ZHCSBU4E October 2012 – September 2020 MSP430F5358 , MSP430F5359 , MSP430F5658 , MSP430F5659 , MSP430F6458 , MSP430F6459 , MSP430F6658 , MSP430F6659
PRODUCTION DATA
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 功能方框图
- 5 Revision History
- 6 Device Comparison
- 7 Terminal Configuration and Functions
-
8 Specifications
- 8.1 Absolute Maximum Ratings
- 8.2 ESD Ratings
- 8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
- 8.4 Active Mode Supply Current Into VCC Excluding External Current
- 8.5 Low-Power Mode Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 8.6 Low-Power Mode With LCD Supply Currents (Into VCC) Excluding External Current
- 8.7 Thermal Resistance Characteristics
- 8.8 Schmitt-Trigger Inputs – General-Purpose I/O
- 8.9 Inputs – Ports P1, P2, P3, and P4
- 8.10 Leakage Current – General-Purpose I/O
- 8.11 Outputs – General-Purpose I/O (Full Drive Strength)
- 8.12 Outputs – General-Purpose I/O (Reduced Drive Strength)
- 8.13 Output Frequency – Ports P1, P2, and P3
- 8.14 Typical Characteristics – Outputs, Reduced Drive Strength (PxDS.y = 0)
- 8.15 Typical Characteristics – Outputs, Full Drive Strength (PxDS.y = 1)
- 8.16 Crystal Oscillator, XT1, Low-Frequency Mode
- 8.17 Crystal Oscillator, XT2
- 8.18 Internal Very-Low-Power Low-Frequency Oscillator (VLO)
- 8.19 Internal Reference, Low-Frequency Oscillator (REFO)
- 8.20 DCO Frequency
- 8.21 PMM, Brownout Reset (BOR)
- 8.22 PMM, Core Voltage
- 8.23 PMM, SVS High Side
- 8.24 PMM, SVM High Side
- 8.25 PMM, SVS Low Side
- 8.26 PMM, SVM Low Side
- 8.27 Wake-up Times From Low-Power Modes
- 8.28 Timer_A – Timers TA0, TA1, and TA2
- 8.29 Timer_B – Timer TB0
- 8.30 Battery Backup
- 8.31 USCI (UART Mode)
- 8.32 USCI (SPI Master Mode)
- 8.33 USCI (SPI Slave Mode)
- 8.34 USCI (I2C Mode)
- 8.35 LCD_B Operating Characteristics
- 8.36 LCD_B Electrical Characteristics
- 8.37 12-Bit ADC, Power Supply and Input Range Conditions
- 8.38 12-Bit ADC, Timing Parameters
- 8.39 12-Bit ADC, Linearity Parameters Using an External Reference Voltage
- 8.40 12-Bit ADC, Linearity Parameters Using AVCC as Reference Voltage
- 8.41 12-Bit ADC, Linearity Parameters Using the Internal Reference Voltage
- 8.42 12-Bit ADC, Temperature Sensor and Built-In VMID
- 8.43 REF, External Reference
- 8.44 REF, Built-In Reference
- 8.45 12-Bit DAC, Supply Specifications
- 8.46 12-Bit DAC, Linearity Specifications
- 8.47 12-Bit DAC, Output Specifications
- 8.48 12-Bit DAC, Reference Input Specifications
- 8.49 12-Bit DAC, Dynamic Specifications
- 8.50 12-Bit DAC, Dynamic Specifications (Continued)
- 8.51 Comparator_B
- 8.52 Ports PU.0 and PU.1
- 8.53 USB Output Ports DP and DM
- 8.54 USB Input Ports DP and DM
- 8.55 USB-PWR (USB Power System)
- 8.56 USB-PLL (USB Phase Locked Loop)
- 8.57 Flash Memory
- 8.58 JTAG and Spy-Bi-Wire Interface
-
9 Detailed Description
- 9.1 CPU
- 9.2 Instruction Set
- 9.3 Operating Modes
- 9.4 Interrupt Vector Addresses
- 9.5 Memory Organization
- 9.6 Bootloader (BSL)
- 9.7 JTAG Operation
- 9.8 Flash Memory
- 9.9 Memory Integrity Detection (MID)
- 9.10 RAM
- 9.11 Backup RAM
- 9.12
Peripherals
- 9.12.1 Digital I/O
- 9.12.2 Port Mapping Controller
- 9.12.3 Oscillator and System Clock
- 9.12.4 Power-Management Module (PMM)
- 9.12.5 Hardware Multiplier (MPY)
- 9.12.6 Real-Time Clock (RTC_B)
- 9.12.7 Watchdog Timer (WDT_A)
- 9.12.8 System Module (SYS)
- 9.12.9 DMA Controller
- 9.12.10 Universal Serial Communication Interface (USCI)
- 9.12.11 Timer TA0
- 9.12.12 Timer TA1
- 9.12.13 Timer TA2
- 9.12.14 Timer TB0
- 9.12.15 Comparator_B
- 9.12.16 ADC12_A
- 9.12.17 DAC12_A
- 9.12.18 CRC16
- 9.12.19 Voltage Reference (REF) Module
- 9.12.20 LCD_B
- 9.12.21 USB Universal Serial Bus
- 9.12.22 LDO and PU Port
- 9.12.23 Embedded Emulation Module (EEM) (L Version)
- 9.12.24 Peripheral File Map
- 9.13
Input/Output Diagrams
- 9.13.1 Port P1 (P1.0 to P1.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.13.2 Port P2 (P2.0 to P2.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.13.3 Port P3 (P3.0 to P3.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.13.4 Port P4 (P4.0 to P4.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.13.5 Port P5 (P5.0 and P5.1) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.13.6 Port P5 (P5.2 to P5.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.13.7 Port P6 (P6.0 to P6.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.13.8 Port P7 (P7.2) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.13.9 Port P7 (P7.3) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.13.10 Port P7 (P7.4 to P7.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.13.11 Port P8 (P8.0 to P8.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.13.12 Port P9 (P9.0 to P9.7) Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger
- 9.13.13 Port PU (PU.0/DP, PU.1/DM, PUR) USB Ports (F665x, F565x)
- 9.13.14 Port PU (PU.0 and PU.1) Ports (F645x, F535x)
- 9.13.15 Port PJ (PJ.0) JTAG Pin TDO, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger or Output
- 9.13.16 Port PJ (PJ.1 to PJ.3) JTAG Pins TMS, TCK, TDI/TCLK, Input/Output With Schmitt Trigger or Output
- 9.14 Device Descriptors
- 10Device and Documentation Support
- 11Mechanical, Packaging, and Orderable Information
8.3 Recommended Operating Conditions
| MIN | NOM | MAX | UNIT | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VCC | Supply voltage during program execution and flash programming (AVCC1 = DVCC1 = DVCC2 = DVCC3 = DVCC = VCC)(1)(2) | PMMCOREVx = 0 | 1.8 | 3.6 | V | |
| PMMCOREVx = 0, 1 | 2.0 | 3.6 | ||||
| PMMCOREVx = 0, 1, 2 | 2.2 | 3.6 | ||||
| PMMCOREVx = 0, 1, 2, 3 | 2.4 | 3.6 | ||||
| VCC,USB | Supply voltage during USB operation, USB PLL disabled, USB_EN = 1, UPLLEN = 0 |
PMMCOREVx = 0 | 1.8 | 3.6 | V | |
| PMMCOREVx = 0, 1 | 2.0 | 3.6 | ||||
| PMMCOREVx = 0, 1, 2 | 2.2 | 3.6 | ||||
| PMMCOREVx = 0, 1, 2, 3 | 2.4 | 3.6 | ||||
| Supply voltage during USB operation, USB PLL enabled(6), USB_EN = 1, UPLLEN = 1 | PMMCOREVx = 2 | 2.2 | 3.6 | |||
| PMMCOREVx = 2, 3 | 2.4 | 3.6 | ||||
| VSS | Supply voltage (AVSS1 = AVSS2 = AVSS3 = DVSS1 = DVSS2 = DVSS3 = VSS) | 0 | V | |||
| VBAT,RTC | Backup-supply voltage with RTC operational | TA = 0°C to 85°C | 1.55 | 3.6 | V | |
| TA = –40°C to 85°C | 1.70 | 3.6 | ||||
| VBAT,MEM | Backup-supply voltage with backup memory retained. | TA = –40°C to 85°C | 1.20 | 3.6 | V | |
| TA | Operating free-air temperature | I version | –40 | 85 | °C | |
| TJ | Operating junction temperature | I version | –40 | 85 | °C | |
| CBAK | Capacitance at pin VBAK | 1 | 4.7 | 10 | nF | |
| CVCORE | Capacitor at VCORE(3) | 470 | nF | |||
| CDVCC/ CVCORE | Capacitor ratio of DVCC to VCORE | 10 | ||||
| fSYSTEM | Processor frequency (maximum MCLK frequency)(4)(5) (see Figure 8-1) | PMMCOREVx = 0, 1.8 V ≤ VCC ≤ 3.6 V (default condition) |
0 | 8.0 | MHz | |
| PMMCOREVx = 1, 2 V ≤ VCC ≤ 3.6 V |
0 | 12.0 | ||||
| PMMCOREVx = 2, 2.2 V ≤ VCC ≤ 3.6 V |
0 | 16.0 | ||||
| PMMCOREVx = 3, 2.4 V ≤ VCC ≤ 3.6 V |
0 | 20.0 | ||||
| fSYSTEM_USB | Minimum processor frequency for USB operation | 1.5 | MHz | |||
| USB_wait | Wait state cycles during USB operation | 16 | cycles | |||
(1) TI recommends powering AVCC and DVCC from the same source. A maximum difference of 0.3 V between AVCC and DVCC can be tolerated during power up and operation.
(2) The minimum supply voltage is defined by the supervisor SVS levels when it is enabled. See the Section 8.23 threshold parameters for the exact values and further details.
(3) A capacitor tolerance of ±20% or better is required.
(4) The MSP430 CPU is clocked directly with MCLK. Both the high and low phase of MCLK must not exceed the pulse duration of the specified maximum frequency.
(5) Modules may have a different maximum input clock specification. See the specification of the respective module in this data sheet.
(6) USB operation with USB PLL enabled requires PMMCOREVx ≥ 2 for proper operation.
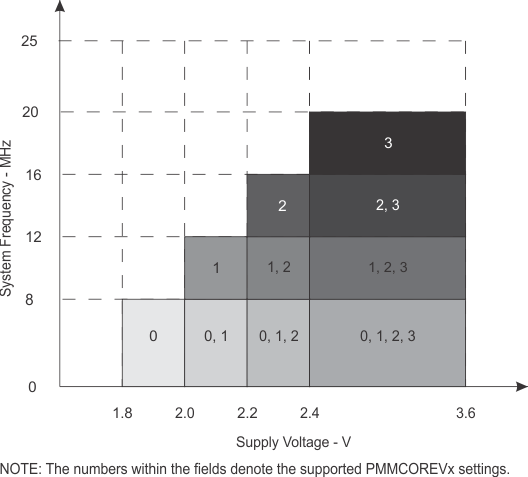 Figure 8-1 Frequency vs Supply Voltage
Figure 8-1 Frequency vs Supply Voltage