ZHCSI51A May 2018 – June 2018 OPA521
PRODUCTION DATA.
8.2.2.2 Circuit Protection
Power-line communications are often located in operating environments that are harsh for electrical components connected to the ac line. Noise or surges from electrical anomalies (such as lightning, capacitor bank switching, inductive switching, or other grid fault conditions) can damage high-performance integrated circuits if proper protection is not provided. The OPA521, however, can survive even the harshest conditions by using a variety of techniques to protect the device. Layout the protection circuitry in order to dissipate as much of the electrical disturbance as possible with a multilayer approach using metal-oxide varistors (MOVs), transient voltage suppression diodes (TVSs), Schottky diodes, and a Zener diode. These components dissipate the electrical disturbance before the anomaly reaches the device. shows the recommended strategy for transient overvoltage protection.
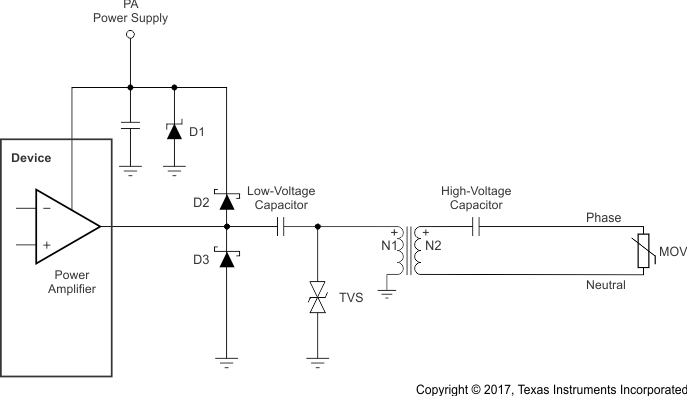 Figure 23. Transient Overvoltage Protection for OPA521
Figure 23. Transient Overvoltage Protection for OPA521 Note that the high-voltage coupling capacitor must be able to withstand pulses up to the clamping protection provided by the MOV. A metalized polypropylene capacitor, such as the 474MKP275KA from Illinois Capacitor, is rated for 50 Hz to 60 Hz and 250 VAC to 310 VAC, and can withstand 24 impulses of 2.5 kV. Table 2 lists several recommended transient protection components.
Table 2. Recommended Transient Protection Components
| COMPONENT | DESCRIPTION | MANUFACTURER | MFR PART NO (OR EQUIVALENT) |
|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | Zener diode | Diodes, Inc. | 1SMB59xxB |
| D2, D3 | Schottky diode | Diodes, Inc. | 1N5819HW |
| TVS | Transient voltage suppressor | Diodec Semiconductor | P6SMBJxxC |
| MOV | Varistor (for 120 VAC, 60 Hz) | LittleFuse | TMOV20RP140E |
| MOV | Varistor (for 240 VAC, 50 Hz) | LittleFuse | TMOV20RP300E |
| HV Cap | High-voltage capacitor | Illinois Capacitor, Inc | 474MKP275KA |