any DC voltage can be monitored.
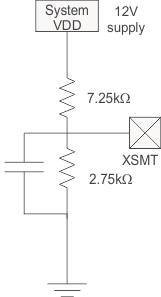 Figure 81. XSMT in External UVP Mode
Figure 81. XSMT in External UVP Mode 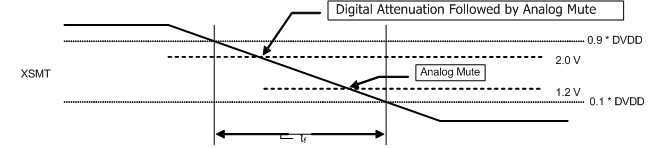 Figure 82. XSMT Timing for Undervoltage Protection
Figure 82. XSMT Timing for Undervoltage Protection The trigger voltage values for the soft mute and hard mute are shown in Table 47. The range of values will vary from device to device, but typical thresholds are shown. XSMT should be set up to nominally be 3.3 V along with DVDD, but derived from a higher system power supply rail.
Table 47. Distribution of Voltage Thresholds
| MIN | TYP | MAX | UNIT | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soft Mute Threshold Voltage | 2 | 2.2 | 0.9 × DVDD | V |
| Hard Mute Threshold Voltage | 0.1 × DVDD | 0.9 | 1.2 | V |